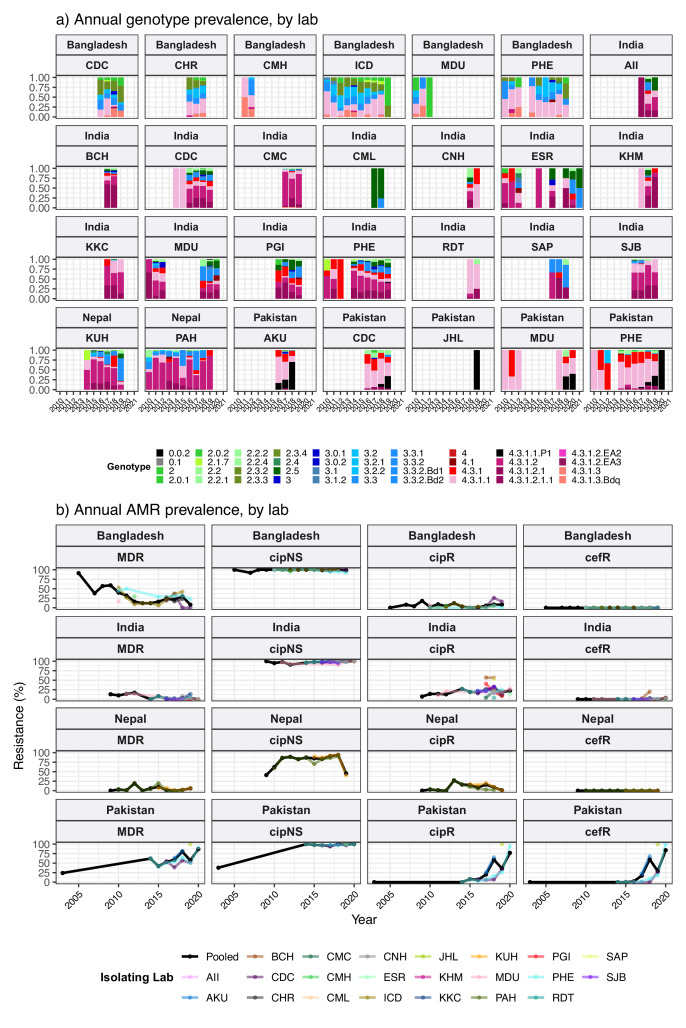
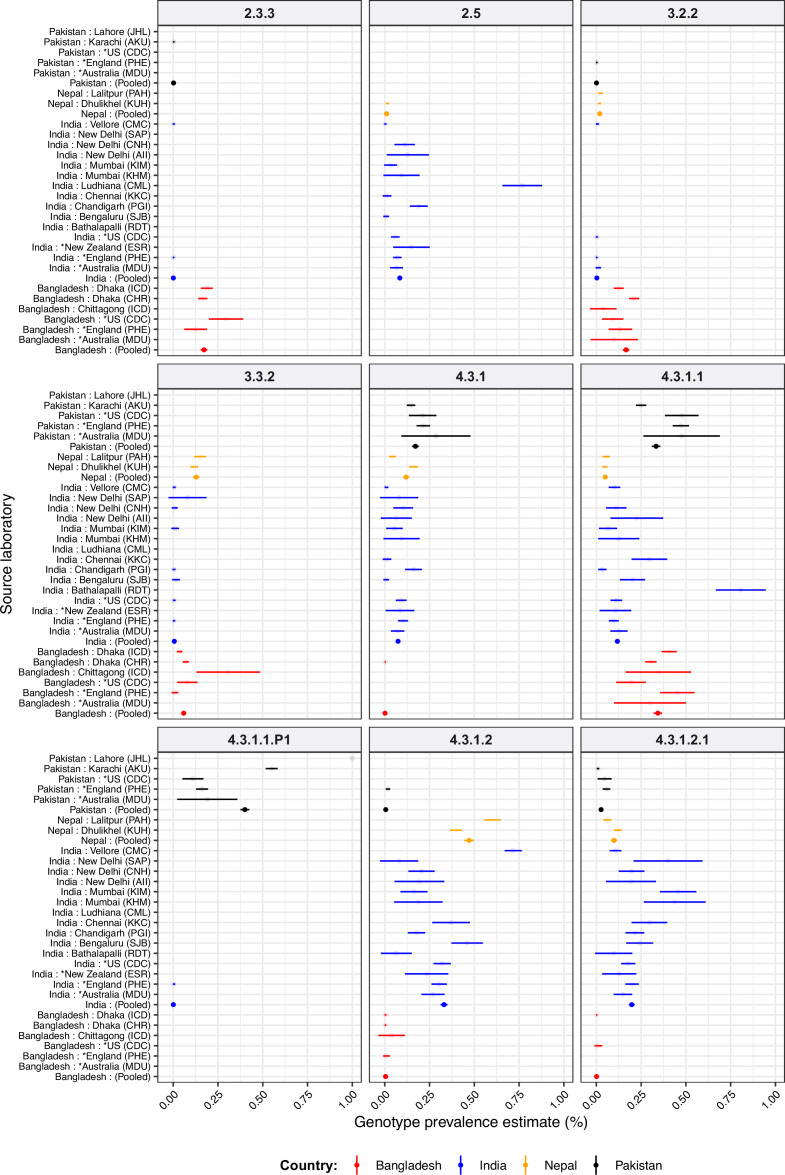
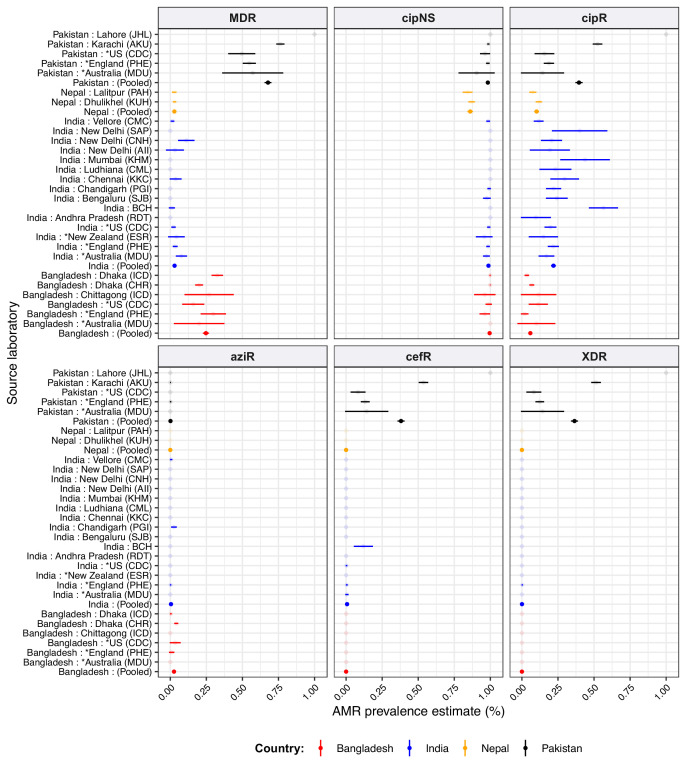
Figure 6. Annual genotype and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) frequencies by isolating lab, for South Asian countries with multiple data sources.
Labs shown are those with ≥20 isolates; and years shown for each lab are those with N≥5 isolates from that year. (a) Bars are coloured to indicate annual genotype prevalence, as per inset legend. (b) Lines indicate annual frequencies of key AMR profiles, coloured by isolating laboratory as per inset legend. MDR, multidrug resistant; XDR, extensively drug resistant; CipNS, ciprofloxacin non-susceptible; CipR, ciprofloxacin resistant; CefR, ceftriaxone resistant. See Supplementary file 9 for three-letter laboratory code master list.