Abstract
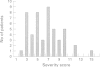
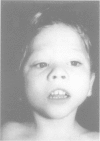
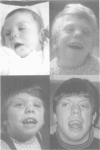
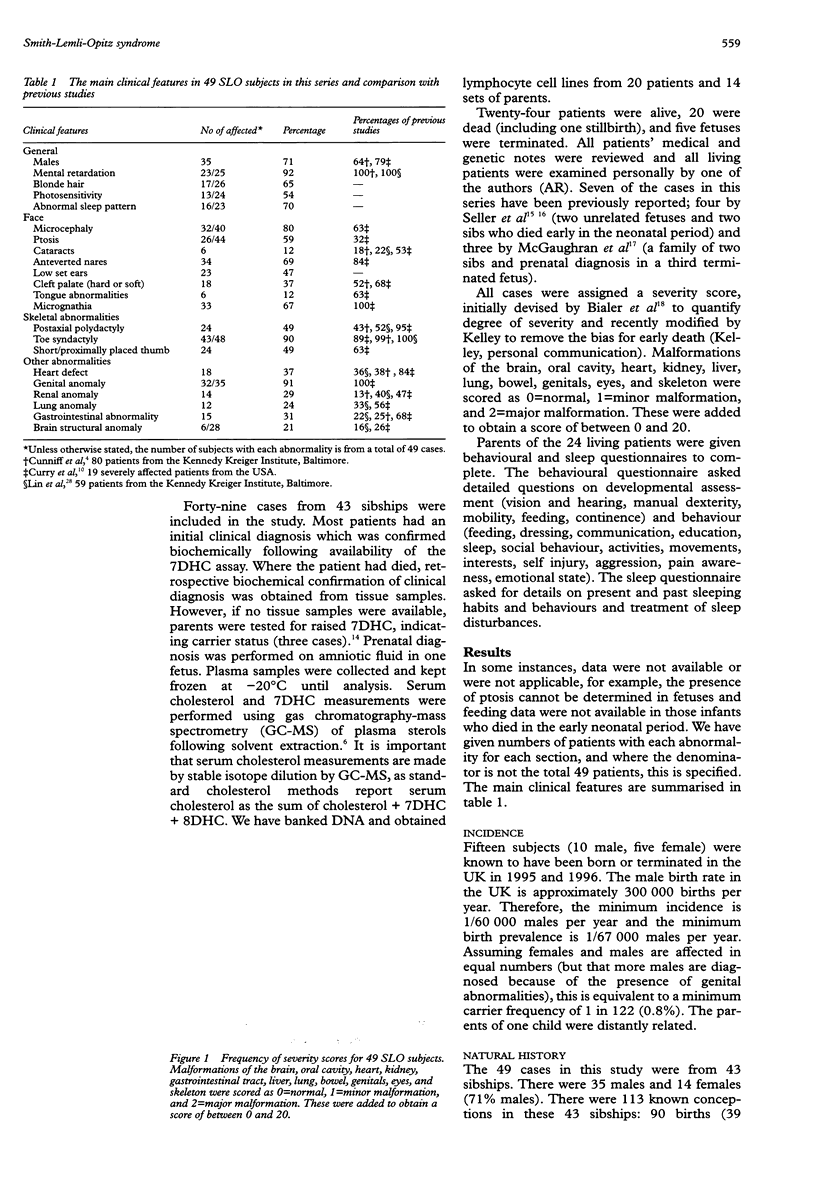
We have reviewed all known UK cases of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Among 49 cases with proven 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase deficiency, half had been terminated or had died in infancy. The minimum incidence is 1 in 60,000. The frequent occurrence of hypospadias may account for 71% of recognised cases being male. Important common features which emerged include short thumbs, severe photosensitivity, aggressive behaviour, and atrioventricular septal defect. The typical facial appearance becomes less obvious with age and 20% of cases did not have 2/3 toe syndactyly. Biochemical measurements of serum 7-dehydrocholesterol did not correlate with clinical severity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abuelo D. N., Tint G. S., Kelley R., Batta A. K., Shefer S., Salen G. Prenatal detection of the cholesterol biosynthetic defect in the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome by the analysis of amniotic fluid sterols. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 10;56(3):281–285. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry R., Wilson H., Robinson J., Sandlin C., Tyson W., Campbell J., Porreco R., Manchester D. Apparent Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome and Miller-Dieker syndrome in a family with segregating translocation t(7;17)(q34;p13.1). Am J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;34(3):358–365. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialer M. G., Penchaszadeh V. B., Kahn E., Libes R., Krigsman G., Lesser M. L. Female external genitalia and müllerian duct derivatives in a 46,XY infant with the smith-lemli-Opitz syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Nov;28(3):723–731. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton P., Mills K., Keeling J., FitzPatrick D. Desmosterolosis: a new inborn error of cholesterol biosynthesis. Lancet. 1996 Aug 10;348(9024):404–404. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)65020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunniff C., Kratz L. E., Moser A., Natowicz M. R., Kelley R. I. Clinical and biochemical spectrum of patients with RSH/Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome and abnormal cholesterol metabolism. Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jan 31;68(3):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry C. J., Carey J. C., Holland J. S., Chopra D., Fineman R., Golabi M., Sherman S., Pagon R. A., Allanson J., Shulman S. Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome-type II: multiple congenital anomalies with male pseudohermaphroditism and frequent early lethality. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jan;26(1):45–57. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehart D. B., Lanoue L., Tint G. S., Sulik K. K. Pathogenesis of malformations in a rodent model for Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jan 31;68(3):328–337. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19970131)68:3<328::aid-ajmg15>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias E. R., Irons M. B., Hurley A. D., Tint G. S., Salen G. Clinical effects of cholesterol supplementation in six patients with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS) Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jan 31;68(3):305–310. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19970131)68:3<305::aid-ajmg11>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda A., Tint G. S., Salen G., Batta A. K., Chen T. S., Shefer S. Defective conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to cholesterol in cultured skin fibroblasts from Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome homozygotes. J Lipid Res. 1995 Jul;36(7):1595–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons M., Elias E. R., Salen G., Tint G. S., Batta A. K. Defective cholesterol biosynthesis in Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Lancet. 1993 May 29;341(8857):1414–1414. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90983-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Aughton D. J., Comstock C. H., von Oeyen P. T., Higgins J. V., Schulz R. Prenatal diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome, type II. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jan 15;49(2):240–243. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320490216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. I. A new face for an old syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jan 31;68(3):251–256. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19970131)68:3<251::aid-ajmg1>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. I. Diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry of 7-dehydrocholesterol in plasma, amniotic fluid and cultured skin fibroblasts. Clin Chim Acta. 1995 Apr 30;236(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(95)06038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. L., Roessler E., Hennekam R. C., Feldman G. L., Kosaki K., Jones M. C., Palumbos J. C., Muenke M. Holoprosencephaly in RSH/Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome: does abnormal cholesterol metabolism affect the function of Sonic Hedgehog? Am J Med Genet. 1996 Dec 30;66(4):478–484. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19961230)66:4<478::AID-AJMG22>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. E., Ardinger H. H., Ardinger R. H., Jr, Cunniff C., Kelley R. I. Cardiovascular malformations in Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jan 31;68(3):270–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. B., Yong S. L. Borderline normal intelligence in the Smith-Lemli-Opitz (RSH) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1980;5(2):137–143. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320050205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaughran J. M., Clayton P. T., Mills K. A., Rimmer S., Moore L., Donnai D. Prenatal diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 10;56(3):269–271. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeever P. A., Young I. D. Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. II: A disorder of the fetal adrenals? J Med Genet. 1990 Jul;27(7):465–466. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.7.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K., Mandel H., Montemagno R., Soothill P., Gershoni-Baruch R., Clayton P. T. First trimester prenatal diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (7-dehydrocholesterol reductase deficiency). Pediatr Res. 1996 May;39(5):816–819. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199605000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwokoro N. A., Mulvihill J. J. Cholesterol and bile acid replacement therapy in children and adults with Smith-Lemli-Opitz (SLO/RSH) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jan 31;68(3):315–321. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19970131)68:3<315::aid-ajmg13>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz J. M. RSH/SLO ("Smith-Lemli-Opitz") syndrome: historical, genetic, and developmental considerations. Am J Med Genet. 1994 May 1;50(4):344–346. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320500408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossiter J. P., Hofman K. J., Kelley R. I. Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome: prenatal diagnosis by quantification of cholesterol precursors in amniotic fluid. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 10;56(3):272–275. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. W., LEMLI L., OPITZ J. M. A NEWLY RECOGNIZED SYNDROME OF MULTIPLE CONGENITAL ANOMALIES. J Pediatr. 1964 Feb;64:210–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seller M. J., Flinter F. A., Docherty Z., Fagg N., Newbould M. Phenotypic diversity in the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Clin Dysmorphol. 1997 Jan;6(1):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seller M. J., Russell J., Tint G. S. Unusual case of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome "type II". Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 10;56(3):265–268. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart F. J., Nevin N. C., Dornan J. C. Prenatal diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 10;56(3):286–287. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320560310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tint G. S., Irons M., Elias E. R., Batta A. K., Frieden R., Chen T. S., Salen G. Defective cholesterol biosynthesis associated with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 13;330(2):107–113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401133300205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tint G. S., Salen G., Batta A. K., Shefer S., Irons M., Elias E. R., Abuelo D. N., Johnson V. P., Lambert M., Lutz R. Correlation of severity and outcome with plasma sterol levels in variants of the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. J Pediatr. 1995 Jul;127(1):82–87. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(95)70261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M., Zori R. T., Alley T., Whidden E., Gray B. A., Williams C. A. Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome in a female with a de novo, balanced translocation involving 7q32: probable disruption of an SLOS gene. Am J Med Genet. 1994 May 1;50(4):368–374. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320500414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman P. A., Hercules D. M., Naylor E. W. Direct analysis of filter paper blood specimens for identification of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome using time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry. Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jan 31;68(3):300–304. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19970131)68:3<300::aid-ajmg10>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]