Abstract
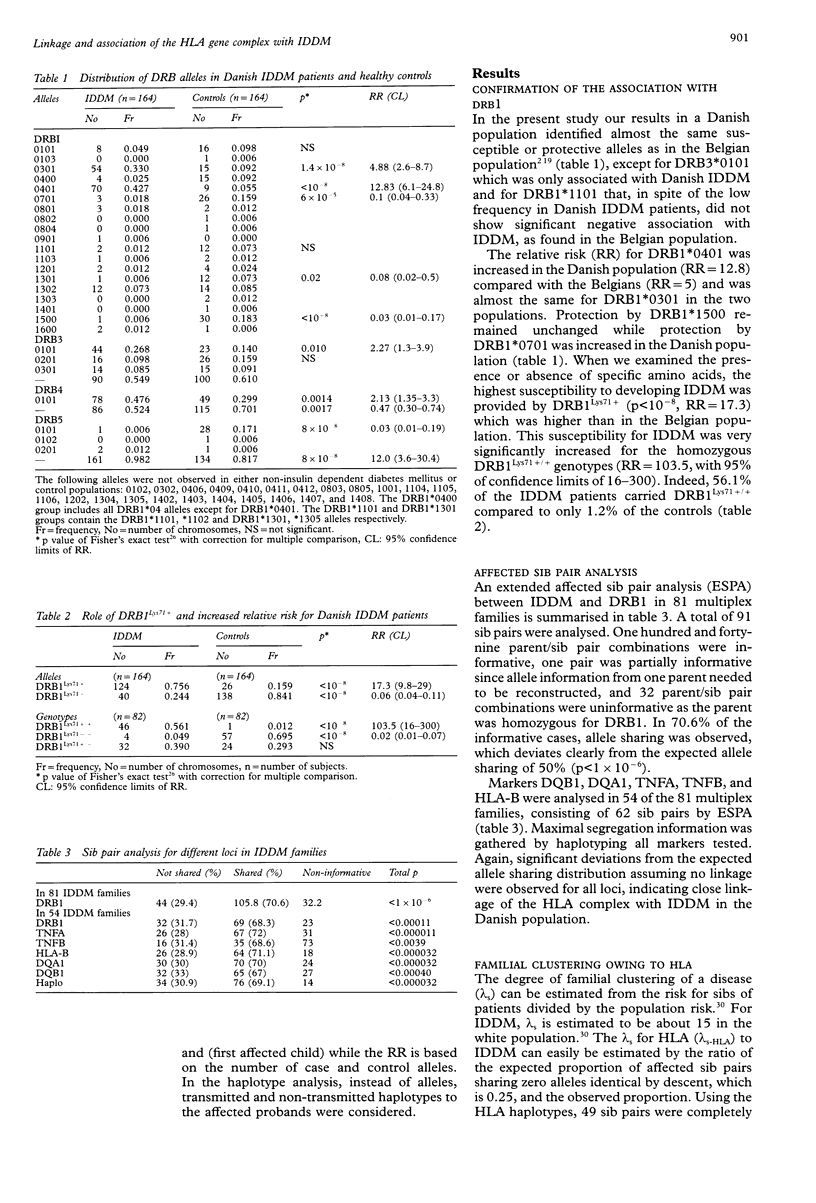
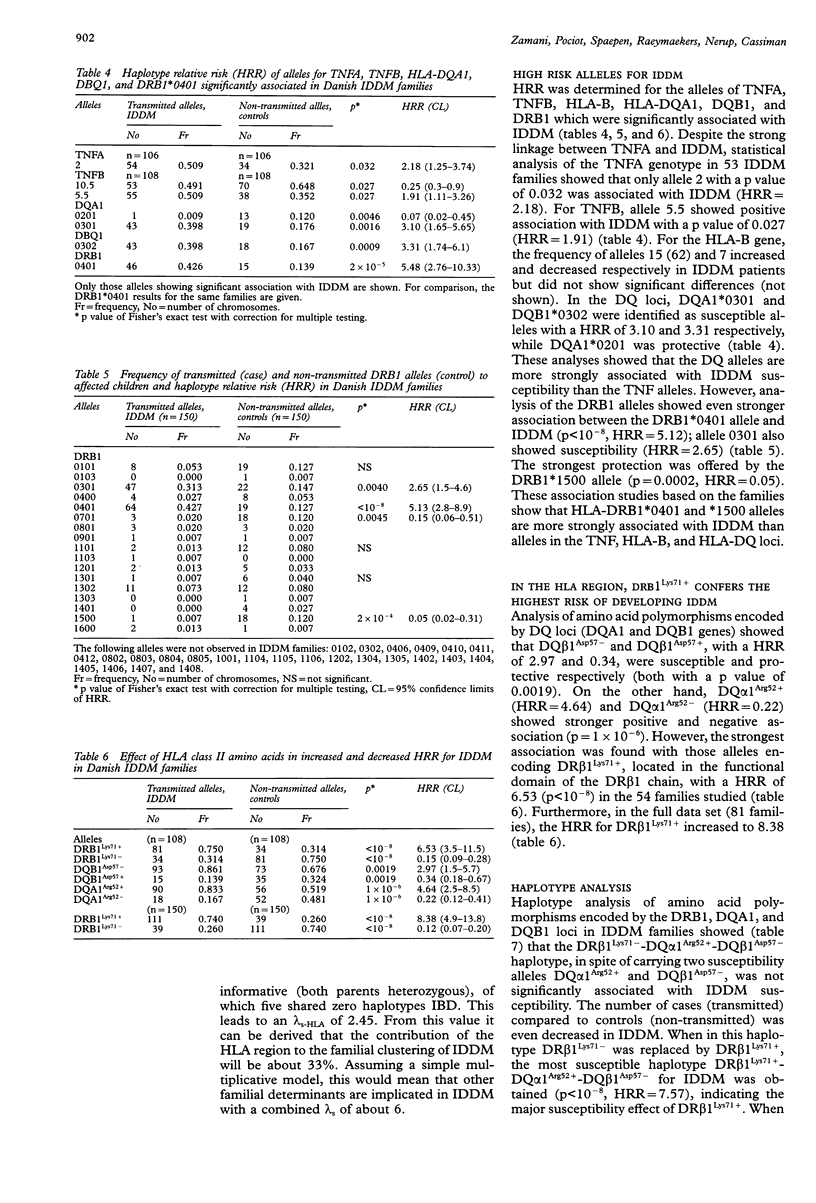
Many studies have shown an association of IDDM with polymorphisms in the HLA region on chromosome 6p21. Previously our case-control study in the Belgian population showed significant association between IDDM and certain HLA class II alleles, in particular Lys71+, encoding DRB1 alleles. In the present study, 81 Danish multiplex IDDM families and 82 healthy Danish controls were examined for polymorphisms in the HLA-DRB genes and 54 of the 81 families for polymorphisms in HLA-B, -DQA1, -DQB1, -TNFA, and -TNFB genes. The results confirm our previous studies in the Belgian population and show that DRB1Lya71+/+ homozygotes have a relative risk (RR) of 103.5. Linkage between IDDM and DRB1 alleles that encode Lys71+ was shown by affected zib pair analysis which showed strong linkage (p < 1 x 10(-6). By family based association studies, the DRB1Lys71+ was identified as the allale which increased susceptibility to develop IDDM most in the HLA region (haplotype relative risk = 8.38). Haplotype analysis confirmed the increased risk contributed by DRB1Lys71+ alleles and in addition showed that DRB1Lys71- provides protection against IDDM even in the presence of DQB1Aep47-. These results indicate that DRB1Lys71+ screening is a powerful test compared to full HLA typing to determine the risk for a random person to develop IDDM in the Danish population, with an even higher probability than shown previously for the Belgians.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awata T., Kuzuya T., Matsuda A., Iwamoto Y., Kanazawa Y., Okuyama M., Juji T. High frequency of aspartic acid at position 57 of HLA-DQ beta-chain in Japanese IDDM patients and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):266–269. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baisch J. M., Weeks T., Giles R., Hoover M., Stastny P., Capra J. D. Analysis of HLA-DQ genotypes and susceptibility in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 28;322(26):1836–1841. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006283222602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T. S., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Urban R. G., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):33–39. doi: 10.1038/364033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyse I., Sandkuyl L. A., Zamani Ghabanbasani M., Gu X. X., Bouillon R., Bex M., Dooms L., Emonds M. P., Duhamel M., Marynen P. Association of particular HLA class II alleles, haplotypes and genotypes with susceptibility to IDDM in the Belgian population. Diabetologia. 1994 Aug;37(8):808–817. doi: 10.1007/BF00404338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G., Woodrow J. C. Evidence for HL-A-linked genes in "juvenile" diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 19;3(5976):133–135. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5976.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. L., Kawaguchi Y., Bennett S. T., Copeman J. B., Cordell H. J., Pritchard L. E., Reed P. W., Gough S. C., Jenkins S. C., Palmer S. M. A genome-wide search for human type 1 diabetes susceptibility genes. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):130–136. doi: 10.1038/371130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman J. S., LaPorte R. E., Stone R. A., Trucco M. Worldwide differences in the incidence of type I diabetes are associated with amino acid variation at position 57 of the HLA-DQ beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7370–7374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk C. T., Rubinstein P. Haplotype relative risks: an easy reliable way to construct a proper control sample for risk calculations. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;51(Pt 3):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb00875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. L., Tobias R., Magnus T. A locus on chromosome 15q26 (IDDM3) produces susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):189–194. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giphart M. J., Roep B. O., Drabbels J., D'Amaro J., Bruining G. J., Abdulkadir J., Verduyn W. Relative contribution of HLA-DQA and -DQB alleles to predisposition to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Hum Immunol. 1992 Jun;34(2):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(92)90040-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto L., Habita C., Beressi J. P., Delepine M., Besse C., Cambon-Thomsen A., Deschamps I., Rotter J. I., Djoulah S., James M. R. Genetic mapping of a susceptibility locus for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus on chromosome 11q. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):161–164. doi: 10.1038/371161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Briant L., Udalova I. A., Sevin A., Nedospasov S. A., Cambon-Thomsen A. Extensive genetic polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor region and relation to extended HLA haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil I., d'Auriol L., Gobet M., Morin L., Lepage V., Deschamps I., Park M. S., Degos L., Galibert F., Hors J. A combination of HLA-DQ beta Asp57-negative and HLA DQ alpha Arg52 confers susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1315–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI114569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M., Seuchter S. A., Baur M. P. The haplotype-relative-risk (HRR) method for analysis of association in nuclear families. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1085–1093. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh S. G., Bodmer J. G. HLA class II nucleotide sequences, 1992. Hum Immunol. 1992 Sep;35(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(92)90090-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel P. A., Dorman J. S., Todd J. A., McDevitt H. O., Trucco M. Aspartic acid at position 57 of the HLA-DQ beta chain protects against type I diabetes: a family study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8111–8115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Thomson G., Motro U., Louis E. J., Hudes E. The affected sib method. IV. Sib trios. Ann Hum Genet. 1985 Oct;49(Pt 4):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platz P., Jakobsen B. K., Morling N., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A., Thomsen M., Christy M., Kromann H., Benn J., Nerup J. HLA-D and -DR antigens in genetic analysis of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1981 Aug;21(2):108–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00251276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pociot F., Rønningen K. S., Bergholdt R., Lorenzen T., Johannesen J., Ye K., Dinarello C. A., Nerup J. Genetic susceptibility markers in Danish patients with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes--evidence for polygenicity in man. Danish Study Group of Diabetes in Childhood. Autoimmunity. 1994;19(3):169–178. doi: 10.3109/08916939408995692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. Assessing the role of HLA-linked and unlinked determinants of disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jan;40(1):1–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønningen K. S., Iwe T., Halstensen T. S., Spurkland A., Thorsby E. The amino acid at position 57 of the HLA-DQ beta chain and susceptibility to develop insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Hum Immunol. 1989 Nov;26(3):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(89)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønningen K. S., Spurkland A., Markussen G., Iwe T., Vartdal F., Thorsby E. Distribution of HLA class II alleles among Norwegian Caucasians. Hum Immunol. 1990 Dec;29(4):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(90)90041-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaid D. J., Sommer S. S. Comparison of statistics for candidate-gene association studies using cases and parents. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Aug;55(2):402–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF B. On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Jun;19(4):251–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A., Cudworth A. G. Type I (insulin-dependent) diabetic multiplex families: mode of genetic transmission. Diabetes. 1980 Dec;29(12):1036–1039. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.12.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamani Ghabanbasani M., Spaepen M., Buyse I., Marynen P., Bex M., Bouillon R., Cassiman J. J. Improved risk assessment for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus by analysis of amino acids in HLA-DQ and DRB1 loci. Eur J Hum Genet. 1994;2(3):177–184. doi: 10.1159/000472361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


