Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afzelius B. A. A human syndrome caused by immotile cilia. Science. 1976 Jul 23;193(4250):317–319. doi: 10.1126/science.1084576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afzelius B. A. The immotile-cilia syndrome and other ciliary diseases. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1979;19:1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken R. J., Ross A., Lees M. M. Analysis of sperm function in Kartagener's syndrome. Fertil Steril. 1983 Nov;40(5):696–698. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)47434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan L. D., Crawford D. C., Chita S. K., Anderson R. H., Tynan M. J. Familial recurrence of congenital heart disease in a prospective series of mothers referred for fetal echocardiography. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Aug 1;58(3):334–337. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso S., Pierpont M. E., Radtke W., Martinez J., Chen S. C., Grant J. W., Dähnert I., Taviaux S., Romey M. C., Demaille J. Heterotaxia syndrome and autosomal dominant inheritance. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Mar 13;56(1):12–15. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C., Devine W. A., Anderson R. H., Debich D. E., Zuberbuhler J. R. Abnormalities of the spleen in relation to congenital malformations of the heart: a survey of necropsy findings in children. Br Heart J. 1990 Feb;63(2):122–128. doi: 10.1136/hrt.63.2.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold G. L., Bixler D., Girod D. Probable autosomal recessive inheritance of polysplenia, situs inversus and cardiac defects in an Amish family. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Sep;16(1):35–42. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britz-Cunningham S. H., Shah M. M., Zuppan C. W., Fletcher W. H. Mutations of the Connexin43 gap-junction gene in patients with heart malformations and defects of laterality. N Engl J Med. 1995 May 18;332(20):1323–1329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199505183322002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. A., Wolpert L. The development of handedness in left/right asymmetry. Development. 1990 May;109(1):1–9. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brueckner M., D'Eustachio P., Horwich A. L. Linkage mapping of a mouse gene, iv, that controls left-right asymmetry of the heart and viscera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5035–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. H. The immotile cilia syndrome. Mice versus man. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1983;399(3):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00612944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J., Corney G. Congenital heart defects and twinning. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma) 1984;33(1):61–69. doi: 10.1017/s0001566000007510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL M. THE MODE OF INHERITANCE IN ISOLATED LAEVOCARDIA AND DEXTROCARDIA AND SITUS INVERSUS. Br Heart J. 1963 Nov;25:803–813. doi: 10.1136/hrt.25.6.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmi R., Magee C. A., Neill C. A., Karrer F. M. Extrahepatic biliary atresia and associated anomalies: etiologic heterogeneity suggested by distinctive patterns of associations. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Mar 15;45(6):683–693. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey B., Devoto M., Jones K. L., Ballabio A. Mapping a gene for familial situs abnormalities to human chromosome Xq24-q27.1. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):403–407. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Brueckner M., Touloukian R. J. Intestinal rotation and fixation abnormalities in heterotaxia: early detection and management. J Pediatr Surg. 1993 Oct;28(10):1281–1285. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(05)80313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu I. S., How S. W., Wang J. K., Wu M. H., Chu S. H., Lue H. C., Hung C. R. Clinical implications of atrial isomerism. Br Heart J. 1988 Jul;60(1):72–77. doi: 10.1136/hrt.60.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. Vertebrate embryo handedness. Nature. 1995 Apr 20;374(6524):681–681. doi: 10.1038/374681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czeizel A. Familial situs inversus and congenital heart defects. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):227–228. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos M. C., Yost H. J. Linkage of cardiac left-right asymmetry and dorsal-anterior development in Xenopus. Development. 1995 May;121(5):1467–1474. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.5.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCicco F., Steele M. W., Pan S., Park S. C. Monosomy of chromosome No. 22. A case report. J Pediatr. 1973 Nov;83(5):836–838. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distefano G., Romeo M. G., Grasso S., Mazzone D., Sciacca P., Mollica F. Dextrocardia with and without situs viscerum inversus in two sibs. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Aug;27(4):929–934. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engesaeth V. G., Warner J. O., Bush A. New associations of primary ciliary dyskinesia syndrome. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1993 Jul;16(1):9–12. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950160103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann W. Congenital heart disease in sibships ascertained by two affected siblings. Humangenetik. 1968;6(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00287149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatrad A. R., Read A. P., Watson G. H. Consanguinity and complex cardiac anomalies with situs ambiguus. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Mar;59(3):242–245. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.3.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuardi M., Gurrieri F., Neri G. Genes for split hand/split foot and laterality defects on 7q22.1 and Xq24-q27.1. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Mar 1;50(1):101–101. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320500125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni-Baruch R., Gottfried E., Pery M., Sahin A., Etzioni A. Immotile cilia syndrome including polysplenia, situs inversus, and extrahepatic biliary atresia. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Jul;33(3):390–393. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. Y., Cook A., Anderson R. H., Allan L. D., Fagg N. Isomerism of the atrial appendages in the fetus. Pediatr Pathol. 1991 Jul-Aug;11(4):589–608. doi: 10.3109/15513819109064792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhta J. C., Smallhorn J. F., Macartney F. J. Two dimensional echocardiographic diagnosis of situs. Br Heart J. 1982 Aug;48(2):97–108. doi: 10.1136/hrt.48.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVEMARK B. I. Implications of agenesis of the spleen on the pathogenesis of conotruncus anomalies in childhood; an analysis of the heart malformations in the splenic agenesis syndrome, with fourteen new cases. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1955 Nov;44(Suppl 104):7–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icardo J. M., Sanchez de Vega M. J. Spectrum of heart malformations in mice with situs solitus, situs inversus, and associated visceral heterotaxy. Circulation. 1991 Dec;84(6):2547–2558. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.6.2547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson M. S., McCormick J. R., Gillies C. G., Gondos B. Kartagener's syndrome with motile spermatozoa. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 28;307(18):1131–1133. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210283071807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTAGENER M., STUCKI P. Bronchiectasis with situs inversus. Arch Pediatr. 1962 Jun;79:193–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katcher A. L. Familial asplenia, other malformations, and sudden death. Pediatrics. 1980 Mar;65(3):633–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroon A. A., Heij J. M., Kuijper W. A., Veerman A. J., van der Baan S. Function and morphology of respiratory cilia in situs inversus. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1991 Jun;16(3):294–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1991.tb00934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landing B. H. Five syndromes (malformation complexes) of pulmonary symmetry, congenital heart disease, and multiple spleens. Pediatr Pathol. 1984;2(2):125–127. doi: 10.3109/15513818409025882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. A., Bond P. M., Copp A. J., Kirwan W. O., Nour S., Balling R., Mariman E., Burn J., Strachan T. A gene for autosomal dominant sacral agenesis maps to the holoprosencephaly region at 7q36. Nat Genet. 1995 Sep;11(1):93–95. doi: 10.1038/ng0995-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERKLIN R. J., VARANO N. R. Situs inversus and cardiac defects. A study of 111 cases of reversed asymmetry. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1963 Mar;45:334–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Frías M. L., Urioste M., Bermejo E., Rodríguez-Pinilla E., Félix V., Paisán L., Martínez S., Egüs J., Gómez F., Aparicio P. Primary midline developmental field. II. Clinical/epidemiological analysis of alteration of laterality (normal body symmetry and asymmetry). Am J Med Genet. 1995 May 8;56(4):382–388. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComb P., Langley L., Villalon M., Verdugo P. The oviductal cilia and Kartagener's syndrome. Fertil Steril. 1986 Sep;46(3):412–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., Porter M. E. Enzymes for microtubule-dependent motility. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6001–6004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkilä S. P., Janas M., Karikoski R., Tarkkila T., Simola K. O. X-linked laterality sequence in a family with carrier manifestations. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Feb 15;49(4):435–438. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320490417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno A., Murphy E. A. Inheritance of Kartagener syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1981;8(3):305–313. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320080309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niikawa N., Kohsaka S., Mizumoto M., Hamada I., Kajii T. Familial clustering of situs inversus totalis, and asplenia and polysplenia syndromes. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Sep;16(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLHEMUS D. W., SCHAFER W. B. Congenital absence of the spleen; syndrome with atrioventricularis and situs inversus; case reports and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):696–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peoples W. M., Moller J. H., Edwards J. E. Polysplenia: a review of 146 cases. Pediatr Cardiol. 1983 Apr-Jun;4(2):129–137. doi: 10.1007/BF02076338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phoon C. K., Neill C. A. Asplenia syndrome--risk factors for early unfavorable outcome. Am J Cardiol. 1994 Jun 15;73(16):1235–1237. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(94)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phoon C. K., Neill C. A. Asplenia syndrome: insight into embryology through an analysis of cardiac and extracardiac anomalies. Am J Cardiol. 1994 Mar 15;73(8):581–587. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(94)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priess J. R. Establishment of initial asymmetry in early Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Aug;4(4):563–568. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90073-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTTENBERG H. D., NEUFELD H. N., LUCAS R. V., Jr, CAREY L. S., ADAMS P., Jr, ANDERSON R. C., EDWARDS J. E. SYNDROME OF CONGENITAL CARDIAC DISEASE WITH ASPLENIA. DISTINCTION FROM OTHER FORMS OF CONGENITAL CYANOTIC CARDIAC DISEASE. Am J Cardiol. 1964 Mar;13:387–406. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(64)90454-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhyu M. S., Knoblich J. A. Spindle orientation and asymmetric cell fate. Cell. 1995 Aug 25;82(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose V., Izukawa T., Moës C. A. Syndromes of asplenia and polysplenia. A review of cardiac and non-cardiac malformations in 60 cases withspecial reference to diagnosis and prognosis. Br Heart J. 1975 Aug;37(8):840–852. doi: 10.1136/hrt.37.8.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi M. B., Burn J., Ho S. Y., Thiene G., Devine W. A., Anderson R. H. Conjoined twins, right atrial isomerism, and sequential segmental analysis. Br Heart J. 1987 Nov;58(5):518–524. doi: 10.1136/hrt.58.5.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossman C. M., Forrest J. B., Lee R. M., Newhouse M. T. The dyskinetic cilia syndrome. Ciliary motility in immotile cilia syndrome. Chest. 1980 Oct;78(4):580–582. doi: 10.1378/chest.78.4.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott H. D. Kartagener's syndrome and the syndrome of immotile cilia. Hum Genet. 1979 Feb 15;46(3):249–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00273308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutland J., Cole P. J. Non-invasive sampling of nasal cilia for measurement of beat frequency and study of ultrastructure. Lancet. 1980 Sep 13;2(8194):564–565. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91995-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHONFELD E. A., FRISCHMAN B. Syndrome of spleen agenesis, defects of the heart and vessels and situs inversus; report of a case suggesting heredity as an etiological factor. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1958 Dec;13(6):636–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel I. Kartagener's syndrome with normal spermatozoa. JAMA. 1987 Sep 11;258(10):1329–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapire D. W., Ho S. Y., Anderson R. H., Rigby M. L. Diagnosis and significance of atrial isomerism. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Aug 1;58(3):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schidlow D. V., Katz S. M., Turtz M. G., Donner R. M., Capasso S. Polysplenia and kartagener syndromes in a sibship: association with abnormal respiratory cilia. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):401–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80439-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo J. W., Brown N. A., Ho S. Y., Anderson R. H. Abnormal laterality and congenital cardiac anomalies. Relations of visceral and cardiac morphologies in the iv/iv mouse. Circulation. 1992 Aug;86(2):642–650. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.2.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
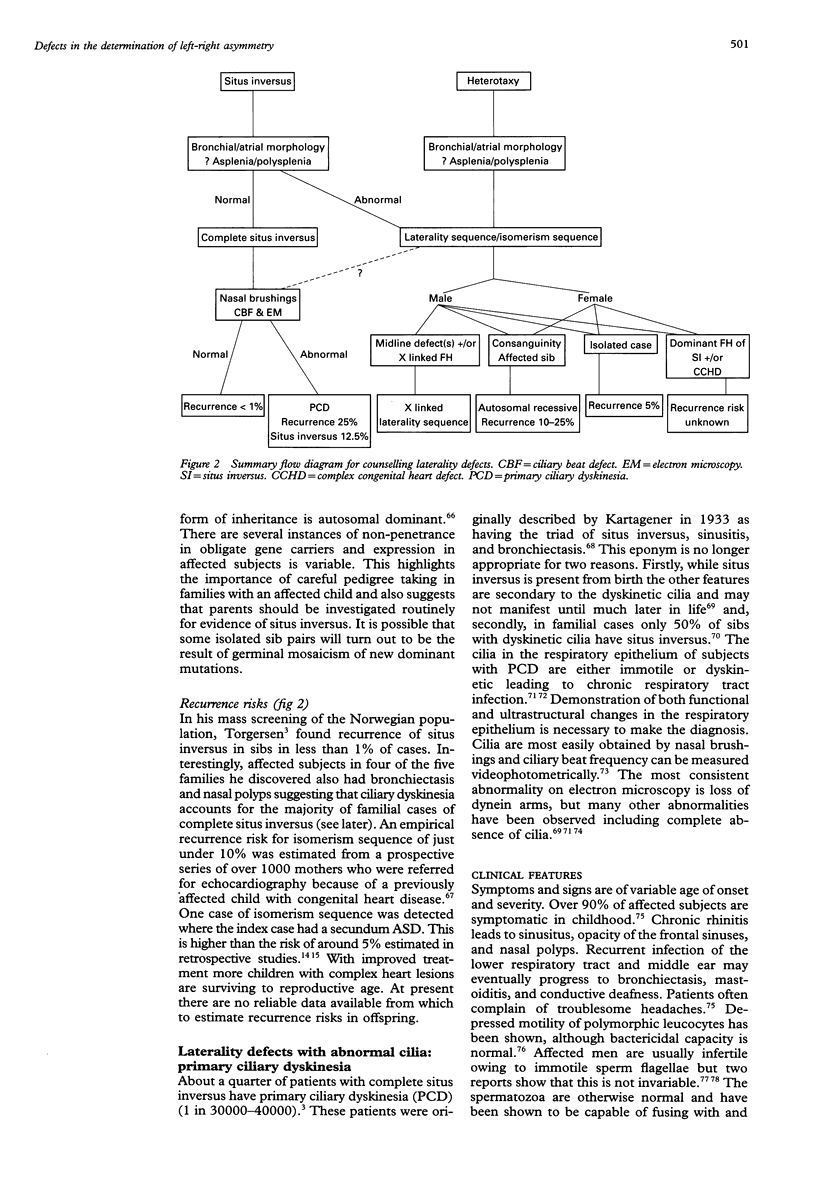
- Sharma S., Devine W., Anderson R. H., Zuberbuhler J. R. Identification and analysis of left atrial isomerism. Am J Cardiol. 1987 Nov 15;60(14):1157–1160. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(87)90410-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splitt M. P., Burn J., Goodship J. Connexin43 mutations in sporadic and familial defects of laterality. N Engl J Med. 1995 Oct 5;333(14):941–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess J. M., Thompson M. W., Czegledy-Nagy E., Turner J. A. Genetic aspects of immotile cilia syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Sep;25(1):149–160. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg S., Markowitz J., Silverberg M., Aiges H., Schneider K., Kahn E., Daum F. Abnormal cilia in a child with the polysplenia syndrome and extrahepatic biliary atresia. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):399–401. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torikata C., Kijimoto C., Koto M. Ultrastructure of respiratory cilia of WIC-Hyd male rats. An animal model for human immotile cilia syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1991 Feb;138(2):341–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerius N. H., Knudsen B. B., Pedersen M. Defective neutrophil motility in patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;13(6):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1983.tb00134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright H., Nelson M. Polysplenia syndrome and congenital short pancreas. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Sep 1;47(3):318–320. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Chang M. H. Association of hiatus hernia with asplenia syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1995 Feb 1;75(4):317–317. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(95)80055-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Li Y. W., Chiu I. S., Wu M. H., Chang Y. C., Hung C. R., Lue H. C. Usefulness of magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of venoatrial connections, atrial morphology, bronchial situs, and other anomalies in right atrial isomerism. Am J Cardiol. 1994 Oct 1;74(7):701–704. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(94)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama T., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Montgomery C. A., Elder F. F., Overbeek P. A. Reversal of left-right asymmetry: a situs inversus mutation. Science. 1993 Apr 30;260(5108):679–682. doi: 10.1126/science.8480178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J. Vertebrate left-right development. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):689–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotogora J., Elian E. Asplenia and polysplenia syndromes with abnormalities of lateralisation in a sibship. J Med Genet. 1981 Aug;18(4):301–302. doi: 10.1136/jmg.18.4.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotogora J., Schimmel M. S., Glaser Y. Familial situs inversus and congenital heart defects. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jan;26(1):181–184. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M., Hutchins G. M. Sisters with polysplenia. Am J Med Genet. 1985 May;21(1):171–176. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]