Abstract
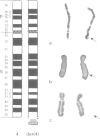
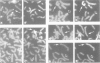
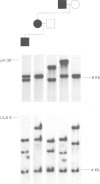
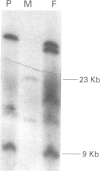
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is a hereditary neuromuscular disorder transmitted in an autosomal dominant fashion. FSHD has been located by linkage analysis in the most distal part of chromosome 4q. The disease is associated with deletions within a 3.2 kb tandem repeat sequence, D4Z4. We have studied a family in which an abnormal chromosome 4 segregates through three generations in phenotypically normal subjects. This chromosome is the derivative of a (4;D or G) (q35;p12) translocation. Molecular analysis of the region 4q35 showed the absence of the segment ranging from the telomere to locus D4F104S1. Probe p13E-11 (D4F104S1), which detects polymorphic EcoRI fragments containing D4Z4, in Southern blot analysis showed only one allele in the carriers of the abnormal chromosome 4. Probe p13E-11 EcoRI fragments are contained in the subtelomeric region of 4q and their rearrangements associated with FSHD suggested that the gene responsible for the muscular dystrophy could be subject to a position effect variegation (PEV) because of its proximity to subtelomeric heterochromatin. The absence of the 4q telomeric region in our phenotypically normal cases indicates that haploinsufficiency of the region containing D4Z4 does not cause FSHD.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aparicio O. M., Billington B. L., Gottschling D. E. Modifiers of position effect are shared between telomeric and silent mating-type loci in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1279–1287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson U., Altherr M. R., Wasmuth J. J., Winokur S. T. High resolution fluorescence in situ hybridization to linearly extended DNA visually maps a tandem repeat associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy immediately adjacent to the telomere of 4q. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Oct;3(10):1801–1805. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.10.1801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capel B., Rasberry C., Dyson J., Bishop C. E., Simpson E., Vivian N., Lovell-Badge R., Rastan S., Cattanach B. M. Deletion of Y chromosome sequences located outside the testis determining region can cause XY female sex reversal. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):301–307. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Viegas-Pequignot E. High resolution R- and G-banding on the same preparation. Hum Genet. 1981;57(1):93–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00271176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. R., Stajich J. M., Speer M. C., Vance J. M., Stewart C. S., Yamaoka L. H., Samson F., Fardeau M., Potter T. G., Roses A. D. Linkage studies in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):424–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Position-effect variegation after 60 years. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):422–426. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90304-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt J. E., Lyle R., Clark L. N., Valleley E. M., Wright T. J., Wijmenga C., van Deutekom J. C., Francis F., Sharpe P. T., Hofker M. Analysis of the tandem repeat locus D4Z4 associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1287–1295. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén M. A., Stacey M., Armstrong S. J. Does junk DNA regulate gene expression in humans? Clin Mol Pathol. 1995 Jun;48(3):M118–M123. doi: 10.1136/mp.48.3.m118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. E., Garver K. L., Diggans G., Clemens M., Wenger S. L., Steele M. W., Jones M. C., Israel J. Interstitial and terminal deletions of the long arm of chromosome 4: further delineation of phenotypes. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Nov;31(3):533–548. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320310308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt P. W., Compston D. A., Harper P. S. Estimation of age dependent penetrance in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy by minimising ascertainment bias. J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;26(12):755–760. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.12.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews K. D., Mills K. A., Bosch E. P., Ionasescu V. V., Wiles K. R., Buetow K. H., Murray J. C. Linkage localization of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) in 4q35. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):428–431. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K. A., Buetow K. H., Xu Y., Ritty T. M., Mathews K. D., Bodrug S. E., Wijmenga C., Balazs I., Murray J. C. Genetic and physical mapping on chromosome 4 narrows the localization of the gene for facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):432–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfarazi M., Wijmenga C., Upadhyaya M., Weiffenbach B., Hyser C., Mathews K., Murray J., Gilbert J., Pericak-Vance M., Lunt P. Regional mapping of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy gene on 4q35: combined analysis of an international consortium. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):396–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simola K. O., Knuutila S., Kaitila I., Pirkola A., Pohja P. Familial aniridia and translocation t(4;11)(q22;p13) without Wilms' tumor. Hum Genet. 1983;63(2):158–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00291536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Jardine P., Maynard J., Farnham J., Sarfarazi M., Wijmenga C., Hewitt J. E., Frants R., Harper P. S., Lunt P. W. Molecular analysis of British facioscapulohumeral dystrophy families for 4q DNA rearrangements. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):981–987. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Lunt P., Sarfarazi M., Broadhead W., Farnham J., Harper P. S. The mapping of chromosome 4q markers in relation to facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):404–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiffenbach B., Bagley R., Falls K., Hyser C., Storvick D., Jacobsen S. J., Schultz P., Mendell J., Willems van Dijk K., Milner E. C. Linkage analyses of five chromosome 4 markers localizes the facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) gene to distal 4q35. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):416–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijmenga C., Hewitt J. E., Sandkuijl L. A., Clark L. N., Wright T. J., Dauwerse H. G., Gruter A. M., Hofker M. H., Moerer P., Williamson R. Chromosome 4q DNA rearrangements associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1992 Sep;2(1):26–30. doi: 10.1038/ng0992-26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijmenga C., Sandkuijl L. A., Moerer P., van der Boorn N., Bodrug S. E., Ray P. N., Brouwer O. F., Murray J. C., van Ommen G. J., Padberg G. W. Genetic linkage map of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy and five polymorphic loci on chromosome 4q35-qter. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):411–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijmenga C., Winokur S. T., Padberg G. W., Skraastad M. I., Altherr M. R., Wasmuth J. J., Murray J. C., Hofker M. H., Frants R. R. The human skeletal muscle adenine nucleotide translocator gene maps to chromosome 4q35 in the region of the facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy locus. Hum Genet. 1993 Sep;92(2):198–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00219692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijmenga C., Wright T. J., Baan M. J., Padberg G. W., Williamson R., van Ommen G. J., Hewitt J. E., Hofker M. H., Frants R. R. Physical mapping and YAC-cloning connects four genetically distinct 4qter loci (D4S163, D4S139, D4F35S1 and D4F104S1) in the FSHD gene-region. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1667–1672. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winokur S. T., Bengtsson U., Feddersen J., Mathews K. D., Weiffenbach B., Bailey H., Markovich R. P., Murray J. C., Wasmuth J. J., Altherr M. R. The DNA rearrangement associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy involves a heterochromatin-associated repetitive element: implications for a role of chromatin structure in the pathogenesis of the disease. Chromosome Res. 1994 May;2(3):225–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01553323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. J., Wijmenga C., Clark L. N., Frants R. R., Williamson R., Hewitt J. E. Fine mapping of the FSHD gene region orientates the rearranged fragment detected by the probe p13E-11. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1673–1678. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Marie S. K., Passos-Bueno M. R., Vainzof M., Campiotto S., Cerqueira A., Wijmenga C., Padberg G., Frants R. High proportion of new mutations and possible anticipation in Brazilian facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy families. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):99–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. J., Byers B., Moolgavkar S. H. Allelic instability in mitosis: a unified model for dominant disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10178–10182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deutekom J. C., Wijmenga C., van Tienhoven E. A., Gruter A. M., Hewitt J. E., Padberg G. W., van Ommen G. J., Hofker M. H., Frants R. R. FSHD associated DNA rearrangements are due to deletions of integral copies of a 3.2 kb tandemly repeated unit. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2037–2042. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]