Abstract
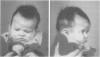
The craniosynostosis syndromes are a heterogeneous group of sporadic, autosomal dominant disorders with significant clinical overlap. Recently, we described a large family with autosomal dominant craniosynostosis suggestive of Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, in which linkage to the Saethre-Chotzen syndrome loci on 7p had been excluded. We now report the presence of a mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) in this family. The mutation, P250R, had been previously reported in 10 patients with non-syndromic craniosynostosis. Variable expression of this mutation is evident especially in two additional members of this family, one of whom is severely affected with pancraniosynostosis. The family provides a further example of genetic heterogeneity and variable expression of the craniosynostosis syndromes and broadens the phenotypic spectrum associated with the FGFR3 mutation P250R. In addition, we found a polymorphism (F384L) in the transmembrane domain of FGFR3 which occurs with a frequency of 3% in the Turkish population but is uncommon among Germans.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellus G. A., Gaudenz K., Zackai E. H., Clarke L. A., Szabo J., Francomano C. A., Muenke M. Identical mutations in three different fibroblast growth factor receptor genes in autosomal dominant craniosynostosis syndromes. Nat Genet. 1996 Oct;14(2):174–176. doi: 10.1038/ng1096-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellus G. A., McIntosh I., Smith E. A., Aylsworth A. S., Kaitila I., Horton W. A., Greenhaw G. A., Hecht J. T., Francomano C. A. A recurrent mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 causes hypochondroplasia. Nat Genet. 1995 Jul;10(3):357–359. doi: 10.1038/ng0795-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lajeunie E., Ma H. W., Bonaventure J., Munnich A., Le Merrer M., Renier D. FGFR2 mutations in Pfeiffer syndrome. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):108–108. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G. A., Orlow S. J., Munro I. R., Przylepa K. A., Jabs E. W. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) transmembrane mutation in Crouzon syndrome with acanthosis nigricans. Nat Genet. 1995 Dec;11(4):462–464. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenke M., Schell U., Hehr A., Robin N. H., Losken H. W., Schinzel A., Pulleyn L. J., Rutland P., Reardon W., Malcolm S. A common mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 gene in Pfeiffer syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):269–274. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., Winter R. M., Rutland P., Pulleyn L. J., Jones B. M., Malcolm S. Mutations in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 gene cause Crouzon syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):98–103. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., Winter R. M., Rutland P., Pulleyn L. J., Jones B. M., Malcolm S. Mutations in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 gene cause Crouzon syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):98–103. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutland P., Pulleyn L. J., Reardon W., Baraitser M., Hayward R., Jones B., Malcolm S., Winter R. M., Oldridge M., Slaney S. F. Identical mutations in the FGFR2 gene cause both Pfeiffer and Crouzon syndrome phenotypes. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):173–176. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell U., Hehr A., Feldman G. J., Robin N. H., Zackai E. H., de Die-Smulders C., Viskochil D. H., Stewart J. M., Wolff G., Ohashi H. Mutations in FGFR1 and FGFR2 cause familial and sporadic Pfeiffer syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Mar;4(3):323–328. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiang R., Thompson L. M., Zhu Y. Z., Church D. M., Fielder T. J., Bocian M., Winokur S. T., Wasmuth J. J. Mutations in the transmembrane domain of FGFR3 cause the most common genetic form of dwarfism, achondroplasia. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90302-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavormina P. L., Shiang R., Thompson L. M., Zhu Y. Z., Wilkin D. J., Lachman R. S., Wilcox W. R., Rimoin D. L., Cohn D. H., Wasmuth J. J. Thanatophoric dysplasia (types I and II) caused by distinct mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3. Nat Genet. 1995 Mar;9(3):321–328. doi: 10.1038/ng0395-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Slaney S. F., Oldridge M., Poole M. D., Ashworth G. J., Hockley A. D., Hayward R. D., David D. J., Pulleyn L. J., Rutland P. Apert syndrome results from localized mutations of FGFR2 and is allelic with Crouzon syndrome. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):165–172. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gernet S., Schuffenhauer S., Golla A., Lichtner P., Balg S., Mühlbauer W., Murken J., Fairley J., Meitinger T. Craniosynostosis suggestive of Saethre-Chotzen syndrome: clinical description of a large kindred and exclusion of candidate regions on 7p. Am J Med Genet. 1996 May 3;63(1):177–184. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960503)63:1<177::AID-AJMG31>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]