Abstract
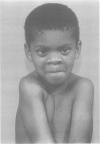
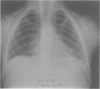
Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is an autosomal dominant disorder, features of which include a patient anterior fontanelle, a bulging calvarium, hypoplasia or aplasia of the clavicles, a wide public symphysis, dental anomalies, vertebral malformation, and short stature. The Cape Town kindred which is under our genetic management was originally described more than four decades ago and now consists of more than 1000 people. Following reports of rearrangements on chromosomes 6 and 8 in people with CCD, we have carried out linkage analyses between highly information microsatellite dinucleotide repeat markers in the rearranged regions and the disorder in a branch of this South African CCD kindred, consisting of 38 subjects, 18 of whom are affected. Maximum lod scores (at theta = 0.00) of 7.14 (for marker D6S459), 4.32 (TCTE), 4.99 (D6S452), 5.97 (D6S269), and 3.95 (D6S465) confirm linkage of the disorder to the short arm of chromosome 6. Our data indicate that the CCD gene is located within a minimal region of approximately 10 cM flanked by the marker D6S451 distally and D6S466 proximally. This information is vital towards isolating and characterising the gene for CCD, and is being used to construct a physical map of 6p21.1-6p21.3. More importantly, mapping of the locus in the South African kindred of mixed ancestry, in which the "founder" of the disorder was of Chinese origin, suggests that a single locus is responsible for classic CCD.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brueton L. A., Reeve A., Ellis R., Husband P., Thompson E. M., Kingston H. M. Apparent cleidocranial dysplasia associated with abnormalities of 8q22 in three individuals. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jun 1;43(3):612–618. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman G. J., Robin N. H., Brueton L. A., Robertson E., Thompson E. M., Siegel-Bartelt J., Gasser D. L., Bailey L. C., Zackai E. H., Muenke M. A gene for cleidocranial dysplasia maps to the short arm of chromosome 6. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Apr;56(4):938–943. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb B. D., Cooper E., Shevell M., Desnick R. J. Genetic mapping of the cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) locus on chromosome band 6p21 to include a microdeletion. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Aug 28;58(2):200–205. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320580222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn G. V., Cohen R. B., Wozney J. M., Levitz C. L., Shore E. M., Zasloff M. A., Kaplan F. S. A bone morphogenetic protein subfamily: chromosomal localization of human genes for BMP5, BMP6, and BMP7. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):759–762. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON W. P. U. Osteo-dental dysplasia (cleido-cranial dysostosis); the "Arnold head". Acta Med Scand. 1951;139(4):292–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M., Bland A. E., Grubber J. M., Marker P. C., Russell L. B., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. The mouse short ear skeletal morphogenesis locus is associated with defects in a bone morphogenetic member of the TGF beta superfamily. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):399–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90510-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski T. J., Jr, Beaudet A. L., Trask B. J., Zoghbi H. Y. Linkage mapping and fluorescence in situ hybridization of TCTE1 on human chromosome 6p: analysis of dinucleotide polymorphisms on native gels. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):921–926. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90180-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauvieux V., Jouanolle A. M., el Kahloun A., Blayau M., Le Gall J. Y., David V. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the FTHPI locus of chromosome 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6969–6969. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundlos S., Mulliken J. B., Abramson D. L., Warman M. L., Knoll J. H., Olsen B. R. Genetic mapping of cleidocranial dysplasia and evidence of a microdeletion in one family. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jan;4(1):71–75. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nienhaus H., Mau U., Zang K. D., Henn W. Pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 in a patient with cleidocranial dysplasia. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jul 1;46(6):630–631. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R. Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science. 1965 Nov 12;150(3698):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3698.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]