Abstract
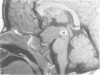
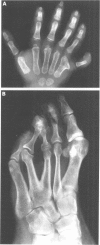
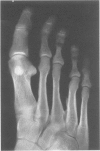
Pallister-Hall syndrome is a human developmental disorder that is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. The phenotypic features of the syndrome include hypothalamic hamartoma, polydactyly, imperforate anus, laryngeal clefting, and other anomalies. Here we describe the clinical characterisation of a family with 22 affected members and the genetic mapping of the corresponding locus. Clinical, radiographic, and endoscopic evaluations showed that this disorder is a fully penetrant trait with variable expressivity and low morbidity. By analysing 60 subjects in two families using anonymous STRP markers, we have established linkage to 7p13 by two point analysis with D7S691 resulting in a lod score of 7.0 at theta = 0, near the GLI3 locus. Deletions and translocations in GLI3 are associated with the Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome. Although Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome has some phenotypic overlap with Pallister-Hall syndrome, these two disorders are clinically distinct. The colocalisation of loci for these distinct phenotypes led us to analyse GLI3 for mutations in patients with Pallister-Hall syndrome. We have previously shown GLI3 mutations in two other small, moderately affected families with Pallister-Hall syndrome. The linkage data reported here suggest that these larger, mildly affected families may also have mutations in GLI3.
Full text
PDF
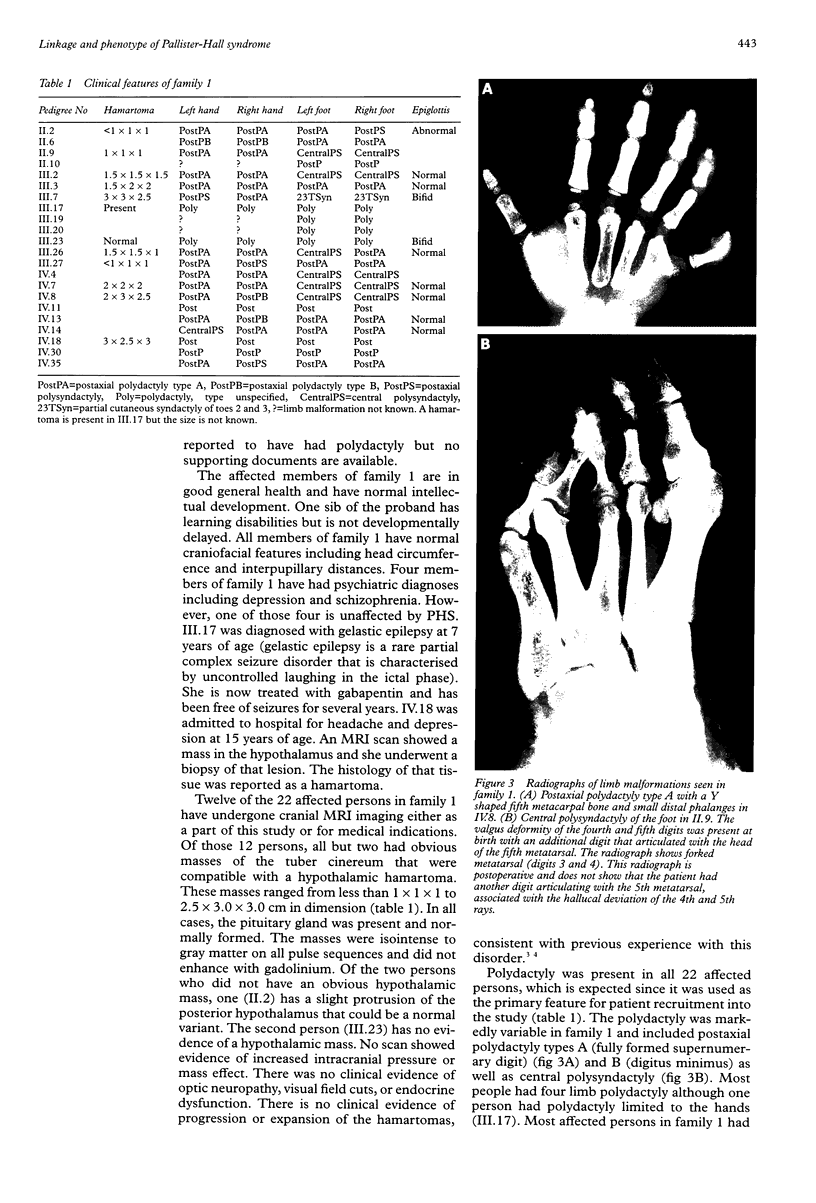
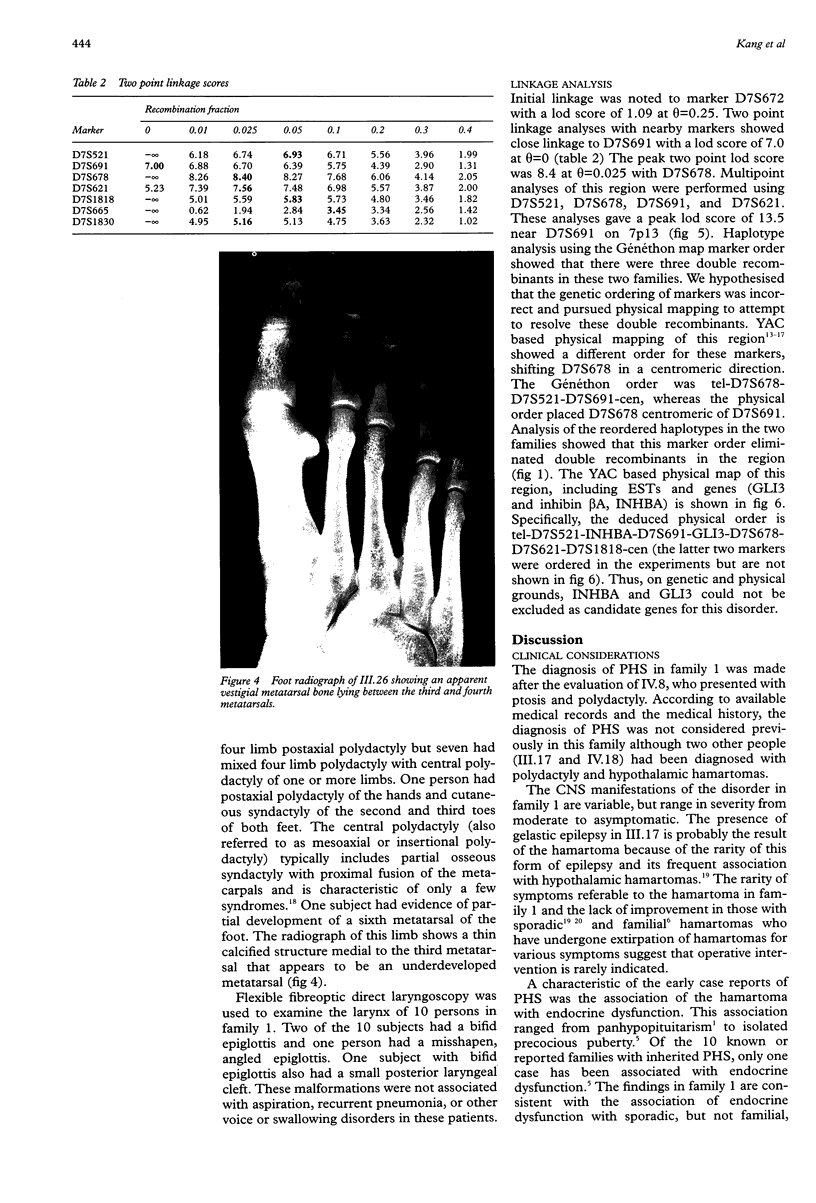
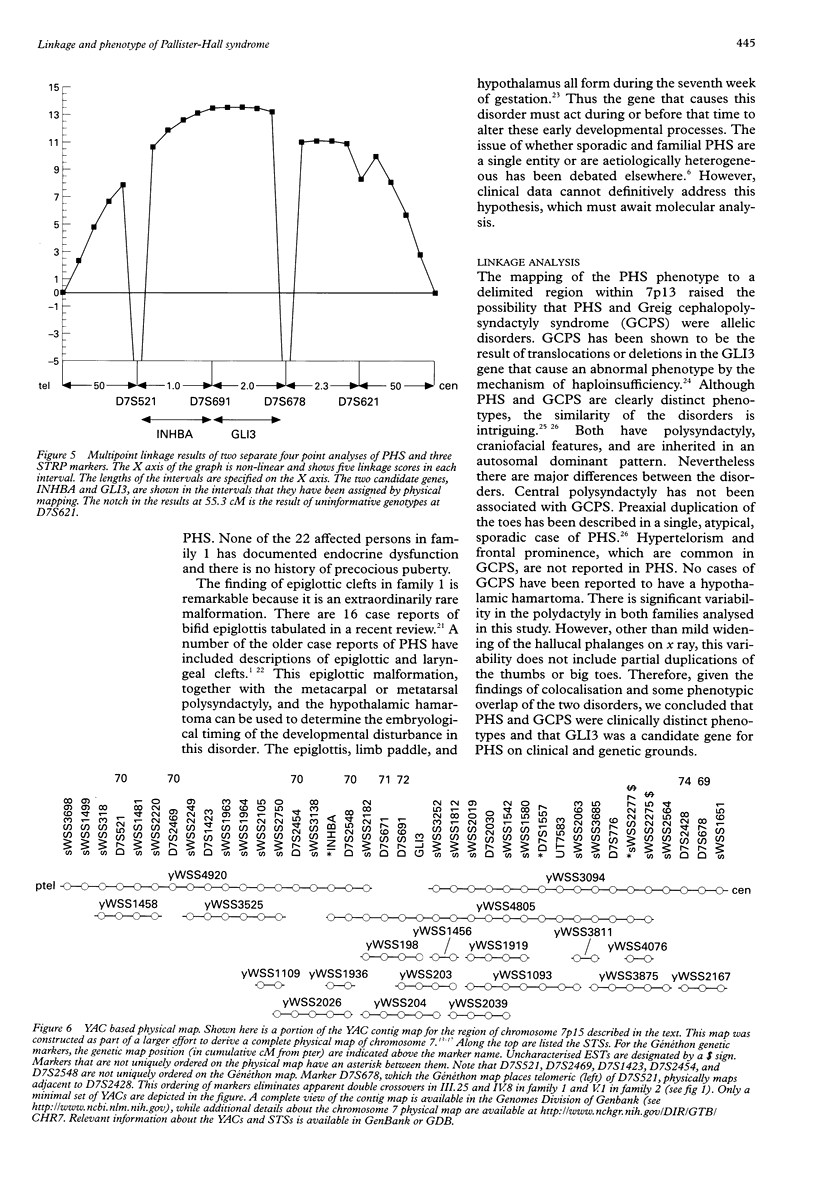

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biesecker L. G., Abbott M., Allen J., Clericuzio C., Feuillan P., Graham J. M., Jr, Hall J., Kang S., Olney A. H., Lefton D. Report from the workshop on Pallister-Hall syndrome and related phenotypes. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Oct 2;65(1):76–81. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19961002)65:1<76::AID-AJMG12>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker L. G., Graham J. M., Jr Pallister-Hall syndrome. J Med Genet. 1996 Jul;33(7):585–589. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.7.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker L. G., Kang S., Schäffer A. A., Abbott M., Kelley R. I., Allen J. C., Clericuzio C., Grebe T., Olney A., Graham J. M., Jr Exclusion of candidate loci and cholesterol biosynthetic abnormalities in familial Pallister-Hall syndrome. J Med Genet. 1996 Nov;33(11):947–951. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.11.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouffard G. G., Iyer L. M., Idol J. R., Braden V. V., Cunningham A. F., Weintraub L. A., Mohr-Tidwell R. M., Peluso D. C., Fulton R. S., Leckie M. P. A collection of 1814 human chromosome 7-specific STSs. Genome Res. 1997 Jan;7(1):59–64. doi: 10.1101/gr.7.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breningstall G. N. Gelastic seizures, precocious puberty, and hypothalamic hamartoma. Neurology. 1985 Aug;35(8):1180–1183. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.8.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarren S. K., Alvord E. C., Jr, Hall J. G. Congenital hypothalamic hamartoblastoma, hypopituitarism, imperforate anus, and postaxial polydactyly--a new syndrome? Part II: Neuropathological considerations. Am J Med Genet. 1980;7(1):75–83. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320070111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg J. D., Holinger L. D., Bressler F. J., Hutchinson L. R. Bifid epiglottis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1996 Feb;105(2):155–157. doi: 10.1177/000348949610500211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. M., Brown F. E., Saunders R. L., Hinkle A. J., Frank J. E., Harris M. S., Klein R. Z. Bifid epiglottis, hand anomalies, and congenital hypopituitarism. Lancet. 1985 Aug 24;2(8452):443–443. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. M., Jr, Harris M., Frank J. E., Little G. A., Klein R. Z. Congenital hypothalamic hamartoblastoma syndrome: natural history and genetic implications. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;200:163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebe T. A., Clericuzio C. Autosomal dominant inheritance of hypothalamic hamartoma associated with polysyndactyly: heterogeneity or variable expressivity? Am J Med Genet. 1996 Dec 11;66(2):129–137. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19961211)66:2<129::AID-AJMG2>3.0.CO;2-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Braden V. V., Fulton R. S., Lim R., Ueltzen M. S., Peluso D. C., Mohr-Tidwell R. M., Idol J. R., Smith L. M., Chumakov I. A human chromosome 7 yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) resource: construction, characterization, and screening. Genomics. 1995 Jan 1;25(1):170–183. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Green P. Sequence-tagged site (STS) content mapping of human chromosomes: theoretical considerations and early experiences. PCR Methods Appl. 1991 Nov;1(2):77–90. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.2.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Idol J. R., Mohr-Tidwell R. M., Braden V. V., Peluso D. C., Fulton R. S., Massa H. F., Magness C. L., Wilson A. M., Kimura J. Integration of physical, genetic and cytogenetic maps of human chromosome 7: isolation and analysis of yeast artificial chromosome clones for 117 mapped genetic markers. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Mar;3(3):489–501. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Mohr R. M., Idol J. R., Jones M., Buckingham J. M., Deaven L. L., Moyzis R. K., Olson M. V. Systematic generation of sequence-tagged sites for physical mapping of human chromosomes: application to the mapping of human chromosome 7 using yeast artificial chromosomes. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):548–564. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Pallister P. D., Clarren S. K., Beckwith J. B., Wiglesworth F. W., Fraser F. C., Cho S., Benke P. J., Reed S. D. Congenital hypothalamic hamartoblastoma, hypopituitarism, imperforate anus and postaxial polydactyly--a new syndrome? Part I: clinical, causal, and pathogenetic considerations. Am J Med Genet. 1980;7(1):47–74. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320070110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S., Graham J. M., Jr, Olney A. H., Biesecker L. G. GLI3 frameshift mutations cause autosomal dominant Pallister-Hall syndrome. Nat Genet. 1997 Mar;15(3):266–268. doi: 10.1038/ng0397-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman Splitt M., Wright C., Perry R., Burn J. Autosomal dominant transmission of Pallister-Hall syndrome. Clin Dysmorphol. 1994 Oct;3(4):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer A. A., Gupta S. K., Shriram K., Cottingham R. W., Jr Avoiding recomputation in linkage analysis. Hum Hered. 1994 Jul-Aug;44(4):225–237. doi: 10.1159/000154222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topf K. F., Kletter G. B., Kelch R. P., Brunberg J. A., Biesecker L. G. Autosomal dominant transmission of the Pallister-Hall syndrome. J Pediatr. 1993 Dec;123(6):943–946. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80392-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vortkamp A., Gessler M., Grzeschik K. H. GLI3 zinc-finger gene interrupted by translocations in Greig syndrome families. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):539–540. doi: 10.1038/352539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]