Abstract
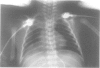
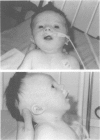
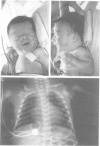
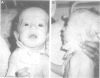
We report on five patients presenting with features of two congenital disorders, DiGeorge syndrome (DGS) and CHARGE association. CHARGE association is usually sporadic and its origin is as yet unknown. Conversely, more than 90% of DGS patients are monosomic for the 22q11.2 chromosomal region. In each of the five patients, both cytogenetic and molecular analysis for the 22q11.2 region were normal. In view of the broad clinical spectrum and the likely genetic heterogeneity of both disorders, these cases are consistent with the extended phenotype of either DGS without 22q11.2 deletion or CHARGE association, especially as several features of CHARGE association have been reported in rare patients with 22q11.2 deletion association phenotypes. On the other hand, these could be novel cases of an independent association involving a complex defect of neural crest cells originating from the pharyngeal pouches.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake K. D., Russell-Eggitt I. M., Morgan D. W., Ratcliffe J. M., Wyse R. K. Who's in CHARGE? Multidisciplinary management of patients with CHARGE association. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Feb;65(2):217–223. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown O. E., Burns D. K., Smith T. H., Rutledge J. C. Bilateral posterior choanal atresia: a morphologic and histologic study, and computed tomographic correlation. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1987 Aug;13(2):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0165-5876(87)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey A. H., Kelly D., Halford S., Wadey R., Wilson D., Goodship J., Burn J., Paul T., Sharkey A., Dumanski J. Molecular genetic study of the frequency of monosomy 22q11 in DiGeorge syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;51(5):964–970. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J. C. Spectrum of the DiGeorge "syndrome". J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):955–956. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80599-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi M., Tenconi R., Turolla L., Silvan C., Bortotto L., Artifoni L. Apparent CHARGE association and chromosome anomaly: chance or contiguous gene syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Nov 1;41(2):246–250. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland W. W., Fogel B. J., Brown W. T., Kay H. E. Foetal thymic transplant in a case of Digeorge's syndrome. Lancet. 1968 Dec 7;2(7580):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91694-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormier-Daire V., Iserin L., Théophile D., Sidi D., Vervel C., Padovani J. P., Vekemans M., Munnich A., Lyonnet S. Upper limb malformations in DiGeorge syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Mar 13;56(1):39–41. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport S. L., Hefner M. A., Mitchell J. A. The spectrum of clinical features in CHARGE syndrome. Clin Genet. 1986 Apr;29(4):298–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. A., Sadler T. W. Effects of vitamin A on endocardial cushion development in the mouse heart. Teratology. 1981 Oct;24(2):139–148. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420240205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daw S. C., Taylor C., Kraman M., Call K., Mao J., Schuffenhauer S., Meitinger T., Lipson T., Goodship J., Scambler P. A common region of 10p deleted in DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes. Nat Genet. 1996 Aug;13(4):458–460. doi: 10.1038/ng0896-458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demczuk S., Aurias A. DiGeorge syndrome and related syndromes associated with 22q11.2 deletions. A review. Ann Genet. 1995;38(2):59–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmaze C., Prieur M., Amblard F., Aikem M., LeDeist F., Demczuk S., Zucman J., Plougastel B., Delattre O., Croquette M. F. Physical mapping by FISH of the DiGeorge critical region (DGCR): involvement of the region in familial cases. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Dec;53(6):1239–1249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. A., Salvin J., Sellinger B., Budarf M. L., McDonald-McGinn D. M., Zackai E. H., Emanuel B. S. Prevalence of 22q11 microdeletions in DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes: implications for genetic counselling and prenatal diagnosis. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):813–817. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Courtney K. B., Wessels R. A., Huhta J., Carpenter R. J., Rich D. C., Ledbetter D. H. Prenatal diagnosis of deletion 17p13 associated with DiGeorge anomaly. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Sep;31(1):1–4. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320310102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F. DiGeorge syndrome: an historical review of clinical and cytogenetic features. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):803–806. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Elder F. F., Haffner P., Northrup H., Ledbetter D. H. Cytogenetic findings in a prospective series of patients with DiGeorge anomaly. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):605–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halford S., Wadey R., Roberts C., Daw S. C., Whiting J. A., O'Donnell H., Dunham I., Bentley D., Lindsay E., Baldini A. Isolation of a putative transcriptional regulator from the region of 22q11 deleted in DiGeorge syndrome, Shprintzen syndrome and familial congenital heart disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2099–2107. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G. CATCH 22. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):801–802. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hittner H. M., Hirsch N. J., Kreh G. M., Rudolph A. J. Colobomatous microphthalmia, heart disease, hearing loss, and mental retardation--a syndrome. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1979 Mar-Apr;16(2):122–128. doi: 10.3928/0191-3913-19790301-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C. K., Kaufman R. L., Podos S. M. Ocular colobomata, cardiac defect, and other anomalies: a study of seven cases including two sibs. J Med Genet. 1975 Sep;12(3):289–293. doi: 10.1136/jmg.12.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Opitz J. M. The DiGeorge anomaly as a developmental field defect. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1986;2:113–127. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. Migration and differentiation of neural crest cells. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1980;16:31–85. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. L., Muster A. J., Newfeld E. A., Paul M. H. Concordant aortic arch anomalies in monozygotic twins. J Pediatr. 1973 Sep;83(3):459–461. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80274-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischner H. W. DiGeorge syndrome(s). J Pediatr. 1972 Nov;81(5):1042–1044. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80575-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Peter H. H., Wilken M., Jüppner H., Kallfelz H. C., Krohn H. P., Miller K., Rieger C. H. The DiGeorge syndrome. I. Clinical evaluation and course of partial and complete forms of the syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Jun;147(5):496–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00441974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oley C. A., Baraitser M., Grant D. B. A reappraisal of the CHARGE association. J Med Genet. 1988 Mar;25(3):147–156. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.3.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst H. F., Wright W. C., LeRiche J., Stiehm E. R. Partial DiGeorge syndrome with substantial cell-mediated immunity. Am J Dis Child. 1976 Mar;130(3):316–319. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1976.02120040094018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagon R. A., Graham J. M., Jr, Zonana J., Yong S. L. Coloboma, congenital heart disease, and choanal atresia with multiple anomalies: CHARGE association. J Pediatr. 1981 Aug;99(2):223–227. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80454-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poswillo D. The pathogenesis of the Treacher Collins syndrome (mandibulofacial dysostosis). Br J Oral Surg. 1975 Jul;13(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0007-117x(75)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan A. K., Goodship J. A., Wilson D. I., Philip N., Levy A., Seidel H., Schuffenhauer S., Oechsler H., Belohradsky B., Prieur M. Spectrum of clinical features associated with interstitial chromosome 22q11 deletions: a European collaborative study. J Med Genet. 1997 Oct;34(10):798–804. doi: 10.1136/jmg.34.10.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambler P. J., Carey A. H., Wyse R. K., Roach S., Dumanski J. P., Nordenskjold M., Williamson R. Microdeletions within 22q11 associated with sporadic and familial DiGeorge syndrome. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90501-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert J. R., Graham J. M., Jr, MacDonald C. Pathologic features of the CHARGE association: support for involvement of the neural crest. Teratology. 1985 Jun;31(3):331–336. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulik K. K., Johnston M. C., Daft P. A., Russell W. E., Dehart D. B. Fetal alcohol syndrome and DiGeorge anomaly: critical ethanol exposure periods for craniofacial malformations as illustrated in an animal model. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1986;2:97–112. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes P. L., White M. R. Inherited partial trisomy 8q (22 leads to qter). Am J Dis Child. 1978 May;132(5):498–501. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120300058012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. I., Britton S. B., McKeown C., Kelly D., Cross I. E., Strobel S., Scambler P. J. Noonan's and DiGeorge syndromes with monosomy 22q11. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Feb;68(2):187–189. doi: 10.1136/adc.68.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. I., Burn J., Scambler P., Goodship J. DiGeorge syndrome: part of CATCH 22. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):852–856. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Herva R., Koivisto M., Aula P. A deletion in chromosome 22 can cause DiGeorge syndrome. Hum Genet. 1981;57(3):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00278938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]