Abstract
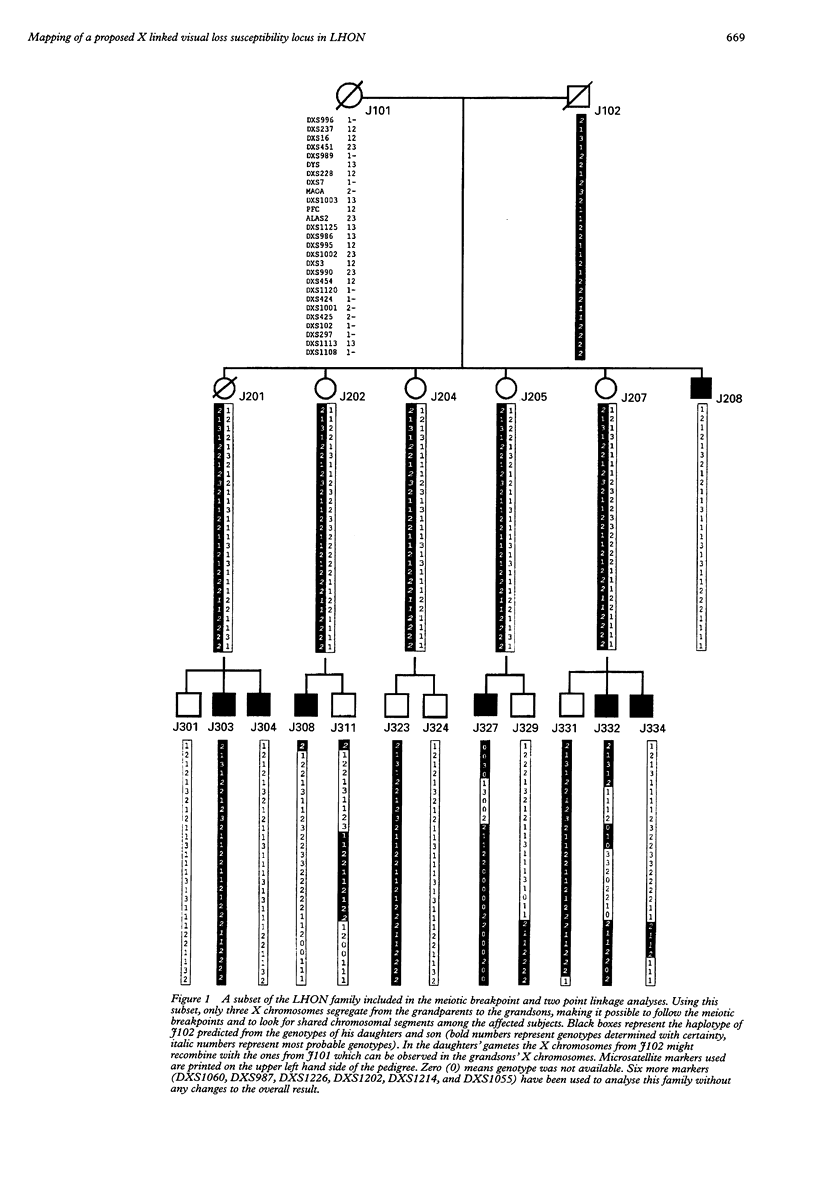
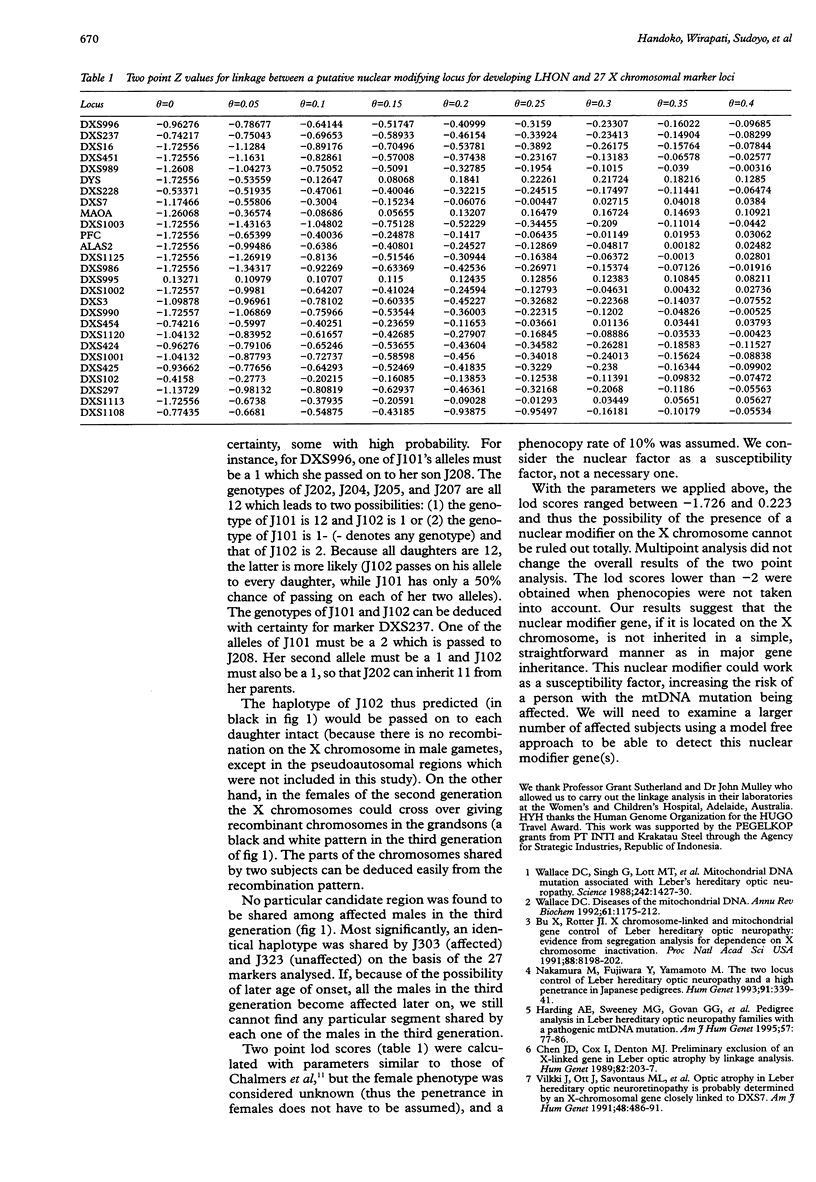
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a maternally inherited degenerative disorder characterised by an acute or subacute optic nerve degeneration resulting in visual failure. Mitochondrial DNA mutations have been reported and a nuclear modifier gene(s) on the X chromosome is thought to play an important role in the onset of this disorder. We analysed a LHON family with a novel and more accurate approach using 27 X chromosomal microsatellite markers. Meiotic breakpoint mapping and two point lod score did not point to any particular area on the X chromosome which might contain the X susceptibility locus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bu X. D., Rotter J. I. X chromosome-linked and mitochondrial gene control of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: evidence from segregation analysis for dependence on X chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8198–8202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho M. R., Müller B., Rötzer E., Berninger T., Kommerell G., Blankenagel A., Savontaus M. L., Meitinger T., Lorenz B. Leber's hereditary optic neuroretinopathy and the X-chromosomal susceptibility factor: no linkage to DXs7. Hum Hered. 1992;42(5):316–320. doi: 10.1159/000154089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers R. M., Davis M. B., Sweeney M. G., Wood N. W., Harding A. E. Evidence against an X-linked visual loss susceptibility locus in Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jul;59(1):103–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Cox I., Denton M. J. Preliminary exclusion of an X-linked gene in Leber optic atrophy by linkage analysis. Hum Genet. 1989 Jun;82(3):203–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00291154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Sweeney M. G., Govan G. G., Riordan-Eva P. Pedigree analysis in Leber hereditary optic neuropathy families with a pathogenic mtDNA mutation. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jul;57(1):77–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juvonen V., Vilkki J., Aula P., Nikoskelainen E., Savontaus M. L. Reevaluation of the linkage of an optic atrophy susceptibility gene to X-chromosomal markers in Finnish families with Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy (LHON) Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):289–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Fujiwara Y., Yamamoto M. The two locus control of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy and a high penetrance in Japanese pedigrees. Hum Genet. 1993 May;91(4):339–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00217353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oostra R. J., Kemp S., Bolhuis P. A., Bleeker-Wagemakers E. M. No evidence for 'skewed' inactivation of the X-chromosome as cause of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy in female carriers. Hum Genet. 1996 Apr;97(4):500–505. doi: 10.1007/BF02267075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebel K., Mertz A., Winkelmann M., Nagaraja R., Rappold G. Localization of the adenine nucleotide translocase gene ANT2 to chromosome Xq24-q25 with tight linkage to DXS425. Genomics. 1994 Dec;24(3):605–606. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoyo H., Sitepu M., Malik S., Poesponegoro H. D., Marzuki S. Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy in Indonesia: two families with the mtDNA 11778G>A and 14484T>C mutations. Hum Mutat. 1998;Suppl 1:S271–S274. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380110186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney M. G., Davis M. B., Lashwood A., Brockington M., Toscano A., Harding A. E. Evidence against an X-linked locus close to DXS7 determining visual loss susceptibility in British and Italian families with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Oct;51(4):741–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilkki J., Ott J., Savontaus M. L., Aula P., Nikoskelainen E. K. Optic atrophy in Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy is probably determined by an X-chromosomal gene closely linked to DXS7. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):486–491. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C. Diseases of the mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1175–1212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Singh G., Lott M. T., Hodge J. A., Schurr T. G., Lezza A. M., Elsas L. J., 2nd, Nikoskelainen E. K. Mitochondrial DNA mutation associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.3201231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuchenko O., Wehnert M., Bailey J., Sun Z. S., Lee C. C. Isolation, mapping, and genomic structure of an X-linked gene for a subunit of human mitochondrial complex I. Genomics. 1996 Nov 1;37(3):281–288. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


