Abstract
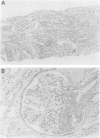
We describe a 5 year old boy with a de novo t(10;13) translocation and optic nerve coloboma-renal disease (ONCR). On the basis of GTG banding analysis of prometaphase chromosomes, the patient's karyotype was interpreted as either 46,XY,t(10;13)(q24.3;q12.3) or t(10;13) (q25.2;q14.1). Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) studies using a YAC clone containing the PAX2 gene and YAC clones adjoining FRA10B at 10q25.2 showed that the 10q breakpoint had occurred just within the PAX2 gene and was proximal to FRA10B. These FISH results suggest that the translocation causes a disruption of the PAX2 gene and leads to ONCR, in agreement with the recent reports of PAX2 mutations in two unrelated families with ONCR. Furthermore, we refined the regional mapping of the human PAX2 gene to the junction of bands 10q24.3 and 10q25.1.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker G. J., Kincaid-Smith P. Reflux nephropathy: the glomerular lesion and progression of renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol. 1993 Aug;7(4):365–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00857540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budarf M. L., Collins J., Gong W., Roe B., Wang Z., Bailey L. C., Sellinger B., Michaud D., Driscoll D. A., Emanuel B. S. Cloning a balanced translocation associated with DiGeorge syndrome and identification of a disrupted candidate gene. Nat Genet. 1995 Jul;10(3):269–278. doi: 10.1038/ng0795-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callen D. F., Baker E., Eyre H. J., Chernos J. E., Bell J. A., Sutherland G. R. Reassessment of two apparent deletions of chromosome 16p to an ins(11;16) and a t(1;16) by chromosome painting. Ann Genet. 1990;33(4):219–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Deutsch U., Chowdhury K., Nornes H. O., Gruss P. Pax2, a new murine paired-box-containing gene and its expression in the developing excretory system. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):787–795. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles M. R., Wallis L. J., Fidler A. E., Spurr N. K., Goodfellow P. J., Reeve A. E. Expression of the PAX2 gene in human fetal kidney and Wilms' tumor. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 May;3(5):279–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes J., Redeker B., Breen M., Boyle S., Brown J., Fletcher J., Jones S., Bickmore W., Fukushima Y., Mannens M. Aniridia-associated cytogenetic rearrangements suggest that a position effect may cause the mutant phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Mar;4(3):415–422. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karcher H. Zum Morning Glory Syndrome. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1979 Dec;175(6):835–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legros y Carrenard J. R., Martínez Cortés F., Martín Sánchez J. Síndrome de "ojo de gato" con agenesia renal derecha. Aportación de un caso y revisión de la literatura. An Esp Pediatr. 1992 Apr;36(4):317–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschonas N. K., Spurr N. K., Mao J. Report of the first international workshop on human chromosome 10 mapping 1995. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1996;72(2-3):100–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieger G. Zum Krankheitsbild er Handmannschen Sehnervenanomalie "Windenblüten"-("Morning Glory"-) Syndrome? Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1977 May;170(5):697–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyanusin P., McNoe L. A., Sullivan M. J., Weaver R. G., Eccles M. R. Mutation of PAX2 in two siblings with renal-coloboma syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Nov;4(11):2183–2184. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.11.2183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyanusin P., Schimmenti L. A., McNoe L. A., Ward T. A., Pierpont M. E., Sullivan M. J., Dobyns W. B., Eccles M. R. Mutation of the PAX2 gene in a family with optic nerve colobomas, renal anomalies and vesicoureteral reflux. Nat Genet. 1995 Apr;9(4):358–364. doi: 10.1038/ng0495-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmenti L. A., Pierpont M. E., Carpenter B. L., Kashtan C. E., Johnson M. R., Dobyns W. B. Autosomal dominant optic nerve colobomas, vesicoureteral reflux, and renal anomalies. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Nov 6;59(2):204–208. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320590217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton P., Weith A., Urbánek P., Kozmik Z., Busslinger M. Chromosomal localization of seven PAX genes and cloning of a novel family member, PAX-9. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):292–298. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan T., Read A. P. PAX genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Jun;4(3):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Read A. P., Newton V. E., Harris R., Balling R., Gruss P., Strachan T. Waardenburg's syndrome patients have mutations in the human homologue of the Pax-3 paired box gene. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):635–636. doi: 10.1038/355635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ton C. C., Hirvonen H., Miwa H., Weil M. M., Monaghan P., Jordan T., van Heyningen V., Hastie N. D., Meijers-Heijboer H., Drechsler M. Positional cloning and characterization of a paired box- and homeobox-containing gene from the aniridia region. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1059–1074. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. G., Cashwell L. F., Lorentz W., Whiteman D., Geisinger K. R., Ball M. Optic nerve coloboma associated with renal disease. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Mar;29(3):597–605. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]