Abstract
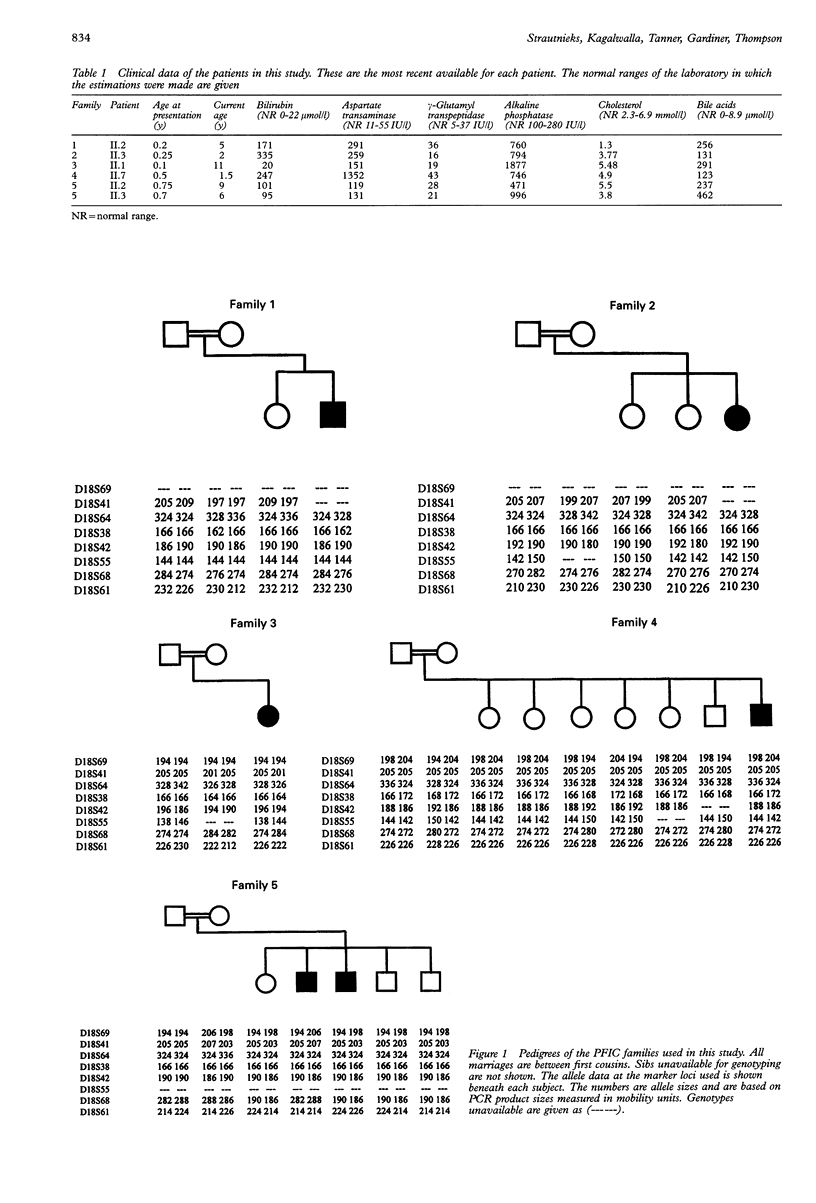
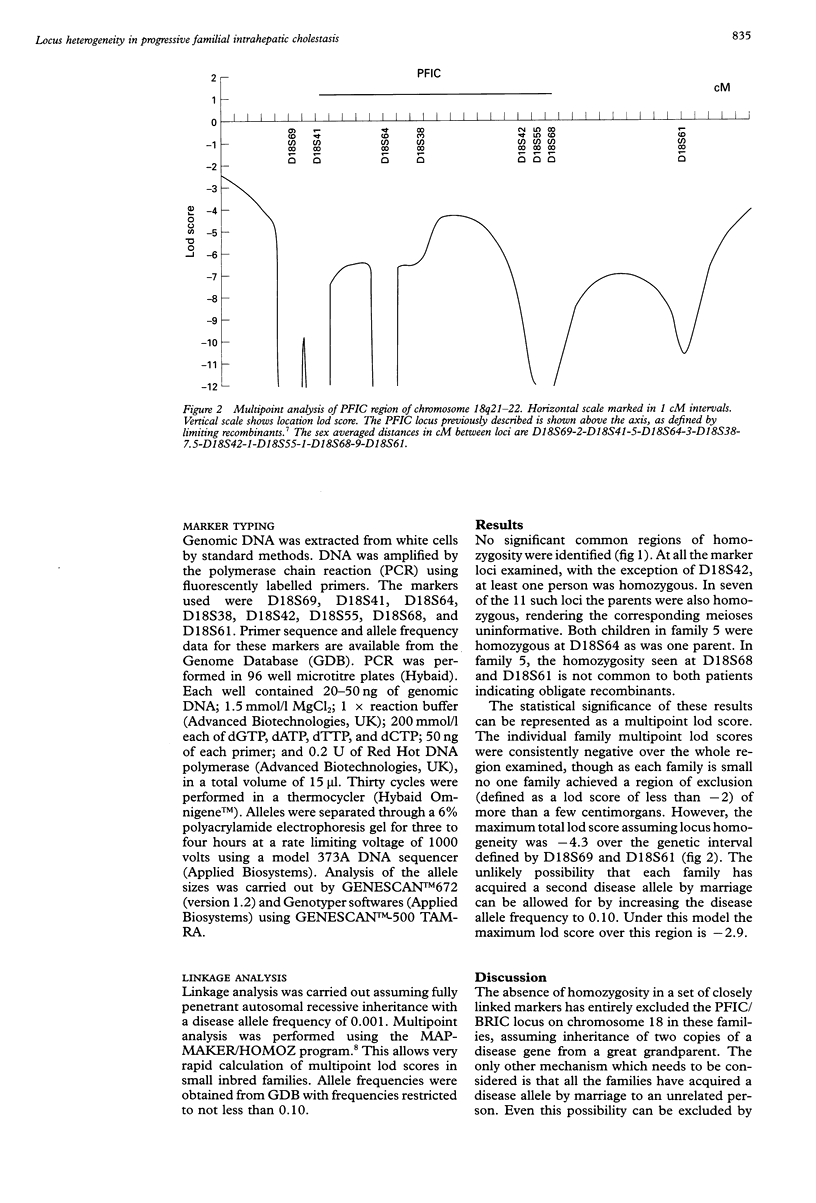
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC or Byler disease) is a rare autosomal recessive form of severe and fatal cholestatic liver disease. A locus for PFIC has recently been mapped to chromosome 18q21-q22 in the original Byler pedigree. This region harbours the locus for a related phenotype, benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis (BRIC), suggesting that these traits are allelic. Linkage analysis was undertaken in five consanguineous PFIC pedigrees from Saudi Arabia using marker loci (D18S69, D18S41, D18S64, D18S38, D18S42, D18S55, D18S68, and D18S61) which span the Byler disease/BRIC region on 18q21-q22. In this family set the disease locus was excluded from this region, showing that locus heterogeneity exists for the PFIC phenotype.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler M., Chung K. W., Schaffner F. Pericanalicular hepatocytic and bile ductular microfilaments in cholestasis in man. Am J Pathol. 1980 Mar;98(3):603–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton V. E., Knisely A. S., Freimer N. B. Mapping of a locus for progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (Byler disease) to 18q21-q22, the benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis region. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jun;4(6):1049–1053. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.6.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frimmer M., Ziegler K. The transport of bile acids in liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):75–99. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Foguet M., Lübbert H., Meier P. J. Functional expression cloning and characterization of the hepatocyte Na+/bile acid cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10629–10633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwen R. H., Baharloo S., Blankenship K., Raeymaekers P., Juyn J., Sandkuijl L. A., Freimer N. B. Genome screening by searching for shared segments: mapping a gene for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1994 Dec;8(4):380–386. doi: 10.1038/ng1294-380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. Evidence for the presence of an Na+-independent transport system. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):659–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI111257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Setchell K. D., O'Connell N. C., Estrada A., Maggiore G., Schmitz J., Hadchouel M., Bernard O. A new cause of progressive intrahepatic cholestasis: 3 beta-hydroxy-C27-steroid dehydrogenase/isomerase deficiency. J Pediatr. 1994 Sep;125(3):379–384. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83280-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Daly M. J., Lander E. S. Rapid multipoint linkage analysis of recessive traits in nuclear families, including homozygosity mapping. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;56(2):519–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lajeunie E., Ma H. W., Bonaventure J., Munnich A., Le Merrer M., Renier D. FGFR2 mutations in Pfeiffer syndrome. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):108–108. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggiore G., Bernard O., Riely C. A., Hadchouel M., Lemonnier A., Alagille D. Normal serum gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase activity identifies groups of infants with idiopathic cholestasis with poor prognosis. J Pediatr. 1987 Aug;111(2):251–252. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenke M., Schell U., Hehr A., Robin N. H., Losken H. W., Schinzel A., Pulleyn L. J., Rutland P., Reardon W., Malcolm S. A common mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 gene in Pfeiffer syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):269–274. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen I. M., Ornvold K., Jacobsen B. B., Ranek L. Fatal familial cholestatic syndrome in Greenland Eskimo children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Nov;75(6):1010–1016. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutland P., Pulleyn L. J., Reardon W., Baraitser M., Hayward R., Jones B., Malcolm S., Winter R. M., Oldridge M., Slaney S. F. Identical mutations in the FGFR2 gene cause both Pfeiffer and Crouzon syndrome phenotypes. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):173–176. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A. M., Tuchweber B., Yousef I., Brochu P., Turgeon C., Gabbiani G., Morin C. L., Roy C. C. Severe familial cholestasis in North American Indian children: a clinical model of microfilament dysfunction? Gastroenterology. 1981 Oct;81(4):653–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


