Abstract
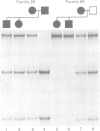
A study of two DNA polymorphisms (i2 RsaI, E237G) in the gene for the beta subunit of the IgE high affinity receptor (FcepsilonRIbeta) was performed in 168 Italian families with atopic asthmatic children. The prevalence of the E237G allele in the Italian population was 4%, so this polymorphism was unsuitable for this study. The i2 RsaI polymorphism minor allele frequency was 44%, and it had a PIC value of 0.37. Linkage analysis indicated a significant allele sharing in affected sib pairs for bronchial hyper-responsiveness (BHR, p=0.048), but not for allergic asthma. These data indicate an association of bronchial hyper-responsiveness with the FcepsilonRIbeta gene.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cookson W. O., Sharp P. A., Faux J. A., Hopkin J. M. Linkage between immunoglobulin E responses underlying asthma and rhinitis and chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1989 Jun 10;1(8650):1292–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92687-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Schroeder M., Goldin L. R., Weeks D. E. Nonparametric simulation-based statistics for detecting linkage in general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Apr;58(4):867–880. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukao T., Kaneko H., Teramoto T., Tashita H., Kondo N. Association between Fc epsilon RI beta and atopic disorder in Japanese population? Lancet. 1996 Aug 10;348(9024):407–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)65025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. R., Cookson W. O. A new variant of the beta subunit of the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E (Fc epsilon RI-beta E237G): associations with measures of atopy and bronchial hyper-responsiveness. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Jul;5(7):959–962. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.7.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizawa N., Yamaguchi E., Furuya K., Ohnuma N., Kodama N., Kojima J., Ohe M., Kawakami Y. Association between high serum total IgE levels and D11S97 on chromosome 11q13 in Japanese subjects. J Med Genet. 1995 May;32(5):363–369. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.5.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küster H., Zhang L., Brini A. T., MacGlashan D. W., Kinet J. P. The gene and cDNA for the human high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor beta chain and expression of the complete human receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12782–12787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinati L. C., Trabetti E., Casartelli A., Boner A. L., Pignatti P. F. Affected sib-pair and mutation analyses of the high affinity IgE receptor beta chain locus in Italian families with atopic asthmatic children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 May;153(5):1682–1685. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.153.5.8630620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandford A. J., Shirakawa T., Moffatt M. F., Daniels S. E., Ra C., Faux J. A., Young R. P., Nakamura Y., Lathrop G. M., Cookson W. O. Localisation of atopy and beta subunit of high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) on chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1993 Feb 6;341(8841):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sham P. C., Curtis D. An extended transmission/disequilibrium test (TDT) for multi-allele marker loci. Ann Hum Genet. 1995 Jul;59(Pt 3):323–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1995.tb00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa T., Mao X. Q., Sasaki S., Enomoto T., Kawai M., Morimoto K., Hopkin J. Association between atopic asthma and a coding variant of Fc epsilon RI beta in a Japanese population. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Aug;5(8):1129–1130. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.8.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa T., Mao X. Q., Sasaki S., Kawai M., Morimoto K., Hopkin J. M. Association between Fc epsilon RI beta and atopic disorder in a Japanese population. Lancet. 1996 Feb 10;347(8998):394–395. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90570-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. P., Sharp P. A., Lynch J. R., Faux J. A., Lathrop G. M., Cookson W. O., Hopkin J. M. Confirmation of genetic linkage between atopic IgE responses and chromosome 11q13. J Med Genet. 1992 Apr;29(4):236–238. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.4.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]