Abstract
The autosomal recessive disorder Bardet-Biedl syndrome is characterised by retinal degeneration, polydactyly, obesity, mental retardation, hypogenitalism, renal dysplasia, and short stature. It is heterogeneous with at least four gene loci (BBS1-4) having been mapped to date. We have studied 18 multiply affected families noting the presence of both major and minor manifestations. Using a fluorescently based PCR technique, we genotyped each family member and assigned linkage to one of the four loci. Given this degree of heterogeneity we hoped to find phenotypic differences between linkage categories. We found 44% of families linked to 11q13 (BBS1) and 17% linked to 16q21 (BBS2). Only one family was linked to 15q22 (BBS4) and none to 3p12. We conclude that BBS1 is the major locus among white Bardet-Biedl patients and that BBS3 is extremely rare. Only subtle phenotypic differences were observed, the most striking of which was a finding of taller affected offspring compared with their parents in the BBS1 category. Affected subjects in the BBS2 and 4 groups were significantly shorter than their parents. Twenty eight percent of pedigrees did not show linkage to any known locus, evidence for at least a fifth gene. We conclude that the different genes responsible for Bardet-Biedl syndrome may influence growth characteristics such as height.
Full text
PDF

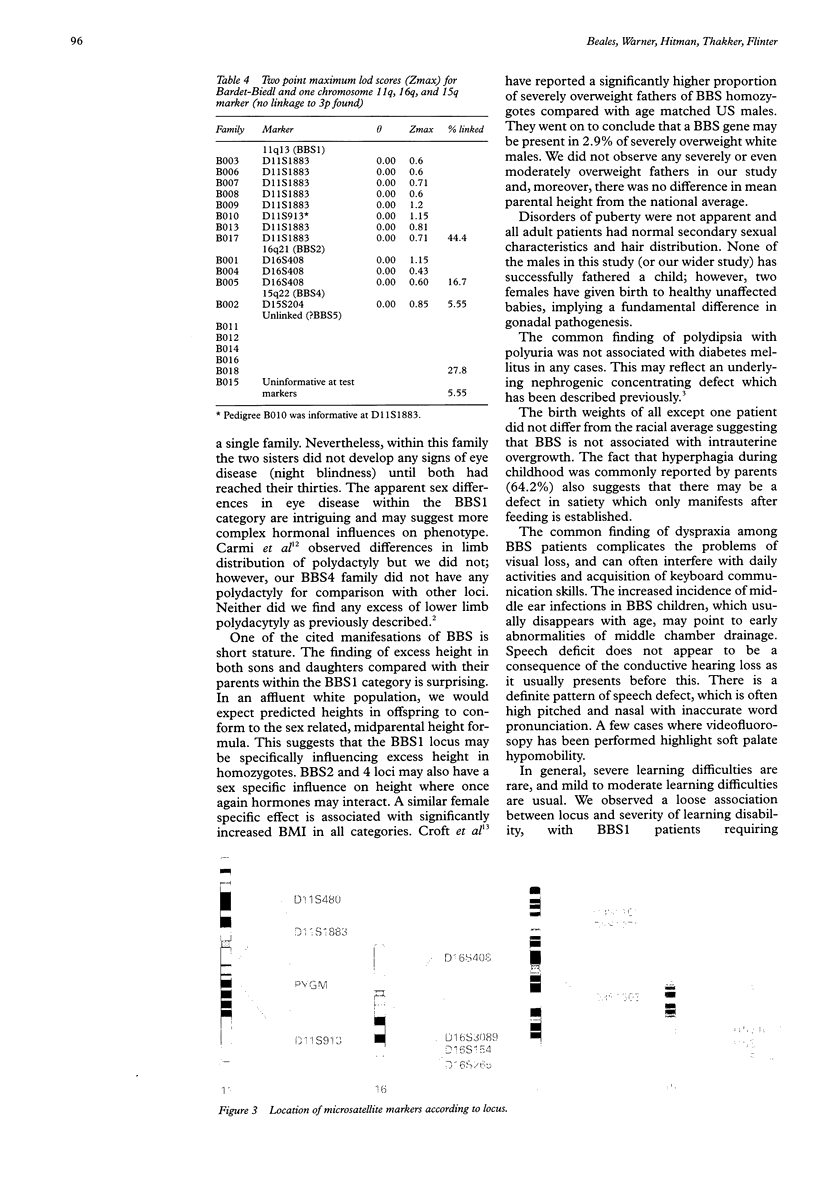


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banfi S., Borsani G., Rossi E., Bernard L., Guffanti A., Rubboli F., Marchitiello A., Giglio S., Coluccia E., Zollo M. Identification and mapping of human cDNAs homologous to Drosophila mutant genes through EST database searching. Nat Genet. 1996 Jun;13(2):167–174. doi: 10.1038/ng0696-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmi R., Elbedour K., Stone E. M., Sheffield V. C. Phenotypic differences among patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome linked to three different chromosome loci. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Nov 6;59(2):199–203. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320590216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmi R., Rokhlina T., Kwitek-Black A. E., Elbedour K., Nishimura D., Stone E. M., Sheffield V. C. Use of a DNA pooling strategy to identify a human obesity syndrome locus on chromosome 15. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jan;4(1):9–13. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S. Positional cloning: let's not call it reverse anymore. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):3–6. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson W. O., Sharp P. A., Faux J. A., Hopkin J. M. Linkage between immunoglobulin E responses underlying asthma and rhinitis and chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1989 Jun 10;1(8650):1292–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92687-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft J. B., Morrell D., Chase C. L., Swift M. Obesity in heterozygous carriers of the gene for the Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Jan 2;55(1):12–15. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320550105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft J. B., Swift M. Obesity, hypertension, and renal disease in relatives of Bardet-Biedl syndrome sibs. Am J Med Genet. 1990 May;36(1):37–42. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320360109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farag T. I., Teebi A. S. Bardet-Biedl and Laurence-Moon syndromes in a mixed Arab population. Clin Genet. 1988 Feb;33(2):78–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1988.tb03414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. S., Parfrey P. S., Harnett J. D., Farid N. R., Cramer B. C., Johnson G., Heath O., McManamon P. J., O'Leary E., Pryse-Phillips W. The cardinal manifestations of Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a form of Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 12;321(15):1002–1009. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910123211503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett J. D., Green J. S., Cramer B. C., Johnson G., Chafe L., McManamon P., Farid N. R., Pryse-Phillips W., Parfrey P. S. The spectrum of renal disease in Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 8;319(10):615–618. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809083191005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwitek-Black A. E., Carmi R., Duyk G. M., Buetow K. H., Elbedour K., Parvari R., Yandava C. N., Stone E. M., Sheffield V. C. Linkage of Bardet-Biedl syndrome to chromosome 16q and evidence for non-allelic genetic heterogeneity. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):392–396. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Baird L., Anderson K. L., Otterud B., Lupski J. R., Lewis R. A. Bardet-Biedl syndrome is linked to DNA markers on chromosome 11q and is genetically heterogeneous. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):108–112. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muragaki Y., Mundlos S., Upton J., Olsen B. R. Altered growth and branching patterns in synpolydactyly caused by mutations in HOXD13. Science. 1996 Apr 26;272(5261):548–551. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5261.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Carmi R., Kwitek-Black A., Rokhlina T., Nishimura D., Duyk G. M., Elbedour K., Sunden S. L., Stone E. M. Identification of a Bardet-Biedl syndrome locus on chromosome 3 and evaluation of an efficient approach to homozygosity mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1331–1335. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]