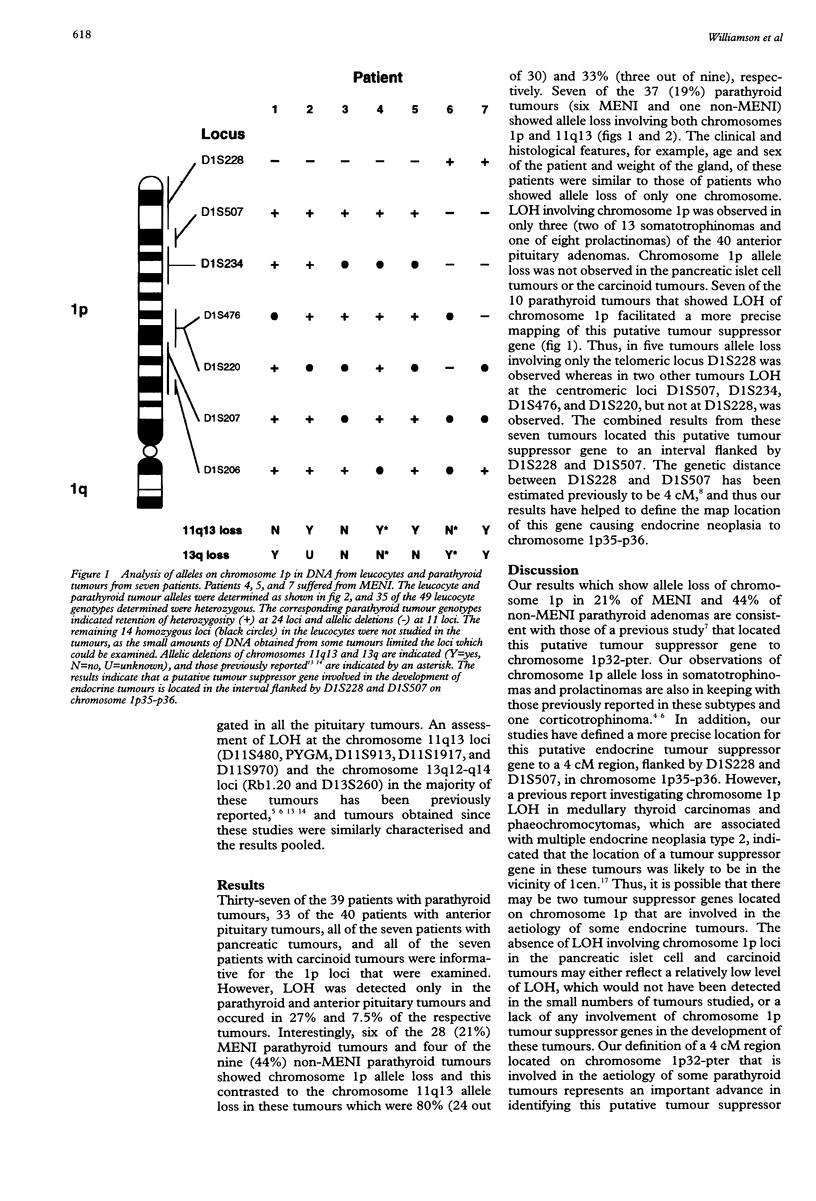
Abstract
The development of some endocrine tumours, such as medullary thyroid carcinomas, phaeochromocytomas, anterior pituitary adenomas, and parathyroid adenomas involve a putative tumour suppressor gene located on chromosome 1p32-pter, a region that represents 111 cM. In order to refine the location of this gene, 93 endocrine tumours (39 parathyroid adenomas, 40 anterior pituitary adenomas, seven pancreatic islet cell adenomas, and seven carcinoids) were investigated for loss of tumour heterozygosity (LOH) using the seven polymorphic loci 1pter-D1S228-D1S507-D1S234-D1S476-D1S22 0-D1S207-D1S206-1cen. LOH was detected in 27% of the parathyroid tumours and in 7.5% of the pituitary tumours, but in none of the pancreatic islet cell or carcinoid tumours. In addition, seven of the 10 parathyroid tumours that showed LOH of chromosome 1p facilitated a more precise mapping of this putative tumour suppressor gene; five tumours involved a loss only of the telomeric locus D1S228, whereas two other tumours showed LOH at the centromeric loci D1S507, D1S234, D1S476, and D1S220, but not D1S228. Thus, our results have mapped this tumour suppressor gene implicated in endocrine tumours to a 4 cM region flanked by D1S228 and D1S507 on chromosome 1p35-p36.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boggild M. D., Jenkinson S., Pistorello M., Boscaro M., Scanarini M., McTernan P., Perrett C. W., Thakker R. V., Clayton R. N. Molecular genetic studies of sporadic pituitary tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Feb;78(2):387–392. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.2.8106627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byström C., Larsson C., Blomberg C., Sandelin K., Falkmer U., Skogseid B., Oberg K., Werner S., Nordenskjöld M. Localization of the MEN1 gene to a small region within chromosome 11q13 by deletion mapping in tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1968–1972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryns V. L., Yi S. M., Tahara H., Gaz R. D., Arnold A. Frequent loss of chromosome arm 1p DNA in parathyroid adenomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1995 May;13(1):9–17. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870130103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dracopoli N. C., Bruns G. A., Brodeur G. M., Landes G. M., Matise T. C., Seldin M. F., Vance J. M., Weith A. Report and abstracts of the First International Workshop on Human Chromosome 1 Mapping 1994. Bethesda, Maryland, March 25-27, 1994. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;67(3):144–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipers P. G., Barnoski B. L., Han J., Carroll A. J., Kidd V. J. Localization of the expressed human p58 protein kinase chromosomal gene to chromosome 1p36 and a highly related sequence to chromosome 15. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):621–629. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90069-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellmeier W., Aguzzi A., Kleiner E., Kurzbauer R., Weith A. Mutually exclusive expression of a helix-loop-helix gene and N-myc in human neuroblastomas and in normal development. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2563–2571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05321.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto H., Ozaki T., Takahashi E., Nomura N., Tabata S., Takahashi H., Ohnuma N., Tanabe M., Iwai J., Yoshida H. Identification of human DAN gene, mapping to the putative neuroblastoma tumor suppressor locus. Oncogene. 1994 Oct;9(10):2785–2791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson C., Skogseid B., Oberg K., Nakamura Y., Nordenskjöld M. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 gene maps to chromosome 11 and is lost in insulinoma. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):85–87. doi: 10.1038/332085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Saito M., Vidal M., Valentine M., Look T., Harlow E., Dyson N., Helin K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7813–7825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Bray P., Ried T., Dawid I. B., Ward D. C. Clustering of C2-H2 zinc finger motif sequences within telomeric and fragile site regions of human chromosomes. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):999–1007. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90013-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moley J. F., Brother M. B., Fong C. T., White P. S., Baylin S. B., Nelkin B., Wells S. A., Brodeur G. M. Consistent association of 1p loss of heterozygosity with pheochromocytomas from patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 syndromes. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 15;52(4):770–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Gardner E., Smith B. A., Mathew C. G., Ponder B. A. Genetic events in tumour initiation and progression in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993 Mar;6(3):166–177. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870060307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang J. T., Lloyd S. E., Wooding C., Farren B., Pottinger B., Harding B., Leigh S. E., Pook M. A., Benham F. J., Gillett G. T. Genetic mapping studies of 40 loci and 23 cosmids in chromosome 11p13-11q13, and exclusion of mu-calpain as the multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 gene. Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;97(6):732–741. doi: 10.1007/BF02346182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce S. H., Trump D., Wooding C., Sheppard M. N., Clayton R. N., Thakker R. V. Loss of heterozygosity studies at the retinoblastoma and breast cancer susceptibility (BRCA2) loci in pituitary, parathyroid, pancreatic and carcinoid tumours. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1996 Aug;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.1996.d01-1561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman S. J., Pook M. A., Wooding C., Pang J. T., Frymoyer P. A., Thakker R. V. Mapping the gene causing X-linked recessive nephrolithiasis to Xp11.22 by linkage studies. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2351–2357. doi: 10.1172/JCI116467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer B. W., Mattei M. G. The human paired domain gene PAX7 (Hup1) maps to chromosome 1p35-1p36.2. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):249–251. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. N., Sublett J. E., Li B., Valentine M. B., Morris S. W., Noll M. The gene for PAX7, a member of the paired-box-containing genes, is localized on human chromosome arm 1p36. Genomics. 1993 Sep;17(3):767–769. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton P., Weith A., Urbánek P., Kozmik Z., Busslinger M. Chromosomal localization of seven PAX genes and cloning of a novel family member, PAX-9. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):292–298. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Bouloux P., Wooding C., Chotai K., Broad P. M., Spurr N. K., Besser G. M., O'Riordan J. L. Association of parathyroid tumors in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 with loss of alleles on chromosome 11. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 27;321(4):218–224. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907273210403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Pook M. A., Wooding C., Boscaro M., Scanarini M., Clayton R. N. Association of somatotrophinomas with loss of alleles on chromosome 11 and with gsp mutations. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2815–2821. doi: 10.1172/JCI116524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V. The molecular genetics of the multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1993 Jan;38(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1993.tb00964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



