Abstract
The neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1CAM) plays a key role during embryonic development of the nervous system and is involved in memory and learning. Mutations in the L1 gene are responsible for four X linked neurological conditions: X linked hydrocephalus (HSAS), MASA syndrome, complicated spastic paraplegia type 1 (SP-1), and X linked agenesis of the corpus callosum. As the clinical picture of these four L1 associated diseases shows considerable overlap and is characterised by Corpus callosum hypoplasia, mental Retardation, Adducted thumbs, Spastic paraplegia, and Hydrocephalus, these conditions have recently been lumped together into the CRASH syndrome. We investigate here whether a genotype-phenotype correlation exists in CRASH syndrome since its clinical spectrum is highly variable and numerous L1 mutations have been described. We found that (1) mutations in the extracellular part of L1 leading to truncation or absence of L1 cause a severe phenotype, (2) mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of L1 give rise to a milder phenotype than extracellular mutations, and (3) extracellular missense mutations affecting amino acids situated on the surface of a domain cause a milder phenotype than those affecting amino acids buried in the core of the domain.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman A., Jouet M., MacFarlane J., Du J. S., Kenwrick S., Chothia C. Outline structure of the human L1 cell adhesion molecule and the sites where mutations cause neurological disorders. EMBO J. 1996 Nov 15;15(22):6050–6059. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd E., Schwartz C. E., Schroer R. J., May M. M., Shapiro S. D., Arena J. F., Lubs H. A., Stevenson R. E. Agenesis of the corpus callosum associated with MASA syndrome. Clin Dysmorphol. 1993 Oct;2(4):332–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coucke P., Vits L., Van Camp G., Serville F., Lyonnet S., Kenwrick S., Rosenthal A., Wehnert M., Munnich A., Willems P. J. Identification of a 5' splice site mutation in intron 4 of the L1CAM gene in an X-linked hydrocephalus family. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):671–673. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS J. H., NORMAN R. M., ROBERTS J. M. Sex-linked hydrocephalus. Report of a family with 15 affected members. Arch Dis Child. 1961 Oct;36:481–485. doi: 10.1136/adc.36.189.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS J. H. The syndrome of sex-linked hydrocephalus. Arch Dis Child. 1961 Oct;36:486–493. doi: 10.1136/adc.36.189.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
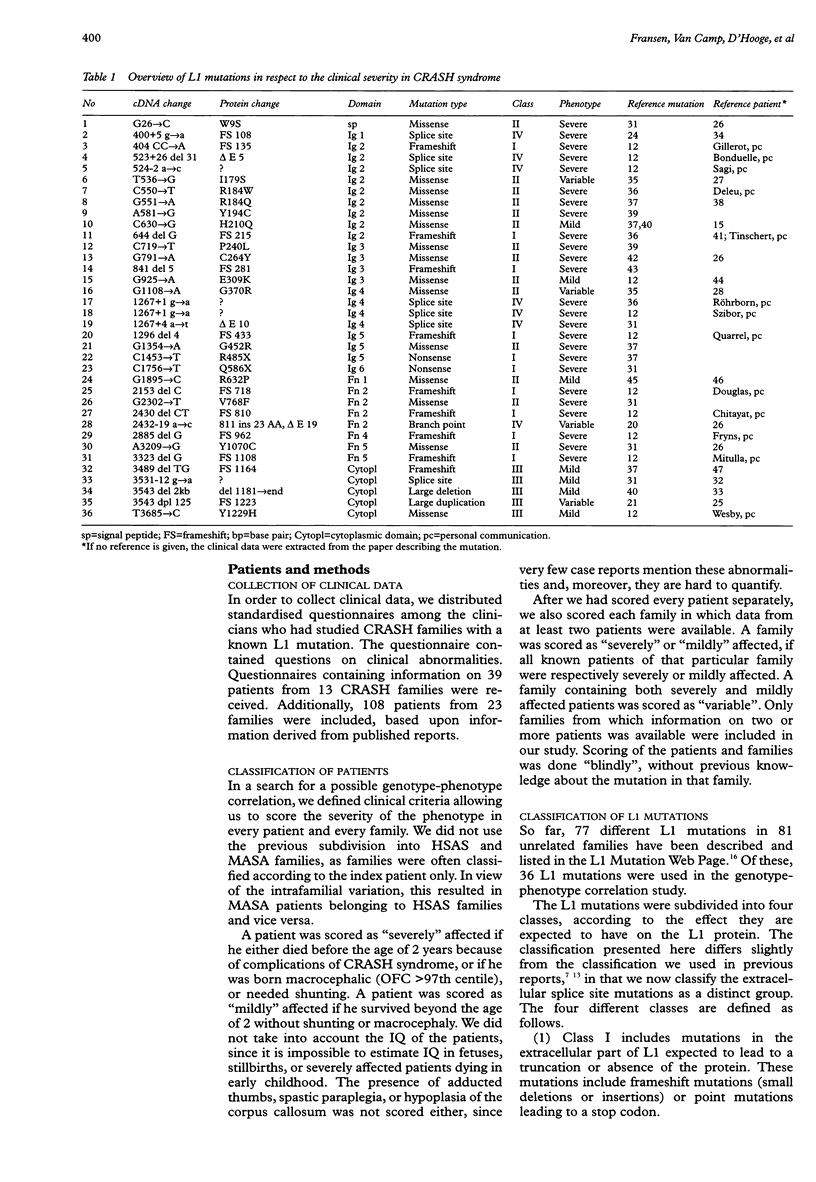
- Fransen E., Lemmon V., Van Camp G., Vits L., Coucke P., Willems P. J. CRASH syndrome: clinical spectrum of corpus callosum hypoplasia, retardation, adducted thumbs, spastic paraparesis and hydrocephalus due to mutations in one single gene, L1. Eur J Hum Genet. 1995;3(5):273–284. doi: 10.1159/000472311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen E., Van Camp G., Vits L., Willems P. J. L1-associated diseases: clinical geneticists divide, molecular geneticists unite. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6(10):1625–1632. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.10.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen E., Vits L., Van Camp G., Willems P. J. The clinical spectrum of mutations in L1, a neuronal cell adhesion molecule. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Jul 12;64(1):73–77. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<73::AID-AJMG11>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Spaepen A., Cassiman J. J., van den Berghe H. X linked complicated spastic paraplegia, MASA syndrome, and X linked hydrocephalus owing to congenital stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius: variable expression of the same mutation at Xq28. J Med Genet. 1991 Jun;28(6):429–431. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.6.429-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu S. M., Orth U., Veske A., Enders H., Klunder K., Schlosser M., Engel W., Schwinger E., Gal A. Five novel mutations in the L1CAM gene in families with X linked hydrocephalus. J Med Genet. 1996 Feb;33(2):103–106. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlavin M. L., Lemmon V. Molecular structure and functional testing of human L1CAM: an interspecies comparison. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):416–423. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
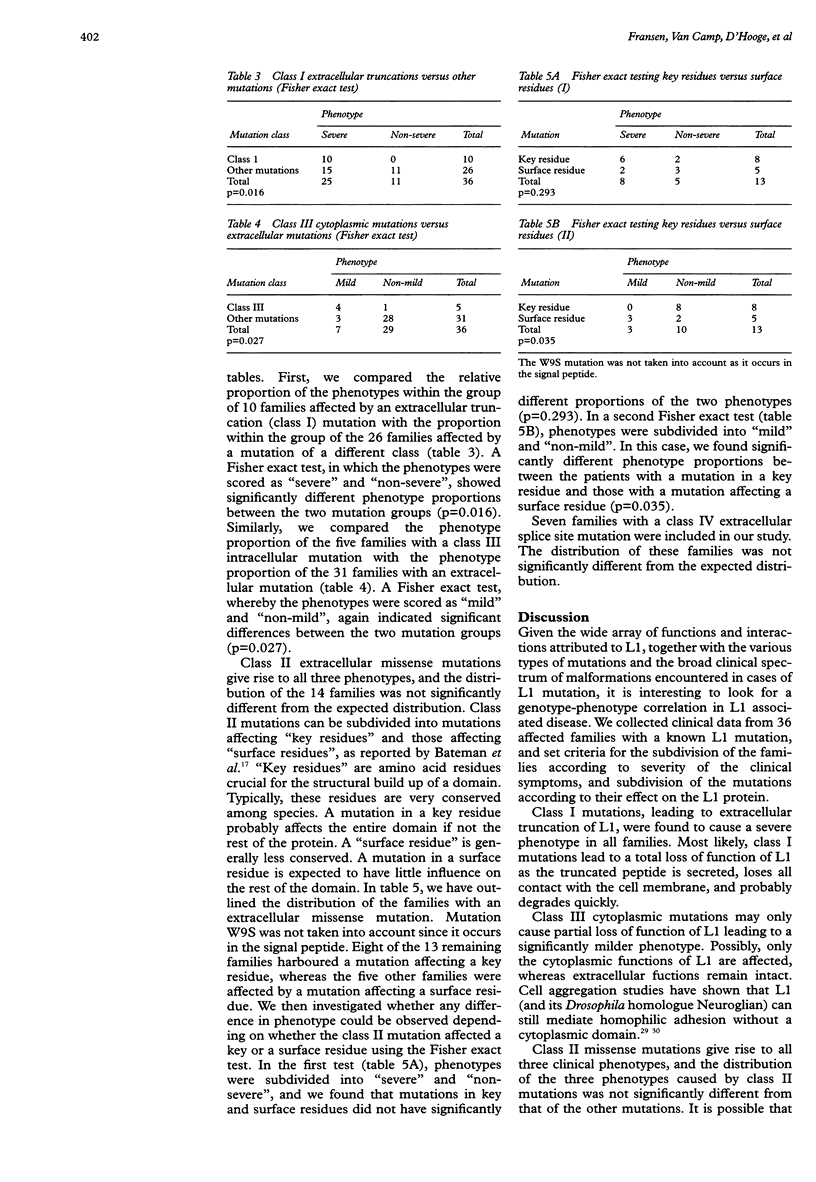
- Hortsch M. The L1 family of neural cell adhesion molecules: old proteins performing new tricks. Neuron. 1996 Oct;17(4):587–593. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Wang Y. M., Marikar Y., Bieber A. J. The cytoplasmic domain of the Drosophila cell adhesion molecule neuroglian is not essential for its homophilic adhesive properties in S2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18809–18817. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Feldman E., Yates J., Donnai D., Paterson J., Siggers D., Kenwrick S. Refining the genetic location of the gene for X linked hydrocephalus within Xq28. J Med Genet. 1993 Mar;30(3):214–217. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Moncla A., Paterson J., McKeown C., Fryer A., Carpenter N., Holmberg E., Wadelius C., Kenwrick S. New domains of neural cell-adhesion molecule L1 implicated in X-linked hydrocephalus and MASA syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1304–1314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Rosenthal A., Armstrong G., MacFarlane J., Stevenson R., Paterson J., Metzenberg A., Ionasescu V., Temple K., Kenwrick S. X-linked spastic paraplegia (SPG1), MASA syndrome and X-linked hydrocephalus result from mutations in the L1 gene. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):402–407. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Rosenthal A., Kenwrick S. Exon 2 of the gene for neural cell adhesion molecule L1 is alternatively spliced in B cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995 Jun;30(2):378–380. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00027-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Rosenthal A., MacFarlane J., Kenwrick S., Donnai D. A missense mutation confirms the L1 defect in X-linked hydrocephalus (HSAS) Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):331–331. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadmon G., Altevogt P. The cell adhesion molecule L1: species- and cell-type-dependent multiple binding mechanisms. Differentiation. 1997 Feb;61(3):143–150. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.1997.6130143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadmon G., Kowitz A., Altevogt P., Schachner M. The neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM enhances L1-dependent cell-cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):193–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadmon G., von Bohlen und Halbach F., Horstkorte R., Eckert M., Altevogt P., Schachner M. Evidence for cis interaction and cooperative signalling by the heat-stable antigen nectadrin (murine CD24) and the cell adhesion molecule L1 in neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 May 1;7(5):993–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaepernick L., Legius E., Higgins J., Kapur S. Clinical aspects of the MASA syndrome in a large family, including expressing females. Clin Genet. 1994 Apr;45(4):181–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1994.tb04019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. X linked recessive inheritance of agenesis of the corpus callosum. J Med Genet. 1983 Apr;20(2):122–124. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.2.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu G., Searby C., King A., Dubowitz M., Davies K. E. Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00401241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthl A., Laurent J. P., Figurov A., Muller D., Schachner M. Hippocampal long-term potentiation and neural cell adhesion molecules L1 and NCAM. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):777–779. doi: 10.1038/372777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macias V. R., Day D. W., King T. E., Wilson G. N. Clasped-thumb mental retardation (MASA) syndrome: confirmation of linkage to Xq28. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):408–414. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Tacke R., Scherer H., Teplow D., Früh K., Schachner M. Neural adhesion molecule L1 as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with binding domains similar to fibronectin. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):701–703. doi: 10.1038/334701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. P. Cell-adhesion molecules, glucocorticoids and long-term-memory formation. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Nov;18(11):502–506. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)92774-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Jouet M., Kenwrick S. Aberrant splicing of neural cell adhesion molecule L1 mRNA in a family with X-linked hydrocephalus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):107–112. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz J. C., Cuppens H., Legius E., Fryns J. P., Glover T., Marynen P., Cassiman J. J. Mutations in L1-CAM in two families with X linked complicated spastic paraplegia, MASA syndrome, and HSAS. J Med Genet. 1995 Jul;32(7):549–552. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.7.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammar M., Aigner S., Altevogt P. Heat-stable antigen (mouse CD24) in the brain: dual but distinct interaction with P-selectin and L1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Feb 8;1337(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(96)00177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander-Stumpel C., Höweler C., Jones M., Sommer A., Stevens C., Tinschert S., Israel J., Fryns J. P. Spectrum of X-linked hydrocephalus (HSAS), MASA syndrome, and complicated spastic paraplegia (SPG1): Clinical review with six additional families. Am J Med Genet. 1995 May 22;57(1):107–116. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320570122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander-Stumpel C., Legius E., Fryns J. P., Cassiman J. J. MASA syndrome: new clinical features and linkage analysis using DNA probes. J Med Genet. 1990 Nov;27(11):688–692. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.11.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serville F., Lyonnet S., Pelet A., Reynaud M., Louail C., Munnich A., Le Merrer M. X-linked hydrocephalus: clinical heterogeneity at a single gene locus. Eur J Pediatr. 1992 Jul;151(7):515–518. doi: 10.1007/BF01957757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straussberg R., Blatt I., Brand N., Kessler D., Katznelson M. B., Goodman R. M. X-linked mental retardation with bilateral clasped thumbs: report of another affected family. Clin Genet. 1991 Nov;40(5):337–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takechi T., Tohyama J., Kurashige T., Maruta K., Uyemura K., Ohi T., Matsukura S., Sakuragawa N. A deletion of five nucleotides in the L1CAM gene in a Japanese family with X-linked hydrocephalus. Hum Genet. 1996 Mar;97(3):353–356. doi: 10.1007/BF02185770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M., Hirano S., Matsuyoshi N., Fujimori T. Cytoplasmic control of cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1992;57:327–334. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1992.057.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp G., Fransen E., Vits L., Raes G., Willems P. J. A locus-specific mutation database for the neural cell adhesion molecule L1CAM (Xq28) Hum Mutat. 1996;8(4):391–391. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1996)8:4<391::AID-HUMU19>3.0.CO;2-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp G., Vits L., Coucke P., Lyonnet S., Schrander-Stumpel C., Darby J., Holden J., Munnich A., Willems P. J. A duplication in the L1CAM gene associated with X-linked hydrocephalus. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):421–425. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vits L., Van Camp G., Coucke P., Fransen E., De Boulle K., Reyniers E., Korn B., Poustka A., Wilson G., Schrander-Stumpel C. MASA syndrome is due to mutations in the neural cell adhesion gene L1CAM. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):408–413. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váradi V., Csécsei K., Szeifert G. T., Tóth Z., Papp Z. Prenatal diagnosis of X linked hydrocephalus without aqueductal stenosis. J Med Genet. 1987 Apr;24(4):207–209. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.4.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. J., Brouwer O. F., Dijkstra I., Wilmink J. X-linked hydrocephalus. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Aug;27(4):921–928. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M., Davies K. E., Bell M. V., Huson S. M., Patterson M. N. MASA syndrome: further clinical delineation and chromosomal localisation. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00273999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. V., Cheng G., Payne H. R., Lemmon V. The cytoplasmic domain of the cell adhesion molecule L1 is not required for homophilic adhesion. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Nov 24;200(3):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)12100-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. V., Kenwrick S., Willems P., Lemmon V. Mutations in the cell adhesion molecule L1 cause mental retardation. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Apr;18(4):168–172. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93896-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeatman G. W. Mental retardation-clasped thumb syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):339–344. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


