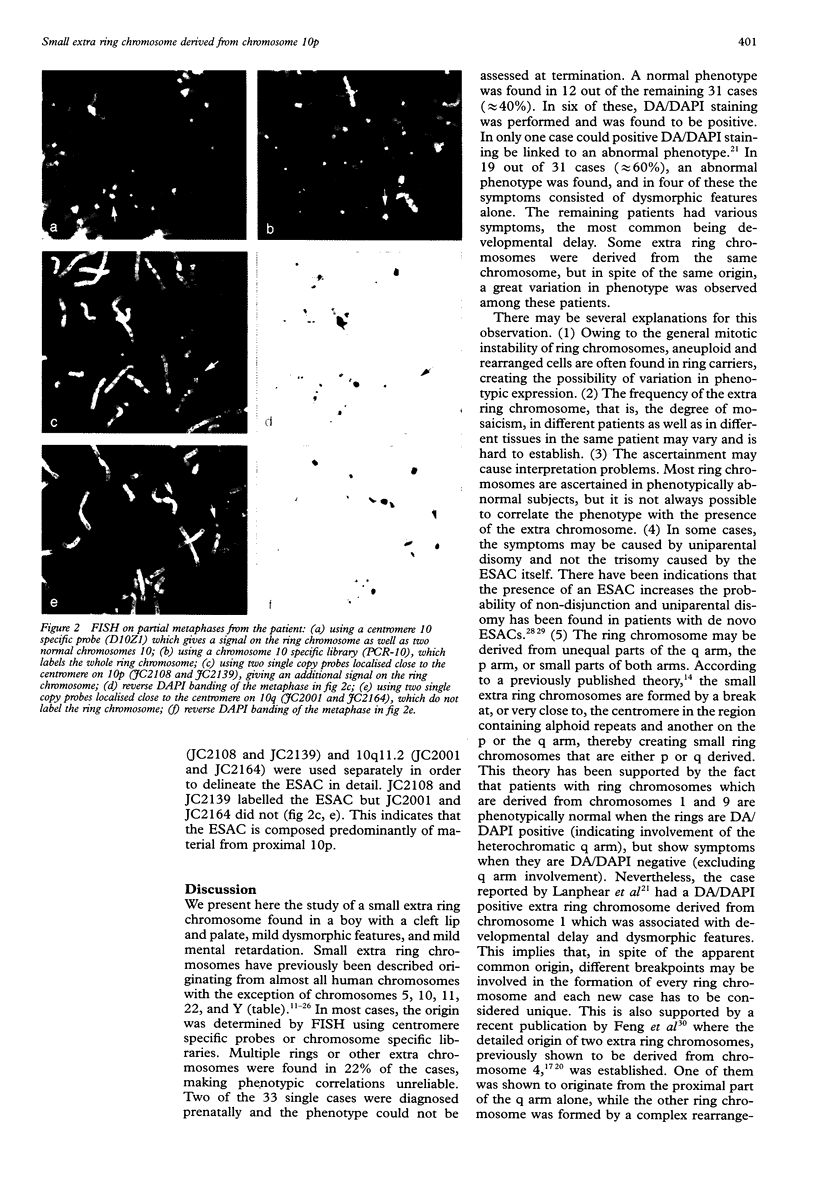
Abstract
We present a case with a small extra ring chromosome which was found in 66% of lymphocytes on routine cytogenetic examination. FISH analyses, using centromere specific and single copy probes, showed that the extra ring chromosome was derived from the most proximal part of 10p, close to the centromere. The patient has a unilateral cleft lip and palate, mild dysmorphic features, and mild mental retardation. Only a limited number of extra ring chromosomes have been characterised so far. To our knowledge, this is the first reported patient with an extra ring chromosome derived from chromosome 10p.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batista D. A., Escallon C., Blakemore K. J., Stetten G. An accessory marker derived from chromosome 20 and its co-existence with a mosaic trisomy 20 cell line. Prenat Diagn. 1995 Feb;15(2):123–127. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blennow E., Annerén G., Bui T. H., Berggren E., Asadi E., Nordenskjöld M. Characterization of supernumerary ring marker chromosomes by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):433–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blennow E., Bui T. H., Kristoffersson U., Vujic M., Annerén G., Holmberg E., Nordenskjöld M. Swedish survey on extra structurally abnormal chromosomes in 39 105 consecutive prenatal diagnoses: prevalence and characterization by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Prenat Diagn. 1994 Nov;14(11):1019–1028. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970141103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blennow E., Nielsen K. B., Telenius H., Carter N. P., Kristoffersson U., Holmberg E., Gillberg C., Nordenskjöld M. Fifty probands with extra structurally abnormal chromosomes characterized by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Jan 2;55(1):85–94. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320550122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brøndum-Nielsen K., Mikkelsen M. A 10-year survey, 1980-1990, of prenatally diagnosed small supernumerary marker chromosomes, identified by FISH analysis. Outcome and follow-up of 14 cases diagnosed in a series of 12,699 prenatal samples. Prenat Diagn. 1995 Jul;15(7):615–619. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970150705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callen D. F., Eyre H. J., Ringenbergs M. L., Freemantle C. J., Woodroffe P., Haan E. A. Chromosomal origin of small ring marker chromosomes in man: characterization by molecular genetics. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;48(4):769–782. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callen D. F., Eyre H., Yip M. Y., Freemantle J., Haan E. A. Molecular cytogenetic and clinical studies of 42 patients with marker chromosomes. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jul 1;43(4):709–715. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callen D. F., Ringenbergs M. L., Fowler J. C., Freemantle C. J., Haan E. A. Small marker chromosomes in man: origin from pericentric heterochromatin of chromosomes 1, 9, and 16. J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;27(3):155–159. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.3.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Tuck-Muller C. M., Batista D. A., Wertelecki W. Identification of supernumerary ring chromosome 1 mosaicism using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Mar 27;56(2):219–233. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel A., Malafiej P., Preece K., Chia N., Nelson J., Smith M. Identification of marker chromosomes in thirteen patients using FISH probing. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Oct 15;53(1):8–18. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320530103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang Y. Y., Eyre H. J., Bohlander S. K., Estop A., McPherson E., Träger T., Riess O., Callen D. F. Mechanisms of small ring formation suggested by the molecular characterization of two small accessory ring chromosomes derived from chromosome 4. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Nov;57(5):1137–1142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith M. A., Yates J. R. Maternal age specific rates for chromosome aberrations and factors influencing them: report of a collaborative european study on 52 965 amniocenteses. Prenat Diagn. 1984 Spring;4(Spec No):5–44. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970040704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamerton J. L., Canning N., Ray M., Smith S. A cytogenetic survey of 14,069 newborn infants. I. Incidence of chromosome abnormalities. Clin Genet. 1975 Oct;8(4):223–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb01498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B., Cross P. K. Extra structurally abnormal chromosomes (ESAC) detected at amniocentesis: frequency in approximately 75,000 prenatal cytogenetic diagnoses and associations with maternal and paternal age. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;40(2):83–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Melville M., Ratcliffe S., Keay A. J., Syme J. A cytogenetic survey of 11,680 newborn infants. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 May;37(4):359–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanphear N., Lamb A., Oppenheimer S., Soukup S. Supernumerary chromosome marker (1) in a developmentally delayed child. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Jul 3;57(3):400–402. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320570307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnyk A. R., Dewald G. Identification of a small supernumerary ring chromosome 8 by fluorescent in situ hybridization in a child with developmental delay and minor anomalies. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Mar 1;50(1):12–14. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320500103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalski K., Rauer M., Williamson N., Perszyk A., Hoo J. J. Identification, counselling, and outcome of two cases of prenatally diagnosed supernumerary small ring chromosomes. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Apr 1;46(1):88–94. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Rasmussen K. Extra marker chromosome in newborn children. Hereditas. 1975;81(2):221–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1975.tb01036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plattner R., Heerema N. A., Howard-Peebles P. N., Miles J. H., Soukup S., Palmer C. G. Clinical findings in patients with marker chromosomes identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;91(6):589–598. doi: 10.1007/BF00205086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Wagstaff J., Bernasconi F., Baccichetti C., Artifoni L., Franzoni E., Suslak L., Shih L. Y., Aviv H., Schinzel A. A. Uniparental disomy explains the occurrence of the Angelman or Prader-Willi syndrome in patients with an additional small inv dup(15) chromosome. J Med Genet. 1993 Sep;30(9):756–760. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.9.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silahtaroglu A. N., Hacihanefioglu S., Yilmaz S., Tarkan Y., Cenani A., Tümer Z. A small supernumerary marker chromosome X identified by in situ hybridization. Clin Genet. 1995 May;47(5):270–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1995.tb04310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple I. K., James R. S., Crolla J. A., Sitch F. L., Jacobs P. A., Howell W. M., Betts P., Baum J. D., Shield J. P. An imprinted gene(s) for diabetes? Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):110–112. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D. De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements and extra marker chromosomes identified at prenatal diagnosis: clinical significance and distribution of breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):995–1013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D. Outcome of cases of de novo structural rearrangements diagnosed at amniocentesis. Prenat Diagn. 1984 Spring;4(Spec No):69–80. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970040706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. J., Ma N. S., Dorman T. E., Wang M. T., Braunschweiger K., Soares L., Schuster M. K., Rothschild C. B., Bowden D. W., Torrey D. Development of 124 sequence-tagged sites and cytogenetic localization of 217 cosmids for human chromosome 10. Genomics. 1994 Jul 1;22(1):55–67. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]