Abstract
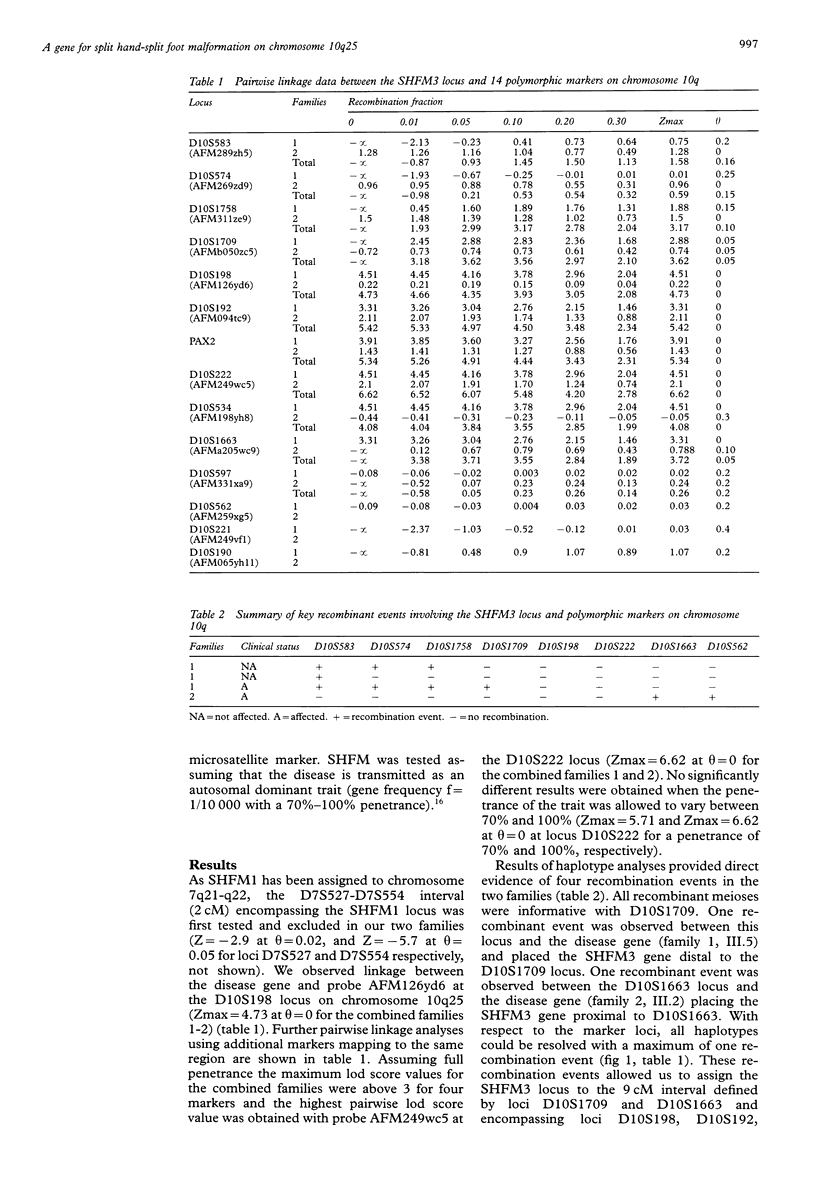
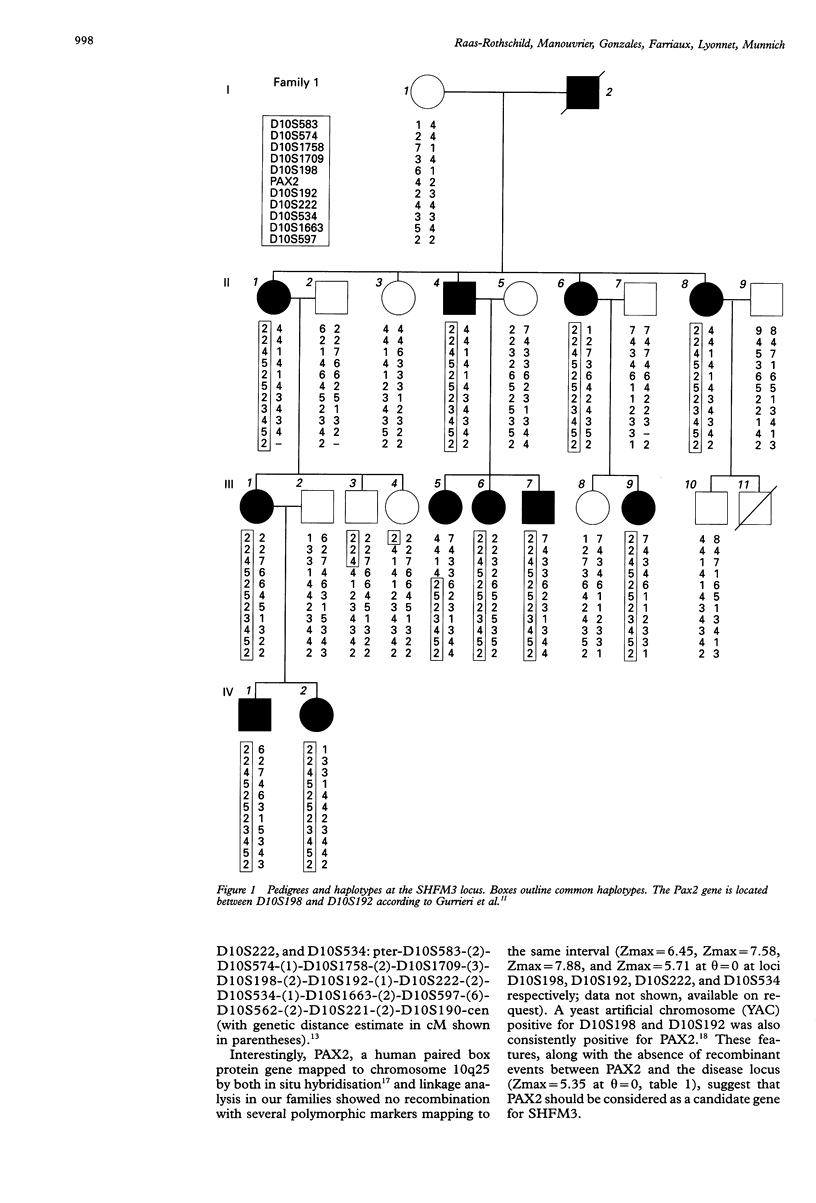
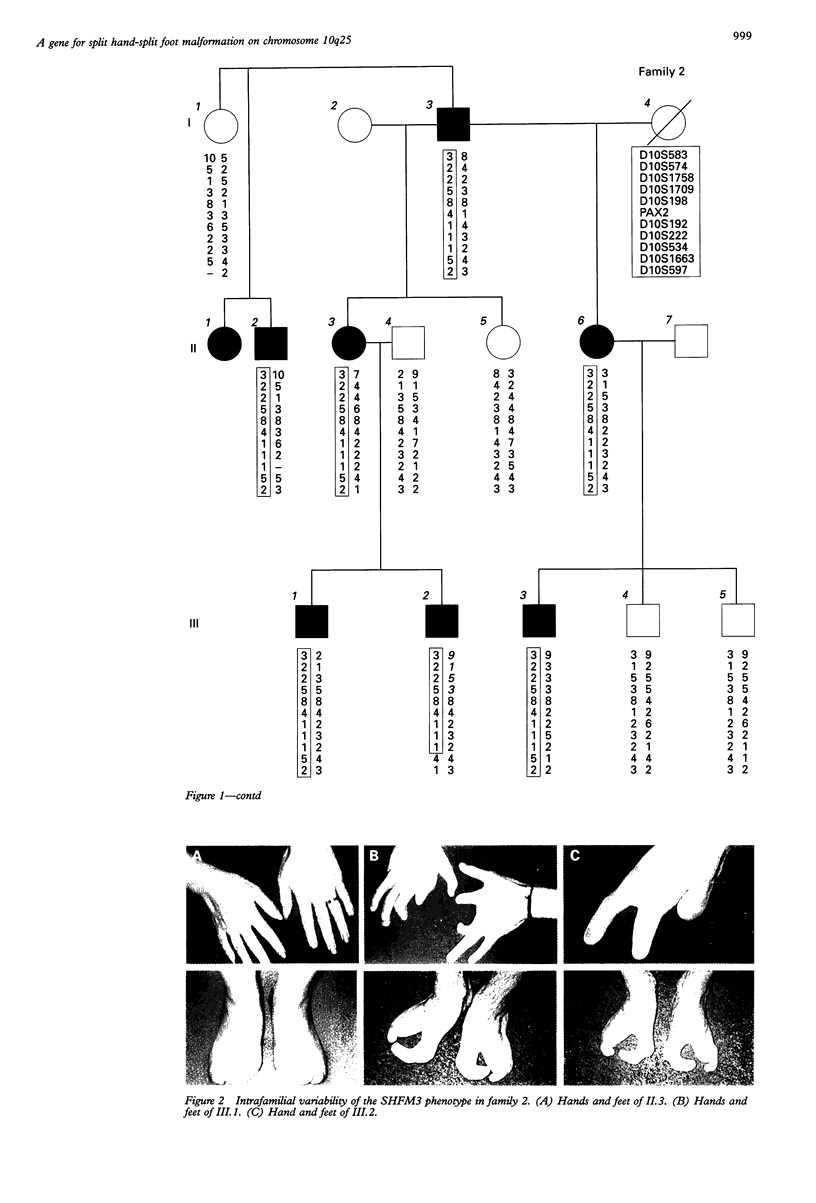
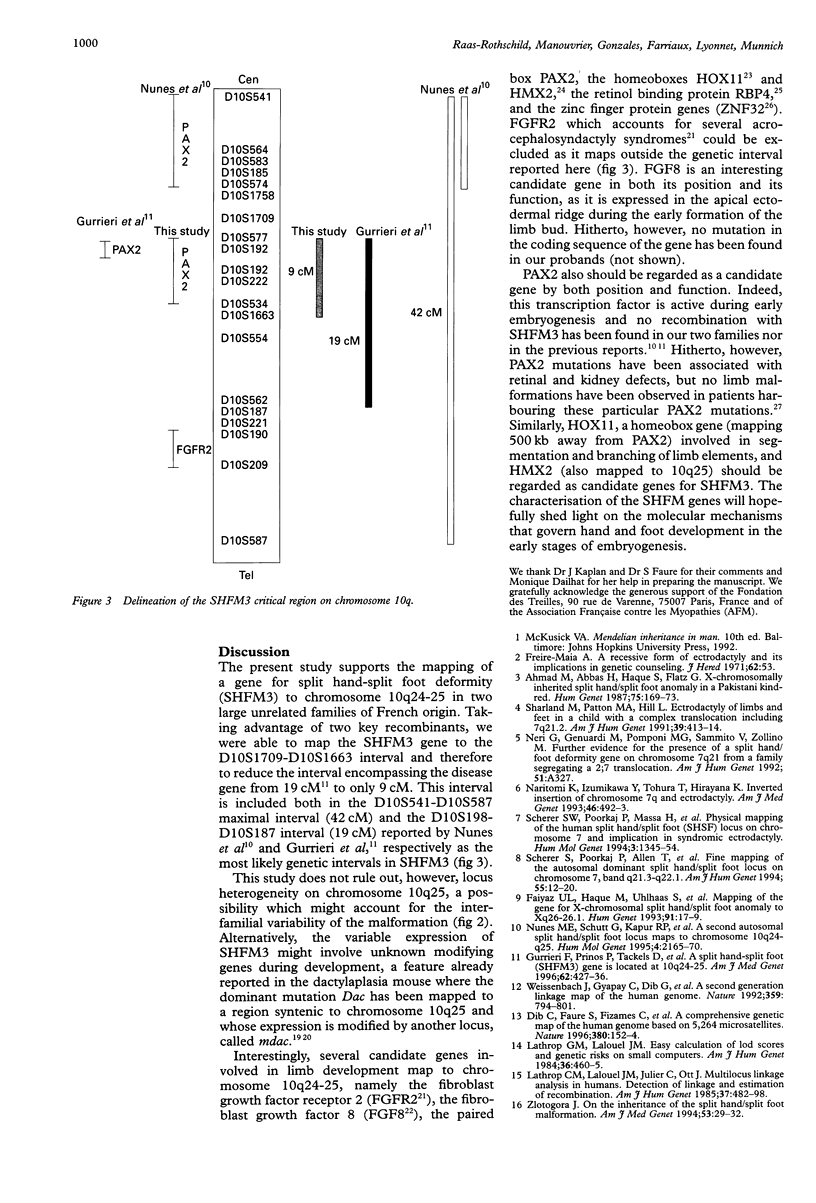
Split hand-split foot malformation (SHFM) is a genetically heterogeneous limb developmental defect characterised by the absence of digital rays and syndactyly of the remaining digits. Three disease loci have recently been mapped to chromosomes 7q21 (SHFM1), Xq26 (SHFM2), and 10q25 respectively (SHFM3). We report the mapping of SHFM3 to chromosome 10q25 in two large SHFM families of French ancestry (Zmax for the combined families = 6.62 at theta = 0 for marker AFM249wc5 at locus D10S222). Two recombinant events reduced the critical region to a 9 cM interval (D10S1709-D10S1663) encompassing several candidate genes including a paired box gene PAX2 (Zmax = 5.35 at theta = 0). The fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF 8), the retinol binding protein (RBP4), the zinc finger protein (ZNF32), and the homeobox genes HMX2 and HOX11 are also good candidates by both their position and their function.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad M., Abbas H., Haque S., Flatz G. X-chromosomally inherited split-hand/split-foot anomaly in a Pakistani kindred. Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;75(2):169–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00591081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Aronson M. M., Thiesen H. J. Human zinc finger gene ZNF23 (Kox16) maps to a zinc finger gene cluster on chromosome 16q22, and ZNF32 (Kox30) to chromosome region 10q23-q24. Hum Genet. 1993 May;91(4):383–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00217362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai C. K. Dactylaplasia in mice a two-locus model for development anomalies. J Hered. 1981 Jul-Aug;72(4):234–237. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a109486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib C., Fauré S., Fizames C., Samson D., Drouot N., Vignal A., Millasseau P., Marc S., Hazan J., Seboun E. A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature. 1996 Mar 14;380(6570):152–154. doi: 10.1038/380152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faiyaz ul Haque M., Uhlhaas S., Knapp M., Schüler H., Friedl W., Ahmad M., Propping P. Mapping of the gene for X-chromosomal split-hand/split-foot anomaly to Xq26-q26.1. Hum Genet. 1993 Mar;91(1):17–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00230215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freire-Maia A. A recessive form of ectrodactyly, and its implications in genetic counseling. J Hered. 1971 Jan-Feb;62(1):53–53. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurrieri F., Prinos P., Tackels D., Kilpatrick M. W., Allanson J., Genuardi M., Vuckov A., Nanni L., Sangiorgi E., Garofalo G. A split hand-split foot (SHFM3) gene is located at 10q24-->25. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Apr 24;62(4):427–436. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960424)62:4<427::AID-AJMG16>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Lane P. W., Ward-Bailey P., Davisson M. T. Mapping the mouse dactylaplasia mutation, Dac, and a gene that controls its expression, mdac. Genomics. 1995 Sep 20;29(2):457–464. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.9981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. A., Gonzalez-Sarmiento R., Kees U. R., Lampert F., Dear N., Boehm T., Rabbitts T. H. HOX11, a homeobox-containing T-cell oncogene on human chromosome 10q24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8900–8904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naritomi K., Izumikawa Y., Tohma T., Hirayama K. Inverted insertion of chromosome 7q and ectrodactyly. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jun 15;46(5):492–493. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes M. E., Schutt G., Kapur R. P., Luthardt F., Kukolich M., Byers P., Evans J. P. A second autosomal split hand/split foot locus maps to chromosome 10q24-q25. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Nov;4(11):2165–2170. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.11.2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston R. A., Post J. C., Keats B. J., Aston C. E., Ferrell R. E., Priest J., Nouri N., Losken H. W., Morris C. A., Hurtt M. R. A gene for Crouzon craniofacial dysostosis maps to the long arm of chromosome 10. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):149–153. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi M., Covone A., Romeo G., Faraonio R., Colantuoni V. Regional mapping of RBP4 to 10q23----q24 and RBP1 to 3q21----q22 in man. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Mar;15(2):185–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01535081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyanusin P., Schimmenti L. A., McNoe L. A., Ward T. A., Pierpont M. E., Sullivan M. J., Dobyns W. B., Eccles M. R. Mutation of the PAX2 gene in a family with optic nerve colobomas, renal anomalies and vesicoureteral reflux. Nat Genet. 1995 Apr;9(4):358–364. doi: 10.1038/ng0495-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S. W., Poorkaj P., Allen T., Kim J., Geshuri D., Nunes M., Soder S., Stephens K., Pagon R. A., Patton M. A. Fine mapping of the autosomal dominant split hand/split foot locus on chromosome 7, band q21.3-q22.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jul;55(1):12–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S. W., Poorkaj P., Massa H., Soder S., Allen T., Nunes M., Geshuri D., Wong E., Belloni E., Little S. Physical mapping of the split hand/split foot locus on chromosome 7 and implication in syndromic ectrodactyly. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1345–1354. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharland M., Patton M. A., Hill L. Ectrodactyly of hands and feet in a child with a complex translocation including 7q21.2. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Jun 15;39(4):413–414. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320390410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H. S., Murray J. C., Leysens N. J., Goodfellow P. J., Solursh M. Phylogenetic conservation and physical mapping of members of the H6 homeobox gene family. Mamm Genome. 1995 Jun;6(6):383–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00355637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton P., Weith A., Urbánek P., Kozmik Z., Busslinger M. Chromosomal localization of seven PAX genes and cloning of a novel family member, PAX-9. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):292–298. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Dowler L. L., Angeloni S. V., Pasztor L. M., MacArthur C. A. Assignment of FGF8 to human chromosome 10q25-q26: mutations in FGF8 may be responsible for some types of acrocephalosyndactyly linked to this region. Genomics. 1995 Nov 1;30(1):109–111. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotogora J. On the inheritance of the split hand/split foot malformation. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Oct 15;53(1):29–32. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320530107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



