Abstract
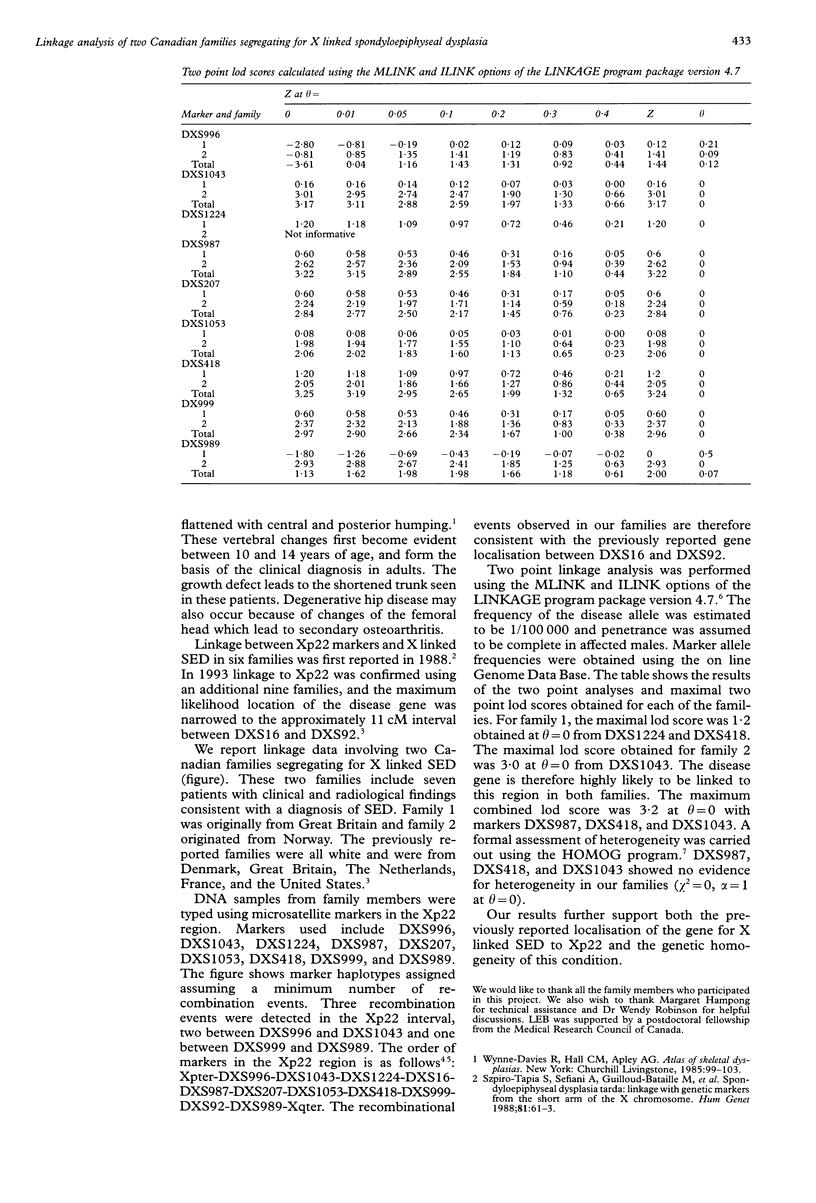
X linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia (SED) is caused by a growth defect of the vertebral bodies leading to characteristic changes in the vertebral bodies and a short trunk. The gene responsible for this disorder has previously been mapped to Xp22, with a maximum likelihood location between markers DXS16 and DXS92. We present linkage data using microsatellite markers on two Canadian X linked SED families, one of Norwegian descent and the other from Great Britain. In the Xp22 region, three recombination events have occurred in these families, two between markers DXS996 and DXS1043 and one between DXS999 and DXS989. One family shows a maximal lod score of 3.0 at theta = 0 with marker DXS1043 and the other family has a maximal lod score of 1.2 at theta = 0 with markers DXS1224 and DXS418. Both families therefore support the previously reported gene localisation.
Full text
PDF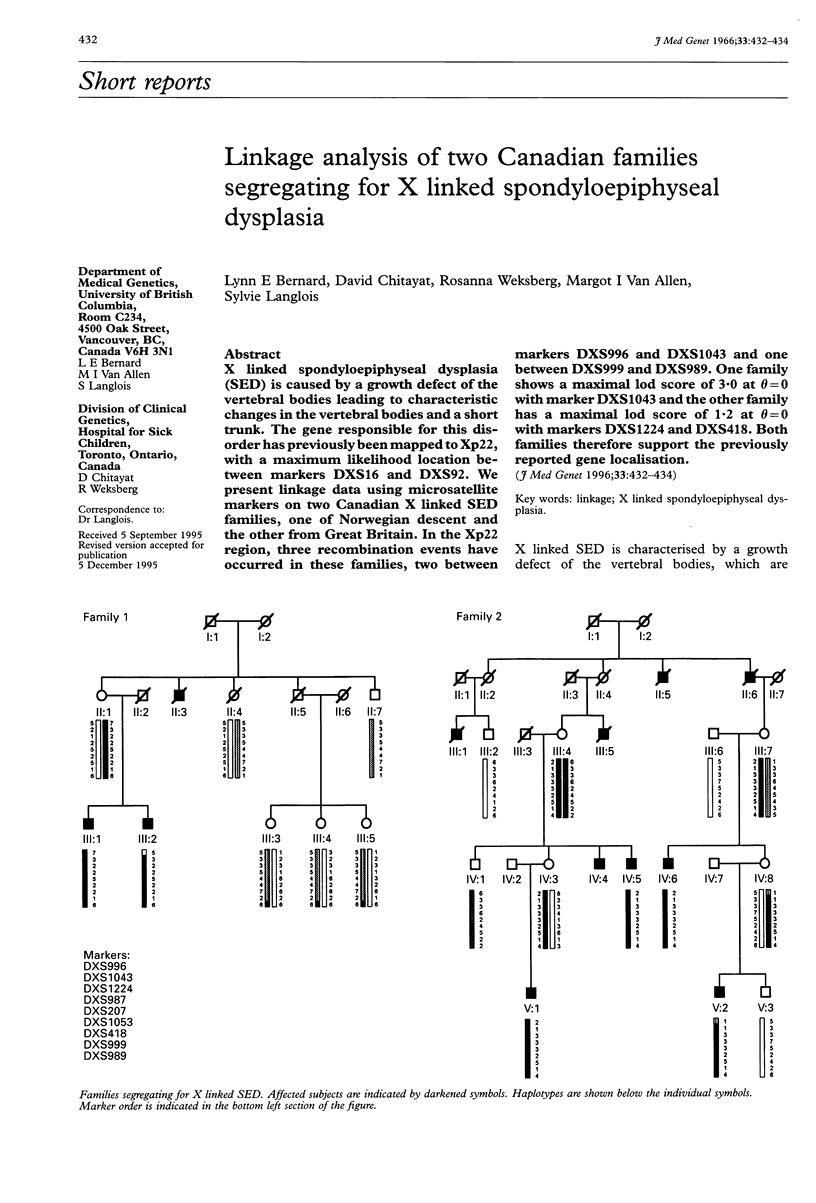

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuertz S., Nelen M., Wilkie A. O., Le Merrer M., Delrieu O., Larget-Piet L., Tranebjaerg L., Bick D., Hamel B., Van Oost B. A. The gene for spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia (SEDL) maps to Xp22 between DXS16 and DXS92. Genomics. 1993 Oct;18(1):100–104. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Efficient computations in multilocus linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;42(3):498–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpiro-Tapia S., Sefiani A., Guilloud-Bataille M., Heuertz S., Le Marec B., Frézal J., Maroteaux P., Hors-Cayla M. C. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda: linkage with genetic markers from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;81(1):61–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00283731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


