Abstract
We report a rare case of paternally transmitted congenital myotonic dystrophy (DM). The proband is a 23 year old, mentally retarded male who suffers severe muscular weakness. He presented with respiratory and feeding difficulties at birth. His two sibs suffer from childhood onset DM. Their late father had the adult type of DM, with onset around 30 years. Only six other cases of paternal transmission of congenital DM have been reported recently. We review the sex related effects on transmission of congenital DM. Decreased fertility of males with adult onset DM and contraction of the repeat upon male transmission contribute to the almost absent occurrence of paternal transmission of congenital DM. Also the fathers of the reported congenitally affected children showed, on average, shorter CTG repeat lengths and hence less severe clinical symptoms than the mothers of children with congenital DM. We conclude that paternal transmission of congenital DM is rare and preferentially occurs with onset of DM past 30 years in the father.
Full text
PDF
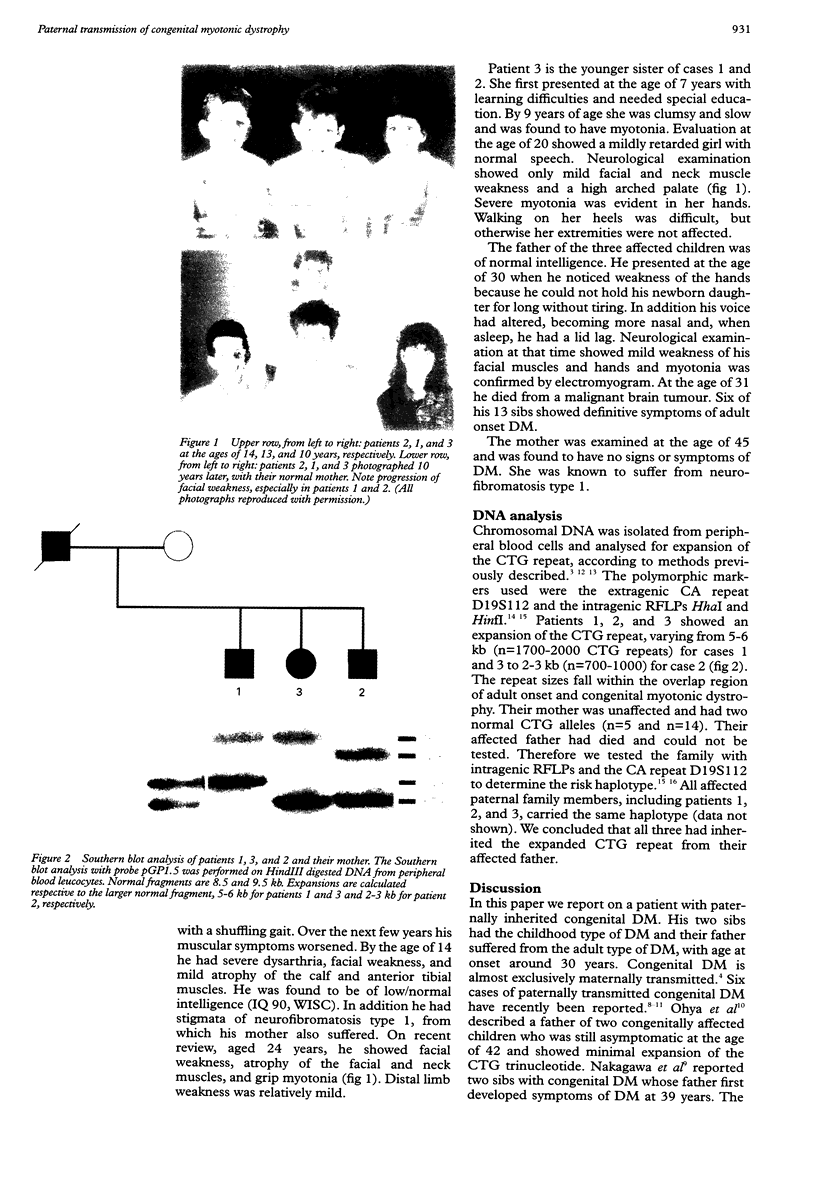


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashizawa T., Anvret M., Baiget M., Barceló J. M., Brunner H., Cobo A. M., Dallapiccola B., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Grandell U., Harley H. Characteristics of intergenerational contractions of the CTG repeat in myotonic dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Mar;54(3):414–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashizawa T., Dunne P. W., Ward P. A., Seltzer W. K., Richards C. S. Effects of the sex of myotonic dystrophy patients on the unstable triplet repeat in their affected offspring. Neurology. 1994 Jan;44(1):120–122. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslanidis C., Jansen G., Amemiya C., Shutler G., Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Chen C., Alleman J., Wormskamp N. G., Vooijs M. Cloning of the essential myotonic dystrophy region and mapping of the putative defect. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):548–551. doi: 10.1038/355548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barceló J. M., Pluscauskas M., MacKenzie A. E., Tsilfidis C., Narang M., Korneluk R. G. Additive influence of maternal and offspring DM-kinase gene CTG repeat lengths in the genesis of congenital myotonic dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jun;54(6):1124–1125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergoffen J., Kant J., Sladky J., McDonald-McGinn D., Zackai E. H., Fischbeck K. H. Paternal transmission of congenital myotonic dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1994 Jul;31(7):518–520. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.7.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. G., Brüggenwirth H. T., Nillesen W., Jansen G., Hamel B. C., Hoppe R. L., de Die C. E., Höweler C. J., van Oost B. A., Wieringa B. Influence of sex of the transmitting parent as well as of parental allele size on the CTG expansion in myotonic dystrophy (DM). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Nov;53(5):1016–1023. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. G., Jansen G., Nillesen W., Nelen M. R., de Die C. E., Höweler C. J., van Oost B. A., Wieringa B., Ropers H. H., Smeets H. J. Brief report: reverse mutation in myotonic dystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 18;328(7):476–480. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302183280705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobo A. M., Poza J. J., Martorell L., López de Munain A., Emparanza J. I., Baiget M. Contribution of molecular analyses to the estimation of the risk of congenital myotonic dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1995 Feb;32(2):105–108. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Fenwick R. G., Jr, King J., Rajnarayan S., Dunne P. W., Dubel J., Nasser G. A., Ashizawa T., de Jong P. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1256–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1546326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley H. G., Rundle S. A., MacMillan J. C., Myring J., Brook J. D., Crow S., Reardon W., Fenton I., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Size of the unstable CTG repeat sequence in relation to phenotype and parental transmission in myotonic dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1164–1174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S., Dyken P. R. Early-onset dystrophia myotonica. Evidence supporting a maternal environmental factor. Lancet. 1972 Jul 8;2(7767):53–55. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91548-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter A., Tsilfidis C., Mettler G., Jacob P., Mahadevan M., Surh L., Korneluk R. The correlation of age of onset with CTG trinucleotide repeat amplification in myotonic dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1992 Nov;29(11):774–779. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.11.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höweler C. J., Busch H. F., Geraedts J. P., Niermeijer M. F., Staal A. Anticipation in myotonic dystrophy: fact or fiction? Brain. 1989 Jun;112(Pt 3):779–797. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.3.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G., Mahadevan M., Amemiya C., Wormskamp N., Segers B., Hendriks W., O'Hoy K., Baird S., Sabourin L., Lennon G. Characterization of the myotonic dystrophy region predicts multiple protein isoform-encoding mRNAs. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):261–266. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G., Willems P., Coerwinkel M., Nillesen W., Smeets H., Vits L., Höweler C., Brunner H., Wieringa B. Gonosomal mosaicism in myotonic dystrophy patients: involvement of mitotic events in (CTG)n repeat variation and selection against extreme expansion in sperm. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):575–585. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M. C., Grimm T., Harley H. G., Harper P. S. Genetic risks for children of women with myotonic dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1084–1091. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Sabourin L., Shutler G., Amemiya C., Jansen G., Neville C., Narang M., Barceló J., O'Hoy K. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1546325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa M., Yamada H., Higuchi I., Kaminishi Y., Miki T., Johnson K., Osame M. A case of paternally inherited congenital myotonic dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1994 May;31(5):397–400. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.5.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. A., Harper P. S. Course, prognosis and complications of childhood-onset myotonic dystrophy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1984 Feb;26(1):62–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1984.tb04407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hoy K. L., Tsilfidis C., Mahadevan M. S., Neville C. E., Barceló J., Hunter A. G., Korneluk R. G. Reduction in size of the myotonic dystrophy trinucleotide repeat mutation during transmission. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):809–812. doi: 10.1126/science.8094260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya K., Tachi N., Chiba S., Sato T., Kon S., Kikuchi K., Imamura S., Yamagata H., Miki T. Congenital myotonic dystrophy transmitted from an asymptomatic father with a DM-specific gene. Neurology. 1994 Oct;44(10):1958–1960. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.10.1958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulton J., Harley H. G., Dasmahapatra J., Brown G. K., Potter C. G., Sykes B. Mitochondrial DNA does not appear to influence the congenital onset type of myotonic dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1995 Sep;32(9):732–735. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.9.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman J. B., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Caskey C. T. Relationship between parental trinucleotide GCT repeat length and severity of myotonic dystrophy in offspring. JAMA. 1993 Apr 21;269(15):1960–1965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilfidis C., MacKenzie A. E., Mettler G., Barceló J., Korneluk R. G. Correlation between CTG trinucleotide repeat length and frequency of severe congenital myotonic dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1992 Jun;1(3):192–195. doi: 10.1038/ng0692-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Passos-Bueno M. R., Cerqueira A., Vainzof M. CTG repeat length in muscle from patients affected with myotonic dystrophy (DM) J Med Genet. 1996 Feb;33(2):173–173. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.2.173-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Die-Smulders C. E., Höweler C. J., Mirandolle J. F., Brunner H. G., Hovers V., Brüggenwirth H., Smeets H. J., Geraedts J. P. Anticipation resulting in elimination of the myotonic dystrophy gene: a follow up study of one extended family. J Med Genet. 1994 Aug;31(8):595–601. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.8.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




