Abstract
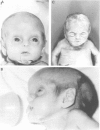
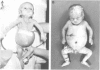
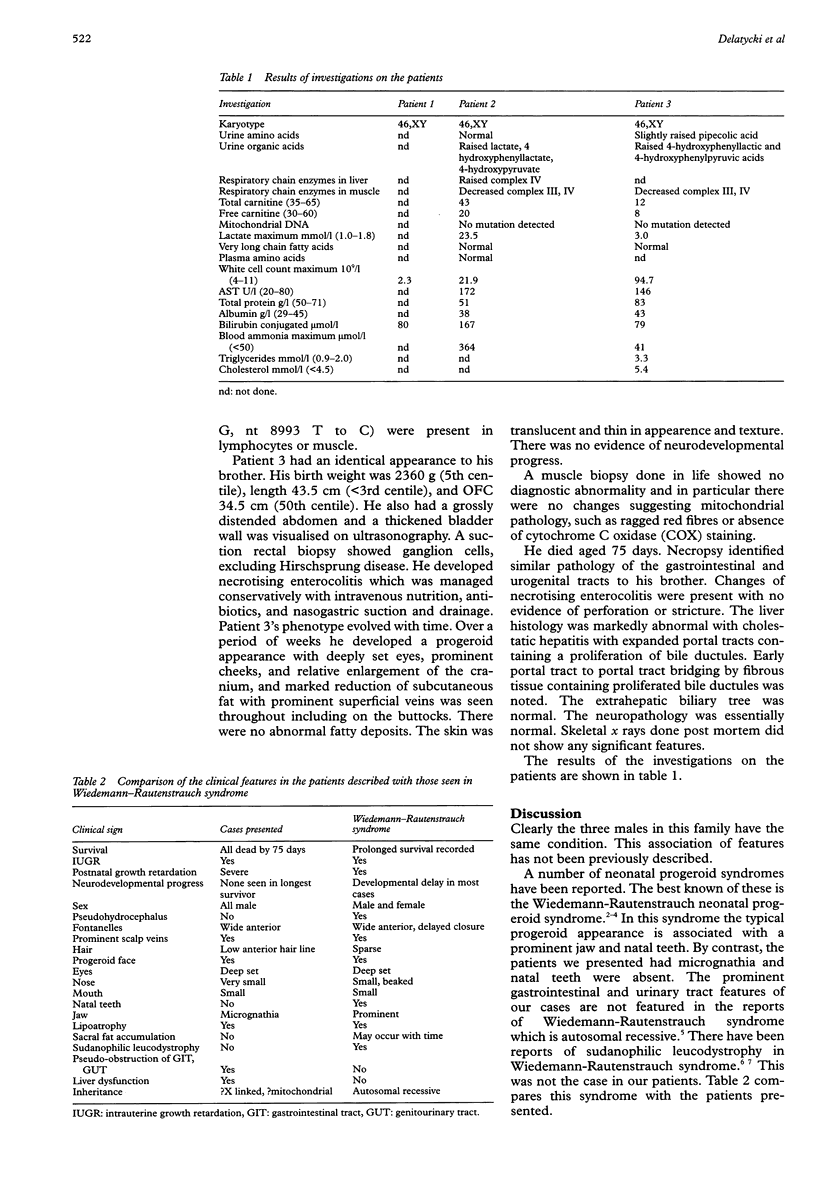
Twin brothers and their maternal uncle with a previously undescribed neonatal progeroid syndrome are presented. In addition to progeroid features, they had pseudo-obstruction of the urinary and gastrointestinal tracts, severe leucocytosis, liver dysfunction, and low complex III and IV in muscle but not in liver. Previously described neonatal progeroid syndromes and syndromes featuring pseudo-obstruction are discussed. The two most likely aetiological mechanisms are an X linked single gene disorder or a mitochondrial disorder. The evidence for these possibilities is presented.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auricchio A., Brancolini V., Casari G., Milla P. J., Smith V. V., Devoto M., Ballabio A. The locus for a novel syndromic form of neuronal intestinal pseudoobstruction maps to Xq28. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Apr;58(4):743–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitoun P., Lachassine E., Sellier N., Sauvion S., Gaudelus J. The Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch neonatal progeroid syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Dysmorphol. 1995 Jul;4(3):239–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagadorn J. I., Wilson W. G., Hogge W. A., Callicott J. H., Beale E. F. Neonatal progeroid syndrome: more than one disease? Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. J., Ashcraft K. W., Beatty E. C., Holder T. M., Leonidas J. C. Natal teeth, patent ductus arteriosus and intestinal pseudo-obstruction: a lethal syndrome in the newborn. Clin Genet. 1976 May;9(5):479–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns D. R., Threlkeld A. B., Miller N. R., Hurko O. Multiple mitochondrial DNA deletions in myo-neuro-gastrointestinal encephalopathy syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993 Jan;115(1):108–109. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73533-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. J., Ceuterick C. M., Leroy J. G., Devos E. A., Roelens J. G. The Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch or neonatal progeroid syndrome. Neuropathological study of a case. Neuropediatrics. 1984 Feb;15(1):43–48. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman S., Blok R. B., Dahl H. H., Danks D. M., Kirby D. M., Chow C. W., Christodoulou J., Thorburn D. R. Leigh syndrome: clinical features and biochemical and DNA abnormalities. Ann Neurol. 1996 Mar;39(3):343–351. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautenstrauch T., Snigula F. Progeria: a cell culture study and clinical report of familial incidence. Eur J Pediatr. 1977 Jan 26;124(2):101–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00477545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin C., Thommen L., Fliegel C., Steinmann B., Bühler U. The neonatal pseudo-hydrocephalic progeroid syndrome (Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch). Report of a new patient and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 May;147(4):433–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00496430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snigula F., Rautenstrauch T. A new neonatal progeroid syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1981 Jul;136(3):325–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00443003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen A., Kaukonen J., Amati P., Timonen R., Haltia M., Weissenbach J., Zeviani M., Somer H., Peltonen L. An autosomal locus predisposing to deletions of mitochondrial DNA. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):146–151. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann H. R. An unidentified neonatal progeroid syndrome: follow-up report. Eur J Pediatr. 1979 Jan 18;130(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00441901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]