Abstract
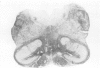
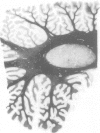
The cases of a brother and sister with dentato-olivary dysplasia are described. Both had severe developmental delay, severe epilepsy of early onset, evolving hypertonic quadriplegia, and death in early childhood. Postmortem examination of the brain in one child showed a particular form of dentato-olivary dysplasia. These children show many features in common with previously described cases of this condition, but this is the first report of occurrence in sibs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth P. G., Vrensen G. F., Uylings H. B., Oorthuys J. W., Stam F. C. Inherited syndrome of microcephaly, dyskinesia and pontocerebellar hypoplasia: a systemic atrophy with early onset. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Jun;97(1):25–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evrard P., Caviness V. S., Jr, Prats-Vinas J., Lyon G. The mechanism of arrest of neuronal migration in the Zellweger malformation: an hypothesis bases upon cytoarchitectonic analysis. Acta Neuropathol. 1978 Feb 20;41(2):109–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00689761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friede R. L., Boltshauser E. Uncommon syndromes of cerebellar vermis aplasia. I: Joubert syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1978 Dec;20(6):758–763. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1978.tb15307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding B. N., Boyd S. G. Intractable seizures from infancy can be associated with dentato-olivary dysplasia. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Aug;104(2):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90305-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding B., Boyd S. Early epileptic encephalopathy with suppression bursts and olivary-dentate dysplasia. Neuropediatrics. 1992 Dec;23(6):336–336. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson P. S., Gilles F. H. Central nervous system abnormalities in trisomy E (17-18) syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Feb;15(2):193–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtahara S., Ohtsuka Y., Yamatogi Y., Oka E. The early-infantile epileptic encephalopathy with suppression-burst: developmental aspects. Brain Dev. 1987;9(4):371–376. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(87)80110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robain O., Dulac O. Early epileptic encephalopathy with suppression bursts and olivary-dentate dysplasia. Neuropediatrics. 1992 Jun;23(3):162–164. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumi S. M. Brain malformations in the trisomy 18 syndrome. Brain. 1970;93(4):821–830. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.4.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. D., McKeever P. A., Squier M. V., Grant J. Lethal olivopontoneocerebellar hypoplasia with dysmorphic features in sibs. J Med Genet. 1992 Oct;29(10):733–735. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.10.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]