Abstract
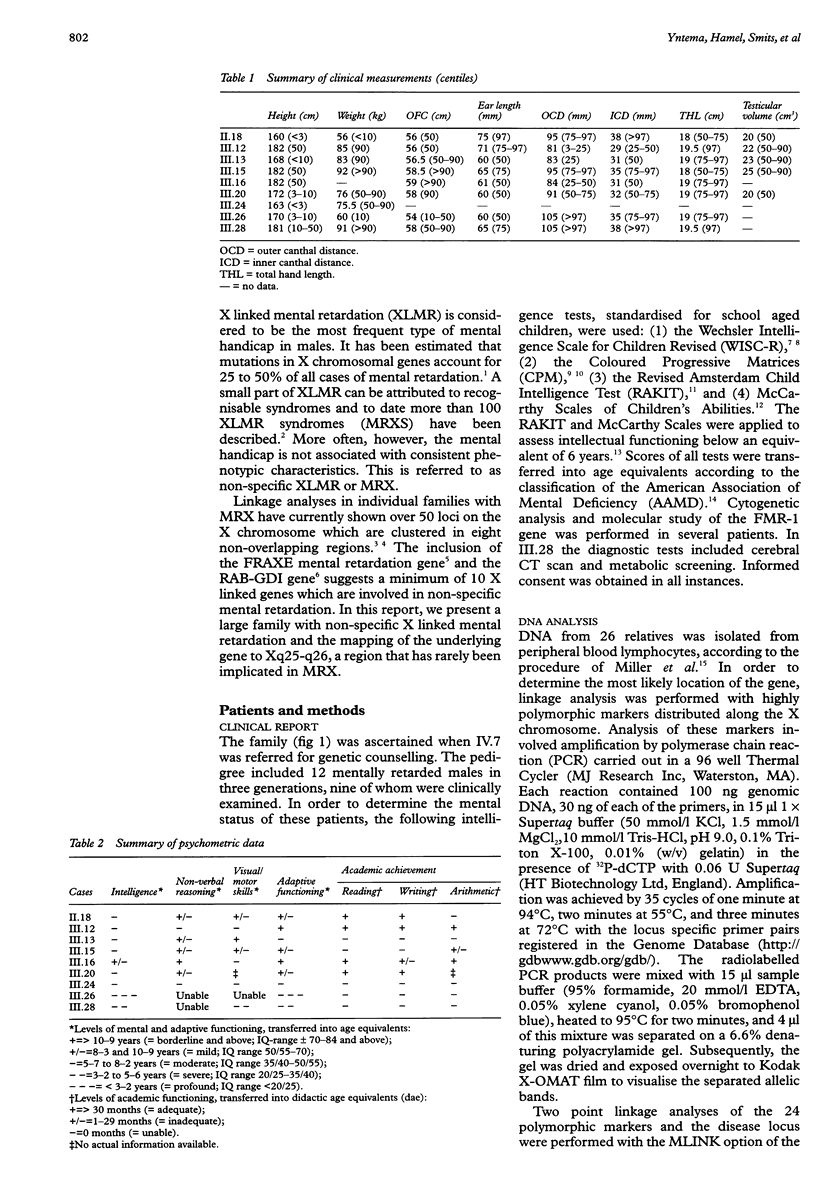
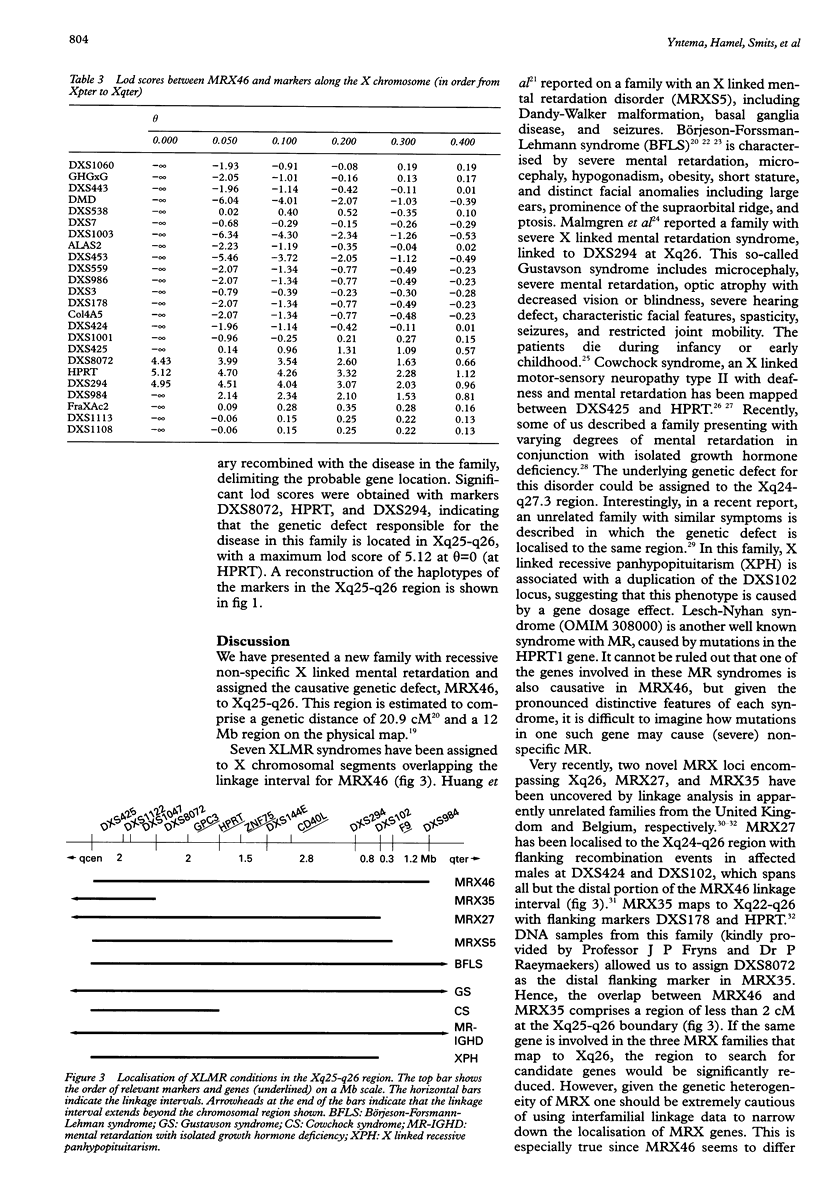
We report linkage data on a new large family with non-specific X linked mental retardation (MRX), using 24 polymorphic markers covering the entire X chromosome. We could assign the underlying disease gene, denoted MRX46, to the Xq25-q26 region. MRX46 is tightly linked to the markers DXS8072, HPRT, and DXS294 with a maximum lod score of 5.12 at theta=0. Recombination events were observed with DXS425 in Xq25 and DXS984 at the Xq26-Xq27 boundary, which localises MRX46 to a 20.9 cM (12 Mb) interval. Several X linked mental retardation syndromes have been mapped to the same region of the X chromosome. In addition, the localisation of two MRX genes, MRX27 and MRX35, partially overlaps with the linkage interval obtained for MRX46. Although an extension of the linkage analysis for MRX35 showed only a minimal overlap with MRX46, it cannot be excluded that the same gene is involved in several of these MRX disorders. On the other hand, given the considerable genetic heterogeneity in MRX, one should be extremely cautious in using interfamilial linkage data to narrow down the localisation of MRX genes. Therefore, unless the underlying gene(s) is characterised by the analysis of candidate genes, MRX46 can be considered a new independent MRX locus.
Full text
PDF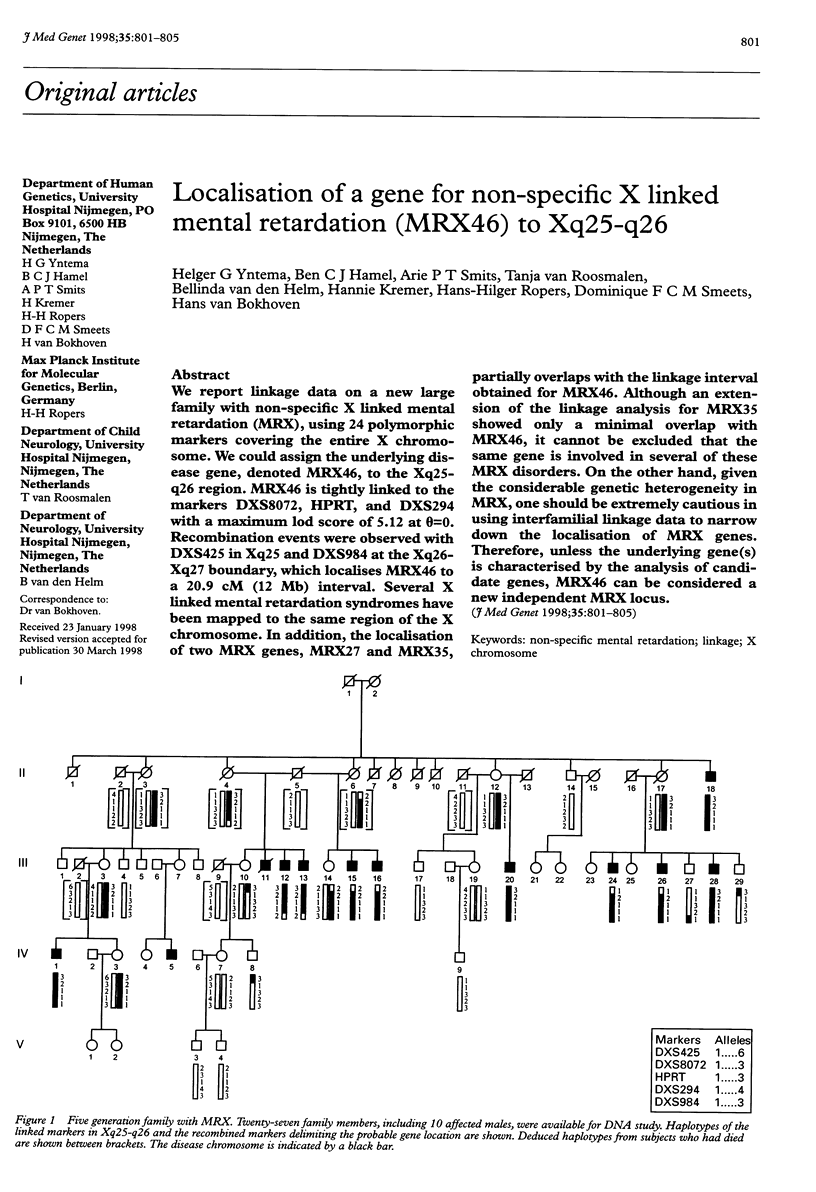


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cowchock F. S., Duckett S. W., Streletz L. J., Graziani L. J., Jackson L. G. X-linked motor-sensory neuropathy type-II with deafness and mental retardation: a new disorder. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Feb;20(2):307–315. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gecz J., Gedeon A. K., Sutherland G. R., Mulley J. C. Identification of the gene FMR2, associated with FRAXE mental retardation. Nat Genet. 1996 May;13(1):105–108. doi: 10.1038/ng0596-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedeon A. K., Donnelly A. J., Mulley J. C., Kerr B., Turner G. How many X-linked genes for non-specific mental retardation (MRX) are there? Am J Med Genet. 1996 Jul 12;64(1):158–162. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<158::AID-AJMG26>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedeon A. K., Glass I. A., Connor J. M., Mulley J. C. Genetic localisation of MRX27 to Xq24-26 defines another discrete gene for non-specific X-linked mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Jul 12;64(1):121–124. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<121::AID-AJMG20>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass I. A., White E. M., Pope M. J., Pirrit L. A., Cockburn F., Connor J. M. Linkage analysis in a large family with nonspecific X-linked mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Feb-Mar;38(2-3):240–243. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu X. X., Decorte R., Marynen P., Fryns J. P., Cassiman J. J., Raeymaekers P. Localisation of a new gene for non-specific mental retardation to Xq22-q26 (MRX35). J Med Genet. 1996 Jan;33(1):52–55. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson K. H., Annerén G., Malmgren H., Dahl N., Ljunggren C. G., Bäckman H. New X-linked syndrome with severe mental retardation, severely impaired vision, severe hearing defect, epileptic seizures, spasticity, restricted joint mobility, and early death. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Mar 1;45(5):654–658. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel B. C., Smits A. P., Otten B. J., van den Helm B., Ropers H. H., Mariman E. C. Familial X-linked mental retardation and isolated growth hormone deficiency: clinical and molecular findings. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Jul 12;64(1):35–41. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<35::AID-AJMG5>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Hejtmancik J. F., Edwards A., Pettigrew A. L., Herrera C. A., Hammond H. A., Caskey C. T., Zoghbi H. Y., Ledbetter D. H. Linkage of the gene for an X-linked mental retardation disorder to a hypervariable (AGAT)n repeat motif within the human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) locus (Xq26). Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1312–1319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr B., Turner G., Mulley J., Gedeon A., Partington M. Non-specific X linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1991 Jun;28(6):378–382. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.6.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagerström-Fermér M., Sundvall M., Johnsen E., Warne G. L., Forrest S. M., Zajac J. D., Rickards A., Ravine D., Landegren U., Pettersson U. X-linked recessive panhypopituitarism associated with a regional duplication in Xq25-q26. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Apr;60(4):910–916. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. L. Construction of human linkage maps: likelihood calculations for multilocus linkage analysis. Genet Epidemiol. 1986;3(1):39–52. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A., Chiurazzi P., Arena J. F., Schwartz C., Tranebjaerg L., Neri G. XLMR genes: update 1996. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Jul 12;64(1):147–157. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<147::AID-AJMG25>3.0.CO;2-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren H., Sundvall M., Dahl N., Gustavson K. H., Annerén G., Wadelius C., Steén-Bondeson M. L., Pettersson U. Linkage mapping of a severe X-linked mental retardation syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1046–1052. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews K. D., Ardinger H. H., Nishimura D. Y., Buetow K. H., Murray J. C., Bartley J. A. Linkage localization of Börjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;34(4):470–474. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilia G., MacMillan S., Nagaraja R., Mumm S., Weissenbach J., Schlessinger D. YAC/STS map of 9 Mb of Xq26 at 100-kb resolution, localizing 6 ESTs, 6 genes, and 32 genetic markers. Genomics. 1996 May 15;34(1):55–62. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest J. M., Fischbeck K. H., Nouri N., Keats B. J. A locus for axonal motor-sensory neuropathy with deafness and mental retardation maps to Xq24-q26. Genomics. 1995 Sep 20;29(2):409–412. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.9987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Boguski M. S., Stewart E. A., Stein L. D., Gyapay G., Rice K., White R. E., Rodriguez-Tomé P., Aggarwal A., Bajorek E. A gene map of the human genome. Science. 1996 Oct 25;274(5287):540–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixth International Workshop on Human X Chromosome Mapping 1995. Banff, Alberta, Canada, June 16-18, 1995. Report and abstracts. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1995;71(4):307–342. doi: 10.1159/000134135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Gedeon A., Mulley J., Sutherland G., Rae J., Power K., Arthur I. Börjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome: clinical manifestations and gene localization to Xq26-27. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;34(4):463–469. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



