Abstract
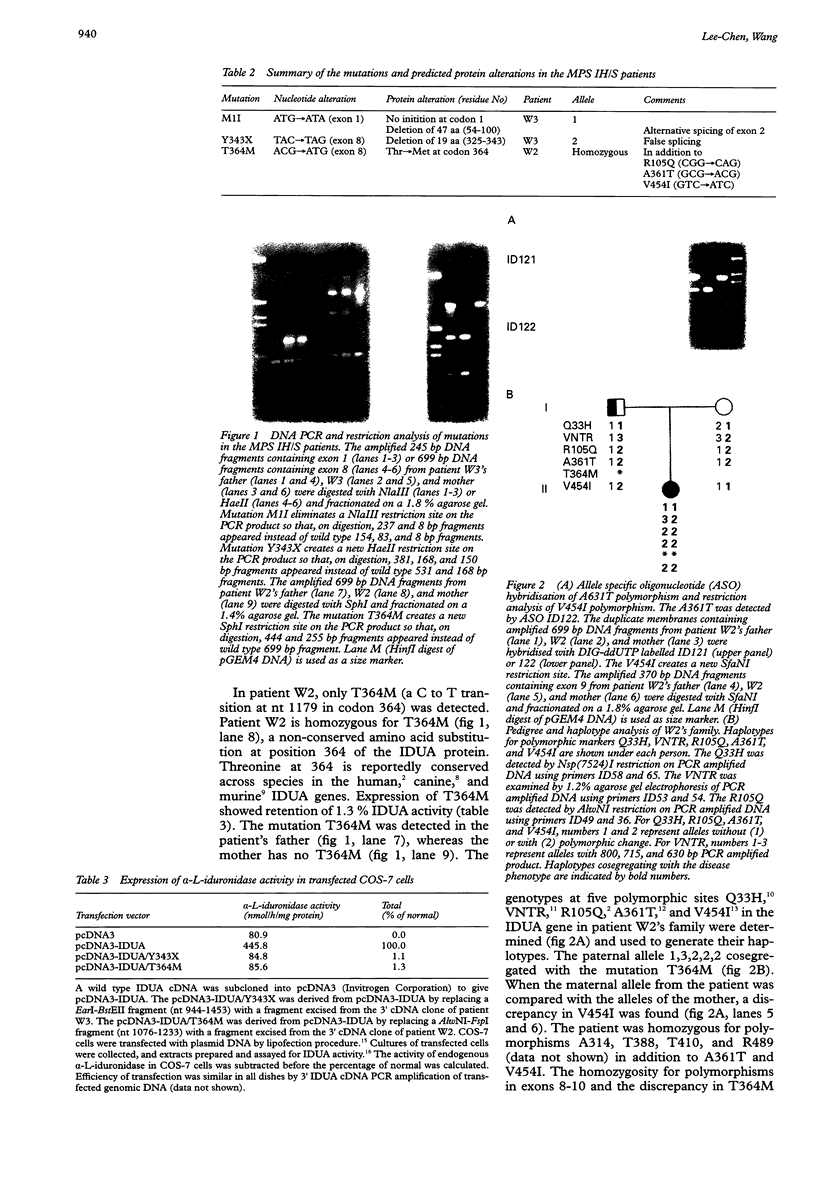
The complementary and genomic DNA segments of the alpha-L-iduronidase gene from two Chinese mucopolysaccharidosis type I Hurler/Scheie (MPS IH/S) patients were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA sequencing was done to study their molecular lesions. Patient W3 has heterozygous mutations; the maternal allele has M1I (G to A transition in the initiation codon ATG) and the paternal allele has Y343X (C to G transversion in exon 8 leading to in frame deletion of codons 325-343 from the mRNA owing to false splicing). Patient W2 is homozygous for mutation T364M (C to T transition in codon 364). The mutation was paternally inherited. A de novo deletion or gene conversion event may have resulted in apparent homozygosity for T364M. Expression of Y343X and T364M showed trace amounts of alpha-L-iduronidase activity compared to that of normal cDNA upon transfection into COS-7 cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunge S., Kleijer W. J., Steglich C., Beck M., Zuther C., Morris C. P., Schwinger E., Hopwood J. J., Scott H. S., Gal A. Mucopolysaccharidosis type I: identification of 8 novel mutations and determination of the frequency of the two common alpha-L-iduronidase mutations (W402X and Q70X) among European patients. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):861–866. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L. A., Nasir J., Zhang H., McDonald H., Applegarth D. A., Hayden M. R., Toone J. Murine alpha-L-iduronidase: cDNA isolation and expression. Genomics. 1994 Nov 15;24(2):311–316. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Muller V., Smithson A., Baggett N. A fluorometric assay using 4-methylumbelliferyl alpha-L-iduronide for the estimation of alpha-L-iduronidase activity and the detection of Hurler and Scheie syndromes. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Mar 1;92(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Vellodi A., Scott H. S., Morris C. P., Litjens T., Clements P. R., Brooks D. A., Cooper A., Wraith J. E. Long-term clinical progress in bone marrow transplanted mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients with a defined genotype. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1993;16(6):1024–1033. doi: 10.1007/BF00711520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Anson D. S., Orsborn A. M., Nelson P. V., Clements P. R., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J. Human alpha-L-iduronidase: cDNA isolation and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9695–9699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Ashton L. J., Eyre H. J., Baker E., Brooks D. A., Callen D. F., Sutherland G. R., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J. Chromosomal localization of the human alpha-L-iduronidase gene (IDUA) to 4p16.3. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Nov;47(5):802–807. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Bunge S., Gal A., Clarke L. A., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J. Molecular genetics of mucopolysaccharidosis type I: diagnostic, clinical, and biological implications. Hum Mutat. 1995;6(4):288–302. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380060403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Guo X. H., Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. Structure and sequence of the human alpha-L-iduronidase gene. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1311–1313. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90053-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Litjens T., Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. PCR detection of two RFLPs in exon I of the alpha-L-iduronidase (IDUA) gene. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):327–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00220095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Nelson P. V., Litjens T., Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. Multiple polymorphisms within the alpha-L-iduronidase gene (IDUA): implications for a role in modification of MPS-I disease phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Sep;2(9):1471–1473. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.9.1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Nelson P. V., MacDonald M. E., Gusella J. F., Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. An 86-bp VNTR within IDUA is the basis of the D4S111 polymorphic locus. Genomics. 1992 Dec;14(4):1118–1120. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus L. J., Sosa-Pineda B., Moskowitz S. M., Menon K. P., Dlott B., Hooper L., Teplow D. B., Shull R. M., Neufeld E. F. Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding canine alpha-L-iduronidase. mRNA deficiency in mucopolysaccharidosis I dog. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6570–6575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieu P. T., Menon K., Neufeld E. F. A mutant stop codon (TAG) in the IDUA gene is used as an acceptor splice site in a patient with Hurler syndrome (MPS IH). Hum Mutat. 1994;3(3):333–336. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380030330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]