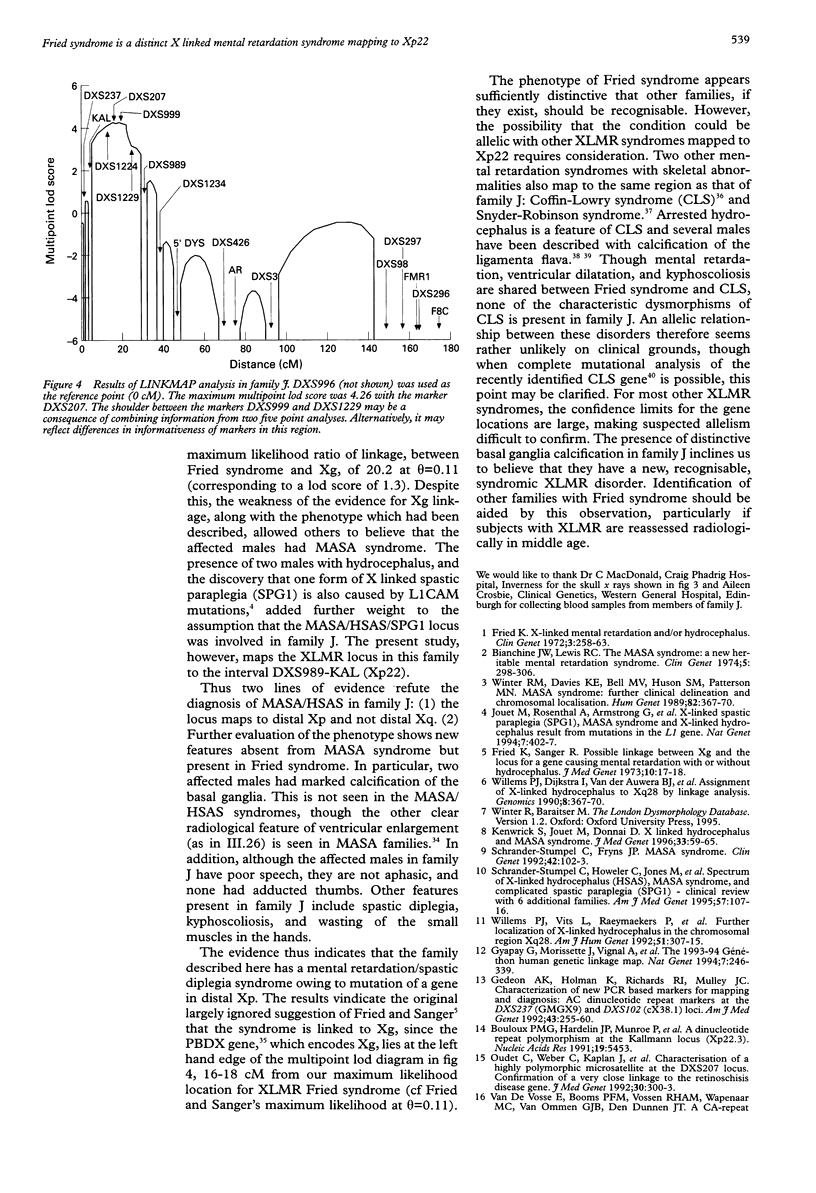
Abstract
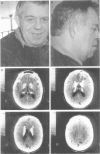
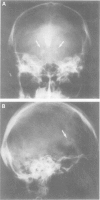
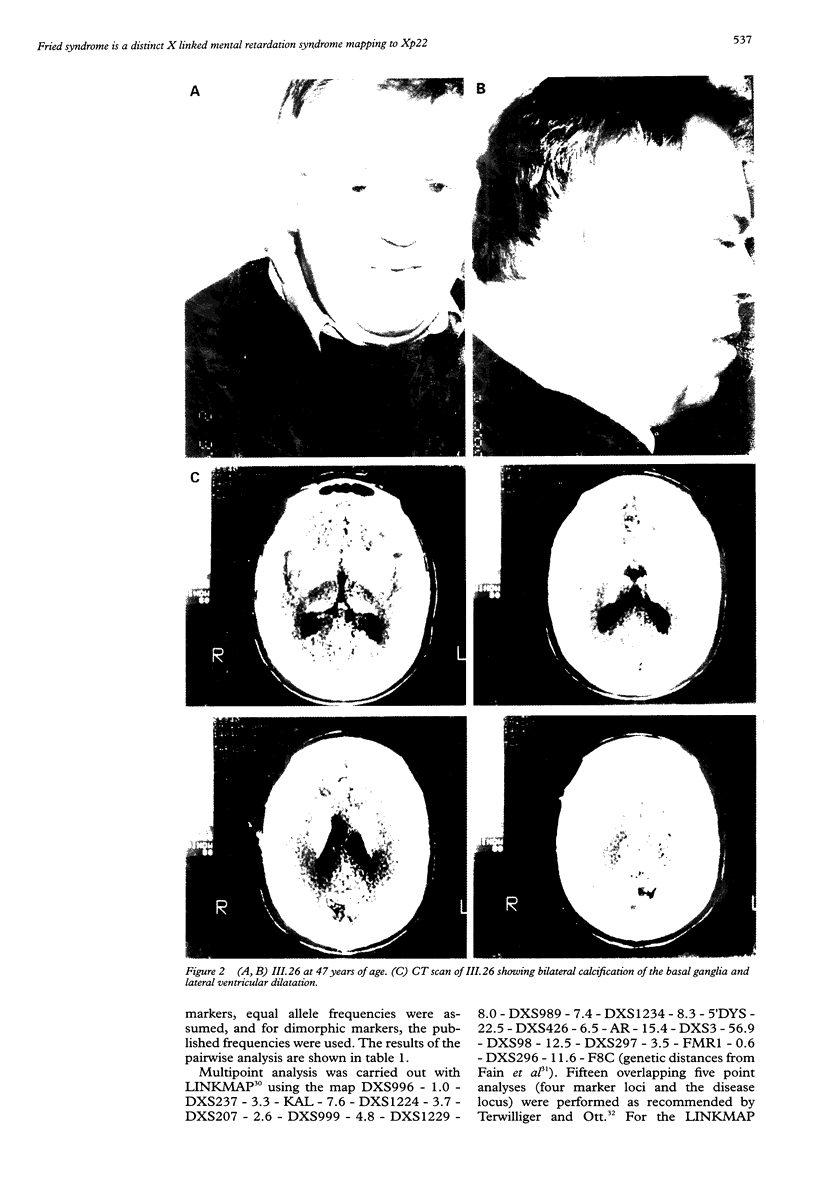
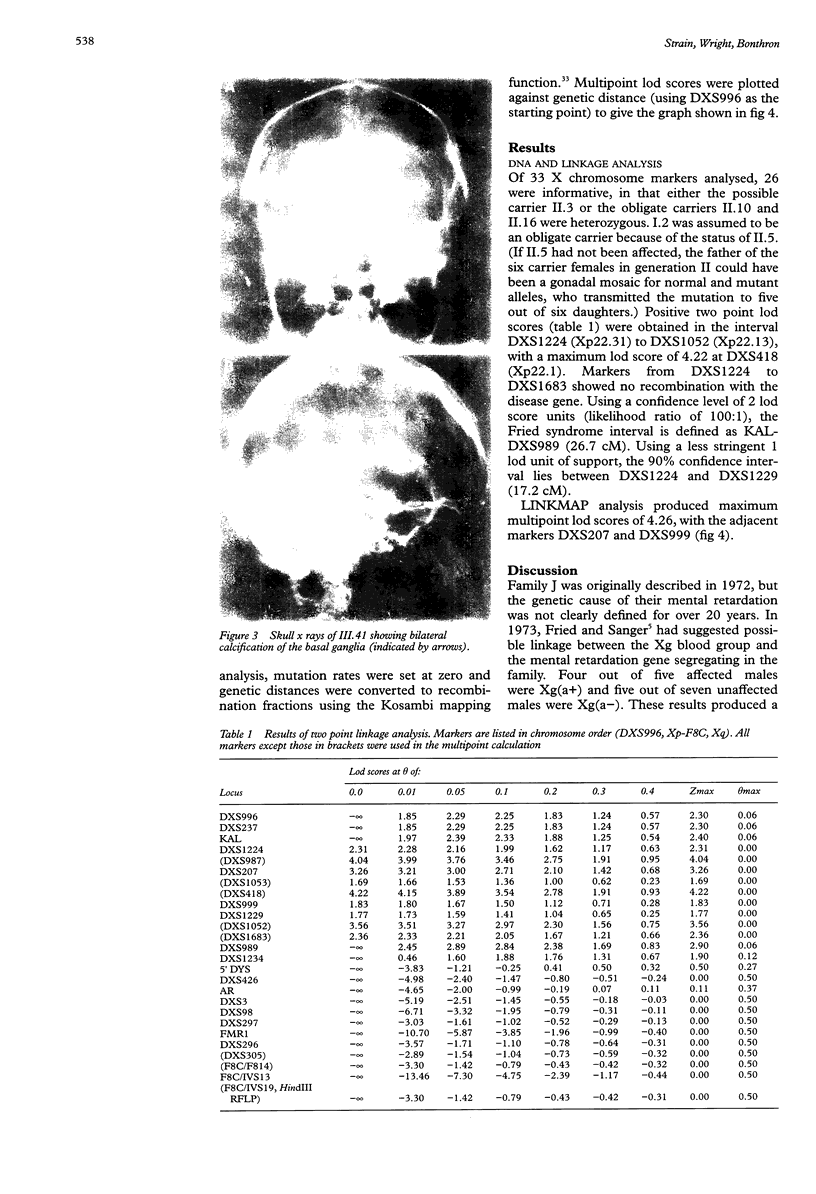
In 1972, Fried described a large Scottish family affected by X linked mental retardation (XLMR), hydrocephalus, and mild facial dysmorphism. The phenotype has considerable similarity to the MASA syndrome, which results from mutations of the L1CAM gene in Xq28, and this family has since been assumed to be an example of this condition. We have reinvestigated the family for linkage to X chromosome markers, and obtained additional clinical information on surviving affected subjects. The phenotype in these patients has evolved into a distinctive syndrome, with severe mental retardation (MR), spastic diplegia, ventricular dilatation, and calcification of the basal ganglia. Linkage to Xq28 markers has been excluded, suggesting that Fried syndrome is not allelic with MASA syndrome. Two point and multipoint linkage analysis indicates that the gene for this condition lies within the interval KAL-DXS989 in Xp22. We propose the designation Fried syndrome to emphasise the disorder's distinctive phenotype.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arena J. F., Schwartz C., Ouzts L., Stevenson R., Miller M., Garza J., Nance M., Lubs H. X-linked mental retardation with thin habitus, osteoporosis, and kyphoscoliosis: linkage to Xp21.3-p22.12. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Jul 12;64(1):50–58. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<50::AID-AJMG7>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs A. H., Kunkel L. M. A polymorphic CACA repeat in the 3' untranslated region of dystrophin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1931–1931. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biancalana V., Trivier E., Weber C., Weissenbach J., Rowe P. S., O'Riordan J. L., Partington M. W., Heyberger S., Oudet C., Hanauer A. Construction of a high-resolution linkage map for Xp22.1-p22.2 and refinement of the genetic localization of the Coffin-Lowry syndrome gene. Genomics. 1994 Aug;22(3):617–625. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchine J. W., Lewis R. C., Jr The MASA syndrome: a new heritable mental retardation syndrome. Clin Genet. 1974;5(4):298–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb01697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd E., Schwartz C. E., Schroer R. J., May M. M., Shapiro S. D., Arena J. F., Lubs H. A., Stevenson R. E. Agenesis of the corpus callosum associated with MASA syndrome. Clin Dysmorphol. 1993 Oct;2(4):332–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M., Bhattacharya S., Lindsay S., Wright A., Jay M., Litt M., Craig I., Davies K. Localization of the microsatellite probe DXS426 between DXS7 and DXS255 on Xp and linkage to X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):935–940. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Econs M. J., Francis F., Rowe P. S., Speer M. C., O'Riordan J. L., Lehrach H., Becker P. A. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the DXS1683 locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):680–680. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis N. A., Ye T. Z., Patton S., German J., Goodfellow P. N., Weller P. Cloning of PBDX, an MIC2-related gene that spans the pseudoautosomal boundary on chromosome Xp. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):394–400. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain P. R., Kort E. N., Chance P. F., Nguyen K., Redd D. F., Econs M. J., Barker D. F. A 2D crossover-based map of the human X chromosome as a model for map integration. Nat Genet. 1995 Mar;9(3):261–266. doi: 10.1038/ng0395-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feener C. A., Boyce F. M., Kunkel L. M. Rapid detection of CA polymorphisms in cloned DNA: application to the 5' region of the dystrophin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):621–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried K., Sanger R. Possible linkage between Xg and the locus for a gene causing mental retardation with or without hydrocephalus. J Med Genet. 1973 Mar;10(1):17–18. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried K. X-linked mental retardation and-or hydrocephalus. Clin Genet. 1972;3(4):258–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Richards S., Verkerk A. J., Holden J. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Warren S. T. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedeon A. K., Holman K., Richards R. I., Mulley J. C. Characterization of new PCR based markers for mapping and diagnosis: AC dinucleotide repeat markers at the DXS237 (GMGX9) and DXS102 (cX38.1) loci. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):255–260. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. B., Kunkel G. R., Fowlkes D. M., Lord S. T. The utility of a HindIII polymorphism of factor VIII examined by rapid DNA analysis. Br J Haematol. 1990 Sep;76(1):75–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Oberlé I., Arveiler B., Hanauer A., Vidaud M., Mandel J. L. Improved DNA markers for efficient analysis of fragile X families. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):543–550. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Oki T., Ono Y., Nogami H. Coffin-Lowry syndrome associated with calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition in the ligamenta flava. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992 Feb;(275):144–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Rosenthal A., Armstrong G., MacFarlane J., Stevenson R., Paterson J., Metzenberg A., Ionasescu V., Temple K., Kenwrick S. X-linked spastic paraplegia (SPG1), MASA syndrome and X-linked hydrocephalus result from mutations in the L1 gene. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):402–407. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Jouet M., Donnai D. X linked hydrocephalus and MASA syndrome. J Med Genet. 1996 Jan;33(1):59–65. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalloz M. R., McVey J. H., Pattinson J. K., Tuddenham E. G. Haemophilia A diagnosis by analysis of a hypervariable dinucleotide repeat within the factor VIII gene. Lancet. 1991 Jul 27;338(8761):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90348-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki K., Yamanaka T., Ishida Y., Oohira A. Calcified ligamenta flava in a patient with Coffin-Lowry syndrome: biochemical analysis of glycosaminoglycans. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1990 Jun;35(2):215–221. doi: 10.1007/BF01876467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander-Stumpel C., Fryns J. P. MASA syndrome. Clin Genet. 1992 Aug;42(2):102–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander-Stumpel C., Höweler C., Jones M., Sommer A., Stevens C., Tinschert S., Israel J., Fryns J. P. Spectrum of X-linked hydrocephalus (HSAS), MASA syndrome, and complicated spastic paraplegia (SPG1): Clinical review with six additional families. Am J Med Genet. 1995 May 22;57(1):107–116. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320570122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleddens H. F., Oostra B. A., Brinkmann A. O., Trapman J. Trinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the androgen receptor gene (AR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1427–1427. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1427-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Callen D. F., Hyland V. J., Kozman H. M., Baker E., Eyre H., Harper P. S., Roberts S. H., Hors-Cayla M. C., Davies K. E. A new DNA marker tightly linked to the fragile X locus (FRAXA). Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1298–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.2573953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trivier E., De Cesare D., Jacquot S., Pannetier S., Zackai E., Young I., Mandel J. L., Sassone-Corsi P., Hanauer A. Mutations in the kinase Rsk-2 associated with Coffin-Lowry syndrome. Nature. 1996 Dec 12;384(6609):567–570. doi: 10.1038/384567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van De Vosse E., Booms P. F., Vossen R. H., Wapenaar M. C., Van Ommen G. J., Den Dunnen J. T. A CA-repeat polymorphism near DXS418 (P122). Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2202–2202. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2202-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Kretz C., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. A new polymorphic marker very closely linked to DXS52 in the q28 region of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00288280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. J., Dijkstra I., Van der Auwera B. J., Vits L., Coucke P., Raeymaekers P., Van Broeckhoven C., Consalez G. G., Freeman S. B., Warren S. T. Assignment of X-linked hydrocephalus to Xq28 by linkage analysis. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. J., Vits L., Raeymaekers P., Beuten J., Coucke P., Holden J. J., Van Broeckhoven C., Warren S. T., Sagi M., Robinson D. Further localization of X-linked hydrocephalus in the chromosomal region Xq28. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):307–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M., Davies K. E., Bell M. V., Huson S. M., Patterson M. N. MASA syndrome: further clinical delineation and chromosomal localisation. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00273999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]