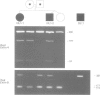
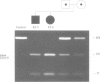
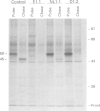
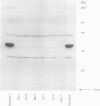
Abstract
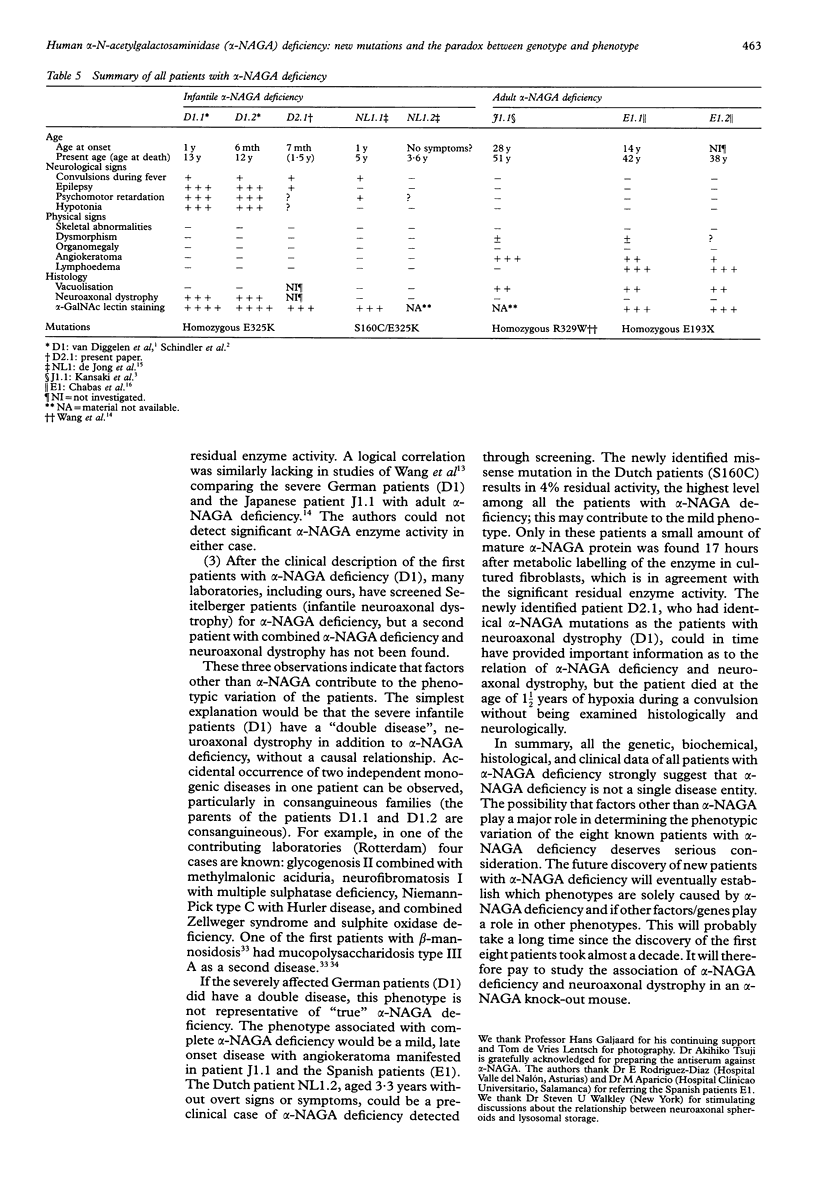
Up to now eight patients with alpha-NAGA deficiency have been described. This includes the newly identified patient reported here who died unexpectedly aged 1 1/2 years of hypoxia during convulsions; necropsy was not performed. Three patients have been genotyped previously and here we report the mutations in the other five patients, including two new mutations (S160C and E193X). The newly identified patient is consanguineous with the first patients reported with alpha-NAGA deficiency and neuroaxonal dystrophy and they all had the alpha-NAGA genotype E325K/E325K. Clinical heterogeneity among patients with alpha-NAGA deficiency is extreme. Two affected sibs, homozygotes for E325K, are severely affected and have the signs and symptoms of infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy, but prominent vacuolisation is lacking. The mildly affected patients (two families, three patients) at the opposite end of the clinical spectrum have clear vacuolisation and angiokeratoma but no overt neurological manifestations. Two of them are homozygous for the stop mutation E193X, leading to complete loss of alpha-NAGA protein. These observations are difficult to reconcile with a simple genotype-phenotype correlation and we suggest that factors or genes other than alpha-NAGA contribute to the clinical heterogeneity of the eight patients with alpha-NAGA deficiency. At the metabolic level, the patients with alpha-NAGA deficiency are similar. The major abnormal urinary oligosaccharides are sialylglycopeptides of the O linked type. Our enzymatic studies indicated that these compounds are not the primary lysosomal storage products.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chabás A., Coll M. J., Aparicio M., Rodriguez Diaz E. Mild phenotypic expression of alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency in two adult siblings. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1994;17(6):724–731. doi: 10.1007/BF00712015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P. C., Denny P. A., Allerton S. E. Determination of sialic acid using 2-thiobarbituric acid in the absence of hazardous sodium arsenite. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jul 15;131(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans M. M., Kroos M. A., de Graaff E., Oostra B. A., Reuser A. J. Two mutations affecting the transport and maturation of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase in an adult case of glycogen storage disease type II. Hum Mutat. 1993;2(4):268–273. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y., Matsumoto Y., Matsumoto M., Toida T., Iida N., Matsubara T., Kanzaki T., Yokota M., Ishizuka I. Isolation and characterization of major urinary amino acid O-glycosides and a dipeptide O-glycoside from a new lysosomal storage disorder (Kanzaki disease). Excessive excretion of serine- and threonine-linked glycan in the patient urine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1693–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Reuser A. J., Janse H. C., Kleijer W. J., Schindler D., Sakuraba H., Tsuji A., Suzuki Y., van Diggelen O. P. Biosynthesis of human alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase: defective phosphorylation and maturation in infantile alpha-NAGA deficiency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):1097–1103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91678-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki T., Wang A. M., Desnick R. J. Lysosomal alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency, the enzymatic defect in angiokeratoma corporis diffusum with glycopeptiduria. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):707–711. doi: 10.1172/JCI115357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki T., Yokota M., Irie F., Hirabayashi Y., Wang A. M., Desnick R. J. Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum with glycopeptiduria due to deficient lysosomal alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity. Clinical, morphologic, and biochemical studies. Arch Dermatol. 1993 Apr;129(4):460–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki T., Yokota M., Mizuno N., Matsumoto Y., Hirabayashi Y. Novel lysosomal glycoaminoacid storage disease with angiokeratoma corporis diffusum. Lancet. 1989 Apr 22;1(8643):875–877. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinekugel P., Michel S., Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. Quantitative correlation between the residual activity of beta-hexosaminidase A and arylsulfatase A and the severity of the resulting lysosomal storage disease. Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;88(5):513–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00219337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden H. U., Klein R. A., Egge H., Peter-Katalinic J., Dabrowski J., Schindler D. Isolation and structural characterization of sialic-acid-containing glycopeptides of the O-glycosidic type from the urine of two patients with an hereditary deficiency in alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Jul;370(7):661–672. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1989.370.2.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., Hu P., Verheijen F. W., van Diggelen O. P., Janse H. C., Kleijer W. J., Beemer F. A., Jennekens F. G. Salla disease variant in a Dutch patient. Potential value of polymorphonuclear leucocytes for heterozygote detection. Eur J Pediatr. 1992 Aug;151(8):590–595. doi: 10.1007/BF01957729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pudek M. R., Jamani A., Bernstein V., Scudamore C., Seccombe D. Low concentration galactose determination in plasma adapted to the Cobas-Bio. Clin Biochem. 1990 Jun;23(3):221–223. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(90)90627-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuser A. J., Kroos M. A., Hermans M. M., Bijvoet A. G., Verbeet M. P., Van Diggelen O. P., Kleijer W. J., Van der Ploeg A. T. Glycogenosis type II (acid maltase deficiency). Muscle Nerve Suppl. 1995;3:S61–S69. doi: 10.1002/mus.880181414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler D., Bishop D. F., Wolfe D. E., Wang A. M., Egge H., Lemieux R. U., Desnick R. J. Neuroaxonal dystrophy due to lysosomal alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 29;320(26):1735–1740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906293202606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler D., Kanzaki T., Desnick R. J. A method for the rapid detection of urinary glycopeptides in alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency and other lysosomal storage diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 1990 Sep;190(1-2):81–91. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(90)90282-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara K., Akasaki M., Funakoshi I., Aula P., Yamashina I. Structural studies of glycoasparagines from urine of a patient with aspartylglycosylaminuria (AGU). FEBS Lett. 1977 Jun 15;78(2):284–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara K., Funakoshi S., Funakoshi I., Alla P., Yamashina I. Characterization of one neutral and two acidic glycoasparagines isolated from the urine of patients with aspartylglycosylaminuria (AGU). J Biochem. 1976 Aug;80(2):195–201. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkley S. U., Baker H. J., Rattazzi M. C., Haskins M. E., Wu J. Y. Neuroaxonal dystrophy in neuronal storage disorders: evidence for major GABAergic neuron involvement. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Jul;104(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90208-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkley S. U. Pathobiology of neuronal storage disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1988;29:191–244. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Desnick R. J. Structural organization and complete sequence of the human alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase gene: homology with the alpha-galactosidase A gene provides evidence for evolution from a common ancestral gene. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Kanzaki T., Desnick R. J. The molecular lesion in the alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase gene that causes angiokeratoma corporis diffusum with glycopeptiduria. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):839–845. doi: 10.1172/JCI117404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Schindler D., Desnick R. Schindler disease: the molecular lesion in the alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase gene that causes an infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1752–1756. doi: 10.1172/JCI114901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger D. A., Sujansky E., Fennessey P. V., Thompson J. N. Human beta-mannosidase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 6;315(19):1201–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611063151906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi T., Hiraiwa M., Kobayashi H., Uda Y., Miyatake T., Tsuji S. Molecular cloning of two species of cDNAs for human alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase and expression in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91264-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota M., Koji M., Yotsumoto S. Histopathologic and ultrastructural studies of angiokeratoma corporis diffusum in Kanzaki disease. J Dermatol. 1995 Jan;22(1):10–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.1995.tb03333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong J., van den Berg C., Wijburg H., Willemsen R., van Diggelen O., Schindler D., Hoevenaars F., Wevers R. alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency with mild clinical manifestations and difficult biochemical diagnosis. J Pediatr. 1994 Sep;125(3):385–391. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diggelen O. P., Schindler D., Kleijer W. J., Huijmans J. M., Galjaard H., Linden H. U., Peter-Katalinic J., Egge H., Dabrowski U., Cantz M. Lysosomal alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency: a new inherited metabolic disease. Lancet. 1987 Oct 3;2(8562):804–804. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92542-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diggelen O. P., Schindler D., Willemsen R., Boer M., Kleijer W. J., Huijmans J. G., Blom W., Galjaard H. alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency, a new lysosomal storage disorder. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1988;11(4):349–357. doi: 10.1007/BF01800424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diggelen O. P., Zhao H., Kleijer W. J., Janse H. C., Poorthuis B. J., van Pelt J., Kamerling J. P., Galjaard H. A fluorimetric enzyme assay for the diagnosis of Morquio disease type A (MPS IV A). Clin Chim Acta. 1990 Feb 28;187(2):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(90)90339-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Pelt J., Dorland L., Duran M., Hokke C. H., Kamerling J. P., Vliegenthart J. F. Sialyl-alpha 2-6-mannosyl-beta 1-4-N-acetylglucosamine, a novel compound occurring in urine of patients with beta-mannosidosis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19685–19689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]