Abstract
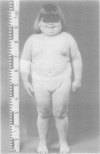
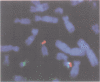
A 7 year old girl is described with congenital hypoplastic anaemia (Diamond-Blackfan anaemia, DBA) and an apparently balanced reciprocal translocation, 46,XX,t(X;19)(p21;q13). The girl has associated features including short stature, unilateral kidney hypoplasia, and a branchial cyst. Fluorescent in situ hybridisation (FISH) studies with 19q specific cosmids showed that the chromosome 19 breakpoint is located between the RYR1 and the XRCC11 loci spanning a physical region of 5 Mb. There is no family history of DBA and the parents and two healthy sibs have normal karyotypes. This is the first report of a balanced translocation associated with DBA and we suggest that the distinct phenotype has resulted from a de novo disruption of a functional gene. DBA can be inherited as an autosomal trait and our observation may indicate a candidate gene for the disorder in the 19q13 region.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman A. C., Gross S. Severe congenital hypoplastic anemia. Transmission from a healthy female to opposite sex step-siblings. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1983 Spring;5(1):99–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth L. K., Batzer M. A., Brandriff B., Branscomb E., de Jong P., Garcia E., Garnes J. A., Gordon L. A., Lamerdin J. E., Lennon G. An integrated metric physical map of human chromosome 19. Nat Genet. 1995 Dec;11(4):422–427. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball S. E., McGuckin C. P., Jenkins G., Gordon-Smith E. C. Diamond-Blackfan anaemia in the U.K.: analysis of 80 cases from a 20-year birth cohort. Br J Haematol. 1996 Sep;94(4):645–653. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1996.d01-1839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Noble N. A. Fibrosis linked to TGF-beta in yet another disease. J Clin Invest. 1995 Aug;96(2):655–656. doi: 10.1172/JCI118107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou D., Miyashita T., Mohrenweiser H. W., Ueki K., Kastury K., Druck T., von Deimling A., Huebner K., Reed J. C., Louis D. N. The BAX gene maps to the glioma candidate region at 19q13.3, but is not altered in human gliomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1996 Jun;88(2):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(95)00341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossen P. E., Kennedy M. A., Heaton D. C., Morrison M. J. Cloning and sequencing of a t(14;19) breakpoint that involves the C mu switch region. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993 Sep;8(1):60–62. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870080110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. K., Wang W. C., Alter B. P. Congenital hypoplastic anemia. Adv Pediatr. 1976;22:349–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani I., Garelli E., Dompè C., Crescenzio N., Locatelli F., Schilirò G., Castaman G., Bagnara G. P., Olivieri N. F., Gabutti V. Mutations in the erythropoietin receptor gene are not a common cause of Diamond-Blackfan anemia. Blood. 1996 Mar 15;87(6):2568–2572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunbar C. E., Smith D. A., Kimball J., Garrison L., Nienhuis A. W., Young N. S. Treatment of Diamond-Blackfan anaemia with haematopoietic growth factors, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor and interleukin 3: sustained remissions following IL-3. Br J Haematol. 1991 Oct;79(2):316–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb04540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORARE S. A. Pure red cell anemia in step siblings. Acta Paediatr. 1963 Mar;52:159–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1963.tb03758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Saunders E. F. Diamond-Blackfan syndrome: evidence against cell-mediated erythropoietic suppression. Blood. 1978 Jun;51(6):1125–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillio A. P., Faulkner L. B., Alter B. P., Reilly L., Klafter R., Heller G., Young D. C., Lipton J. M., Moore M. A., O'Reilly R. J. Treatment of Diamond-Blackfan anemia with recombinant human interleukin-3. Blood. 1993 Aug 1;82(3):744–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. A., Bergmann A., Christensen M., Danganan L., Lee D. A., Ashworth L. K., Nelson D. O., Olsen A. S., Mohrenweiser H. W., Carrano A. V. A 30-Mb metric fluorescence in situ hybridization map of human chromosome 19q. Genomics. 1995 Nov 20;30(2):187–194. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.9886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. H. Pure red-cell aplasia. Occurrence in three generations. Med J Aust. 1982 Jun 12;1(12):519–521. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1982.tb124149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greinix H. T., Storb R., Sanders J. E., Deeg H. J., Doney K. C., Sullivan K. M., Witherspoon R. P. Long-term survival and cure after marrow transplantation for congenital hypoplastic anaemia (Diamond-Blackfan syndrome). Br J Haematol. 1993 Jul;84(3):515–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1993.tb03109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenen P. M., Garcia E., Thoelen R., Aly M., Schoenmakers E. F., Devriendt K., Fryns J. P., Van de Ven W. J. Isolation of cosmids corresponding to the chromosome breakpoints of a de novo autosomal translocation, t(6;19)(p21;q13.1), in a patient with multicystic renal dysplasia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1996;75(4):210–215. doi: 10.1159/000134485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halperin D. S., Freedman M. H. Diamond-blackfan anemia: etiology, pathophysiology, and treatment. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1989 Winter;11(4):380–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn R., Kurczynski E., Schmickel R. The association of Blackfan-Diamond syndrome, physical abnormalities, and an abnormality of chromosome 1. J Pediatr. 1974 Oct;85(4):531–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R., Zanjani E. D., Vila J., Zalusky R., Lutton J. D., Wasserman L. R. Diamond-Blackfan syndrome: lymphocyte-mediated suppression of erythropoiesis. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):899–900. doi: 10.1126/science.986086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter R. E., Hakami N. The occurrence of congenital hypoplastic anemia in half brothers. J Pediatr. 1972 Aug;81(2):346–348. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst J. A., Baraitser M., Wonke B. Autosomal dominant transmission of congenital erythroid hypoplastic anemia with radial abnormalities. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Sep 15;40(4):482–484. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320400422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iriondo A., Garijo J., Baro J., Conde E., Pastor J. M., Sabanés A., Hermosa V., Sainz M. C., Pérez de la Lastra L., Zubizarreta A. Complete recovery of hemopoiesis following bone marrow transplant in a patient with unresponsive congenital hypoplastic anemia (Blackfan-Diamond syndrome). Blood. 1984 Aug;64(2):348–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton J. W., Aldrich J. E., Turner T. L. Congenital erythroid hypoplastic anaemia: autosomal dominant transmission. Scand J Haematol. 1974;13(4):276–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1974.tb00270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Borden J., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):224–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01790090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madanat F., Arnaout M., Hasan A., Tarawneh M., Shomaf M., Khalayleh F. Red cell aplasia resembling Diamond-Blackfan anemia in seven children in a family. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1994 Aug;16(3):260–265. doi: 10.1097/00043426-199408000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott M. G., Apley J., Raper A. B. Congenital (erythroid) hypoplastic anaemia: modified expression in males. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Dec;44(238):757–760. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.238.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Clarke B. J., Hillman D. G., Alter B. P., Housman D. E. Erythroid precursors in congenital hypoplastic (Diamond-Blackfan) anemia. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):489–498. doi: 10.1172/JCI108960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri N. F., Grunberger T., Ben-David Y., Ng J., Williams D. E., Lyman S., Anderson D. M., Axelrad A. A., Correa P., Bernstein A. Diamond-Blackfan anemia: heterogenous response of hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro to the protein product of the steel locus. Blood. 1991 Nov 1;78(9):2211–2215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieff C. A., Yokoyama C. T., Zsebo K. M., Trammell J., Andersen J. W., Nathan D. G., Williams D. A. The production of steel factor mRNA in Diamond-Blackfan anaemia long-term cultures and interactions of steel factor with erythropoietin and interleukin-3. Br J Haematol. 1992 Dec;82(4):640–647. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb06938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia A. P., Propp S., Amarose A. P., Propp R. P., Hall C. A. Chromosome abnormality and hypocalcemia in congenital erythroid hypoplasia. (Blackfan-Diamond syndrome). Am J Med. 1966 Dec;41(6):990–999. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teglund S., Olsen A., Khan W. N., Frängsmyr L., Hammarström S. The pregnancy-specific glycoprotein (PSG) gene cluster on human chromosome 19: fine structure of the 11 PSG genes and identification of 6 new genes forming a third subgroup within the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family. Genomics. 1994 Oct;23(3):669–684. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommerup N. Mendelian cytogenetics. Chromosome rearrangements associated with mendelian disorders. J Med Genet. 1993 Sep;30(9):713–727. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.9.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D. H., Carey J. C., Glader B. E., Rothstein G., Christensen R. D. Congenital hypoplastic (Diamond-Blackfan) anemia in seven members of one kindred. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Feb;35(2):251–256. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yong W. H., Ueki K., Chou D., Reeves S. A., von Deimling A., Gusella J. F., Mohrenweiser H. W., Buckler A. J., Louis D. N. Cloning of a highly conserved human protein serine-threonine phosphatase gene from the glioma candidate region on chromosome 19q13.3. Genomics. 1995 Sep 20;29(2):533–536. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.9972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]