Abstract
BACKGROUND
We invented Endoscopic Ruler, a new endoscopic device to measure the size of varices in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
AIM
To assess the feasibility and safety of Endoscopic Ruler, and evaluate the agreement on identifying large oesophageal varices (OV) between Endoscopic Ruler and the endoscopists, as well as the interobserver agreement on diagnosing large OV using Endoscopic Ruler.
METHODS
We prospectively and consecutively enrolled patients with cirrhosis from 11 hospitals, all of whom got esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) with Endoscopic Ruler. The primary study outcome was a successful measurement of the size of varices using Endoscopic Ruler. The secondary outcomes included adverse events, operation time, the agreement of identifying large OV between the objective measurement of Endoscopic Ruler and the empirical reading of endoscopists, together with the interobserver agreement on diagnosing large OV by Endoscopic Ruler.
RESULTS
From November 2020 to April 2022, a total of 120 eligible patients with cirrhosis were recruited and all of them underwent EGD examinations with Endoscopic Ruler successfully without any adverse event. The median operation time of Endoscopic Ruler was 3.00 min [interquartile range (IQR): 3.00 min]. The kappa value between Endoscopic Ruler and the endoscopists while detecting large OV was 0.52, demonstrating a moderate agreement. The kappa value for diagnosing large OV using Endoscopic Ruler among the six independent observers was 0.77, demonstrating a substantial agreement.
CONCLUSION
The data demonstrates that Endoscopic Ruler is feasible and safe for measuring the size of varices in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Endoscopic Ruler is potential to promote the clinical practice of the two-grade classification system of OV.
Keywords: Oesophageal varices, Cirrhosis, Portal hypertension, Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, Endoscopic ruler
Core Tip: We invented Endoscopic Ruler, a new endoscopic device to measure the size of varices in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. This study demonstrates that Endoscopic Ruler is feasible and safe for measuring the size of varices in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Endoscopic Ruler is potential to promote the clinical practice of the two-grade classification system of oesophageal varices.
INTRODUCTION
Oesophageal varices (OV) is a common complication among patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension[1]. The prevalence of OV is approximately 30%-40% and 85% in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis respectively[2]. Variceal haemorrhage is a potential lethal complication of OV with a six-week morality of 15%-25%[3]. Given the mortality and morbidity associated with variceal haemorrhage, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is recommended as a golden standard for the early detection and screening of high-risk OV in the current guidelines[1-4]. EGD screening is generally performed by endoscopists with different levels of experience. In the procedure, operators assess the locations and sizes of OV according to subjectivity. Therefore, accuracy and consistency in the classification of OV performed by endoscopists will have direct effect on subsequent management.
The recent Baveno VII consensus emphasizes a 2-grade classification system of OV followed from the management perspective[1] in which the varix size is quantitatively classified into either small (< 5 mm) or large (≥ 5 mm). This system was initially created by the North Italian Endoscopy Club, which found the high-risk features of variceal bleeding and was endorsed in the Baveno I consensus meeting in 1992[5,6]. However, this quantitative system is not widely used in clinical practice probably due to the following limitations: A doubtful accuracy due to varix size assessment demanding high-level experience in specialized centers; a lack of data on the interobserver agreement and reproducibility. To overcome these limitations, we invented Endoscopic Ruler, a novel endoscopic device to measure the size of varices in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. The primary aim of this pilot study was to evaluate the feasibility and safety of Endoscopic Ruler. The secondary aim was to assess the agreement on detecting large OV between the objective measurement of Endoscopic Ruler and the empirical reading of endoscopists, as well as the interobserver reliability on identifying large OV using Endoscopic Ruler.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study patients and design
This study was a multicenter pilot study (CHESS2005, ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04639323), in which we prospectively and consecutively recruited cirrhotic patients from 11 hospitals in China from November 2020 to April 2022. Inclusion criteria were: (1) Confirmed cirrhosis based on clinical, biochemical and radiology findings; (2) A schedule to undergo EGD screening; (3) Age between 18 and 75 years; and (4) A written informed consent. Patients were excluded for the following: Active upper gastrointestinal bleeding and without OV diagnosed via EGD (including isolated gastric varices).
The study protocol conformed to the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of principle research institutions. A written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled participant. All authors had an access to the study data and reviewed the final manuscript.
Endoscopic Ruler device and procedure
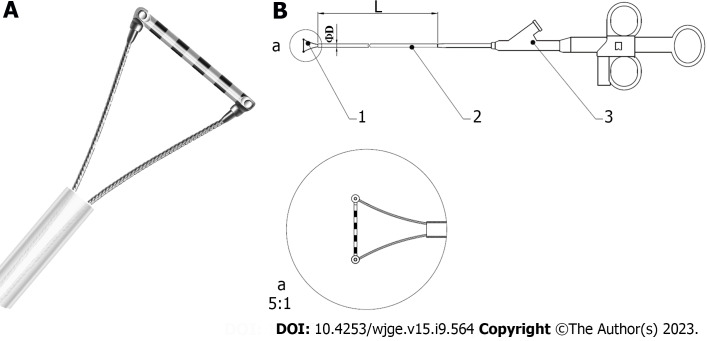
EGD examinations were performed using GIF-HQ290 (Olympus, Japan), GIF-H260Z (Olympus, Japan), or EG-601WR (FUJINON, Japan), with Endoscopic Ruler. Endoscopic Ruler consists of three parts: A tip, a sheath and an operating handle. The measurement range of Endoscopic Ruler is 1-10 mm. There are ten black alternating with white grids and the width of each grid is 1 mm (Figure 1). The procedures were carried out by one specific experienced endoscopist (have performed EGD examinations for more than 10 years and regularly performed endoscopic variceal ligation for at least 3 years) at individual centers. Ten to fifteen minutes before EGD, topical pharyngeal anaesthesia was applied to the posterior pharynx (dyclonine hydrochloride mucilage, 8-10 mL oral, 10 mL/dose; China).
Figure 1.
Diagram of Endoscopic Ruler. A: The tip of Endoscopic Ruler; B: The structure of Endoscopic Ruler. 1: Tip; 2: Sheath; 3: Operating handle.
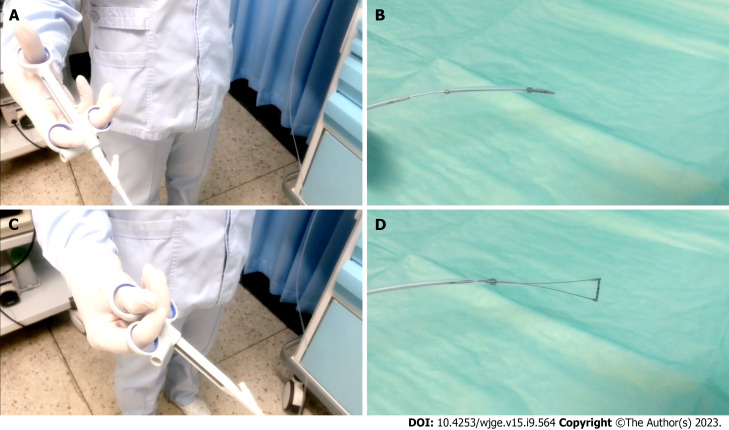
An empirical interpretation of OV performed by endoscopists was prior to the measurement of Endoscopic Ruler and the results would be recorded by a specific recorder at individual centers. Endoscopic Ruler was inserted through the biopsy channel of EGD and with its tip kept in the sheath until the sheath was sent into the region of interest. Endoscopists controlled the direction of the tip according to the angle of EGD and the location of lesions to make Endoscopic Ruler parallel with the target OV (the largest one), and then the varix size was measured. After measurement, Endoscopic Ruler could be drawn out slowly with the tip shut (Figure 2). All major findings with and without Endoscopic Ruler were recorded on digital pictures.
Figure 2.
Measurement procedure of Endoscopic Ruler. A and B: The operating handle of Endoscopic Ruler (A) when the tip is shut (B); C and D: The operating handle of Endoscopic Ruler (C) when the tip is open (D).
Study outcomes
The primary outcome was the successful measurement of varix size using Endoscopic Ruler: From Endoscopic Ruler being sent into the region of interest, the largest OV being measured, to Endoscopic Rule being drawn out. Secondary outcomes were the safety, operation time of Endoscopic Ruler, agreement on diagnosing large OV between the empirical reading of endoscopists and the objective measurement using Endoscopic Ruler as well as interobserver reliability on diagnosing large OV using Endoscopic Ruler.
Safety was assessed according to adverse events associated with the procedures. Operation time was calculated from the time when Endoscopic Ruler was inserted through the biopsy channel of EGD to that when it was drawn out, which was recorded by recorders. Large OV was defined as those with the largest varix size ≥ 5mm[1]. A total of 120 sets of pictures of the 120 patients enrolled with and without Endoscopic Ruler were digitally stored., ten of whom were randomly selected to explore the interobserver agreement. Six independent blinded observers excluding the endoscopists who recorded the procedures evaluated the selected records, including three experienced endoscopists who had performed EGDs more than ten years and regularly performed dedicated lists for variceal screening as well as endoscopic variceal ligation and three inexperienced endoscopists who performed EGD for five to ten years but hadn’t performed regular variceal screening or endoscopic variceal ligation.
Statistical analysis
Categorical data was expressed as numbers (percentages), and continuous variables were expressed as mean (standard deviation) or median (IQR). The agreement on diagnosing large OV between the empirical reading of endoscopists and the objective measurement using Endoscopic Ruler as well as the interobserver reliability on diagnosing large OV using Endoscopic Ruler were assessed according to the kappa value. Cohen's kappa was used in case of two observations (i.e. agreement between endoscopists and Endoscopic Ruler) and Fleiss kappa in case of more than two observations (i.e. interobserver reliability). Kappa values were considered as a slight agreement between 0 and 0.20, a fair agreement between 0.21 and 0.40, a moderate agreement between 0.41 and 0.60, a substantial agreement between 0.61 and 0.80 as well as an almost-perfect agreement between 0.81 and 1.00[7]. A P value of < 0.05 was considered significant. All statistical calculations were performed with R language (version 4.1.3, R Core Team, 2022).
RESULTS
Study population
From November 2020 to April 2022, 122 patients with cirrhosis from 11 hospitals in China were recruited, two of whom with isolated gastric varices were excluded. There were 120 patients involved in the final analysis (mean age of 54.02 years; male 59.17%). Of them, the main etiology of cirrhosis was Hepatitis B virus infection (n = 82, 68.33%). The number of patients with Child-Pugh A, B, and C were 43 (35.83%), 59 (49.17%) and 18 (15.00%) respectively. Baseline characteristics of the enrolled patients were summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients
| Parameters | Patients (n = 120) |
| Age (yr), mean (SD) | 54.02 (11.90) |
| Sex n (%) | |
| Male | 71 (59.16%) |
| Female | 49 (40.83%) |
| Complication, n (%) | |
| Ascites | 36 (30.00%) |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 5 (4.17%) |
| Etiology, n (%) | |
| Hepatitis B infection | 82 (68.33%) |
| Alcoholic liver disease | 11 (9.17%) |
| Autoimmune | 6 (5.00%) |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | 4 (3.33%) |
| Hepatitis C infection | 2 (1.67%) |
| Others | 15 (12.50%) |
| Child-Pugh Class, n (%) | |
| Class A | 43 (35.83%) |
| Class B | 59 (49.17%) |
| Class C | 18 (15.00%) |
| Laboratory tests, median (IQR) | |
| Platelet count (109/L) | 70.00 (59.75) |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 26.50 (21.10) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 32.00 (22.00) |
| Albumin (g/L) | 34.04 (9.45) |
| Total bilirubin (μmol/L) | 26.27 (23.90) |
| Prothrombin time (s) | 14.25 (3.40) |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 61.10 (21.35) |
SD: Standard deviation; IQR: Interquartile range.
Feasibility, safety and operation time of Endoscopic Ruler
All the 120 patients underwent EGD examinations with Endoscopic Ruler successfully, without any adverse event (n = 0, 0%) related to EGD or Endoscopic Ruler. The median operation time of Endoscopic Ruler was 3.00 min (IQR: 3.00 min) (Table 2).
Table 2.
The feasibility, safety, operation time of Endoscopic Ruler, and the agreement on diagnosing large oesophageal varices between endoscopists and Endoscopic Ruler
| Outcome | Patients (n = 120) |
| Primary outcome | |
| Technical success of Endoscopic Ruler, n (%) | 120 (100.00%) |
| Secondary outcomes | |
| Adverse events, n (%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Operation time (min), median (IQR) | 3.00 (3.00) |
| Kappa value | 0.52 (95%CI: 0.31- 0.73) |
95%CI: 95% confidence interval; OV: Oesophageal varices; IQR: Interquartile range.
Agreement on detecting large OV between Endoscopic Ruler and endoscopists
Endoscopic Ruler detected large OV in 101 (84.17%) patients and endoscopists identified 94 large OV among them. In seven cases, the diagnosis of large OV by Endoscopic Ruler was not found by endoscopists. Endoscopic Ruler detected small OV in 19 (15.83%) patients and endoscopists identified small OV in 11 of them. In eight cases, the diagnosis of small OV by Endoscopic Ruler was not confirmed by endoscopists (Figure 3). The agreement between Endoscopic Ruler and endoscopists on diagnosing large OV was moderate, with a kappa value of 0.52 [95% confidence interval (95%CI): 0.31-0.73].
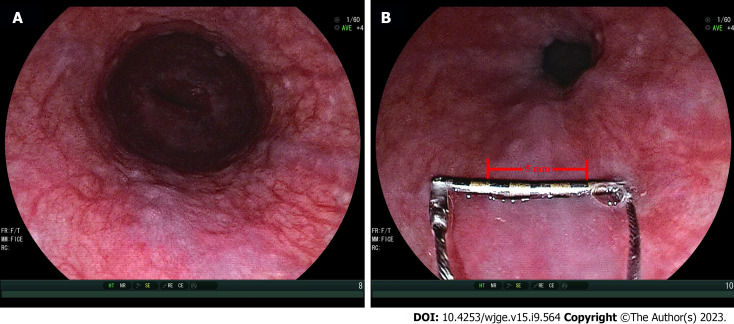
Figure 3.
Representative examples of measurement of varix size by Endoscopic Ruler. A: Small varices by endoscopists (varix size = 3-4 mm); B: Large varices by Endoscopic Ruler (varix size = 5 mm).
Interobserver reliability on detecting large OV
The agreement among the six independent observers on detecting large OV was substantial, with a kappa value of 0.77 (95%CI: 0.61-0.93). The kappa scores on detecting OV using Endoscopic Ruler were 0.71 (95%CI: 0.36-1.00) with a substantial agreement among the three experienced endoscopists, and the same [0.71 (95%CI: 0.36-1.00), P = 1.00] among the three inexperienced endoscopists, respectively (Table 3). The kappa score of the overall agreement on detecting OV through the empirical reading of endoscopists among six observers was 0.52 (95%CI: 0.36-0.68), demonstrating a moderate agreement, and it was significantly smaller than that using Endoscopic Ruler (P < 0.05). The kappa score on detecting OV by empirical reading of endoscopists was 0.57 (95%CI: 0.21-0.93) among the three experienced endoscopists, greater than that [0.40 (95%CI: 0.04-0.76)] among the three inexperienced ones (P < 0.05).
Table 3.
The interobserver reliability on detecting large oesophageal varices
| Assessment | Raters | Kappa value (95%CI) |
| Objective measurement of Endoscopic Ruler | ||
| All observes | 6 | 0.77 (0.61-0.93) |
| Experienced endoscopists | 3 | 0.71 (0.36-1.00) |
| Inexperienced endoscopists | 3 | 0.71 (0.36-1.00) |
| Empirical reading of endoscopists | ||
| All observes | 6 | 0.52 (0.36-0.68) |
| Experienced endoscopists | 3 | 0.57 (0.21-0.93) |
| Inexperienced endoscopists | 3 | 0.40 (0.04-0.76) |
95%CI: 95% confidence interval.
DISCUSSION
A careful endoscopic evaluation is one of the cornerstones for the full-course management of cirrhosis and portal hypertension as well as care of OV[8]. The application of the 2-grade classification system is recommended in the Baveno VII consensus, which has previously been validated as a predictor of variceal haemorrhage[1,2,5]. It is crucial to ensure that OV needing treatment is acted on if the present and accurate classification of small and large OV is the key. At present, the measurement of the varix size is mainly performed visually by endoscopists with subjectivity. Besides, biopsy forceps and other physical standards are applied in some trials but not clinical practice and the aforementioned methods are of a limited credibility and repeatability[9-11]. Shimoda et al[12] reported a virtual scale endoscope (VSE) to help estimate the size of colorectal lesions in real time during colonoscopy. However, its usefulness of VSE was evaluated in a virtual environment instead of actual clinical settings, nor was it applied to measure the size of varices[12]. Li et al[13] demonstrated a self-made virtual endoscopic measuring scale with a moderate accuracy but didn’t conduct a clinical evaluation on its efficacy.
To our knowledge, the present study is the first to demonstrate a special-designed endoscopic device, Endoscopic Ruler, for varix size measurement in clinical trials. Endoscopic Ruler succeeds in measuring the varix size of all enrolled patients without any adverse event associated to the procedures. Endoscopic Ruler is feasible and safe for measuring varix size, meanwhile, its median operation time is only 3.00 minutes, which avoids significant increase of procedural time and complication risk[14].
The agreement analysis demonstrated a moderate agreement between the objective measurement of Endoscopic Ruler and the empirical reading of endoscopists on the diagnosis of large OV. However, there were seven (5.83%) large OV according to Endoscopic Ruler that was misdiagnosed as small OV by endoscopists and eight (6.67%) small OV according to Endoscopic Ruler that was wrongly diagnosed as large OV by endoscopists. That is, without any consideration for other high-risk factors of OV (red signs or Child-Pugh C), there might be 5.83% of patients misdiagnosed with non-high-risk OV, who would miss the primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding; there might be 6.67% of patients wrongly diagnosed with high-risk OV, who might receive an overtreatment. Moreover, the overall kappa value on detecting OV among the six observers using Endoscopic Ruler was greater than that through the empirical reading of endoscopists (0.77 vs. 0.52, P < 0.05). The subjective nature of differentiating small OV from large OV remains a challenge for the 2-grade classification varix system.
The interobserver reliability results suggested that Endoscopic Ruler decreased such discrepancies. Besides, our study revealed that the kappa values on detecting large OV using Endoscopic Ruler were similar with that performed by experienced endoscopists and inexperienced endoscopists (0.71 vs. 0.71, P = 1.00), while the kappa value on detecting OV through the empirical reading of endoscopists among experienced endoscopists was greater than that among inexperienced endoscopists (0.57 vs. 0.40, P < 0.05). That is, with the application of Endoscopic Ruler, the value of an experienced operator was weakened, and it might improve the management of patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension in non-tertiary hospitals without experienced endoscopists. Overall, Endoscopic Ruler might help to optimize the accuracy of the 2-grade classification system for OV followed from a management perspective.
Recently, non-invasive tools, such as Baveno VI criteria[1,15], the liver stiffness- spleen diameter to platelet ratio score[16], capsule endoscopy[17], and other emerging methods have been identified as complementary parameters of EGD to detect and screen high-risk OV[18-20]. However, the use of EGD interpretation by endoscopists as reference standard might bring bias due to the subjectivity and a lack of substantial agreement. Endoscopic Ruler might be used to normalize and promote the development of novel non-invasive methods for OV screening.
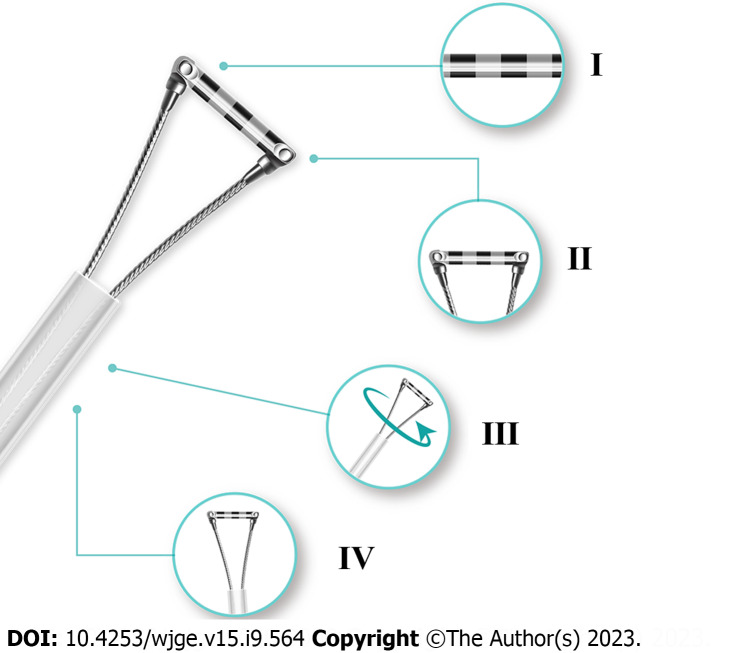
There were still some limitations. The sample size was limited. A well-designed real-world study of Endoscopic Ruler augmenting the sample size and introducing the follow-up and clinical data would be needed for its further popularization in clinical practice. In addition, although adverse events occurred in no procedures of the present study, Endoscopic Ruler had the potential risk to injure patients, such as mucosal damage during operation. Therefore, we improved Endoscopic Ruler according to endoscopists’ experience as follows: (1) Enhancing the contrast of the scale at the tip for easy reading; (2) Shortening the scale range and shrinking the tip for retaining the function of detecting large OV as well as reducing the risk of adverse damage; (3) Adding a feature of synchronous rotation for more convenient practice; and (4) Optimizing the design of more smooth edge for reducing the risk of damage. Figure 4 shows the improved version of the structure.
Figure 4.
Diagram of improved Endoscopic Ruler. I: Clear scale; II: Shorter tip; III: Synchronous rotation; IV: More smooth edge.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, our study demonstrates that Endoscopic Ruler is feasible and safe for measuring the size of varices in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Endoscopic Ruler is potential to promote the clinical practice of the two-grade classification system of OV.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) screening is usually performed by endoscopists with different levels of experience, and the they assess the locations and size of oesophageal varices (OV) according to the subjectivity. The recent Baveno VII consensus emphasized 2-grade classification system of Ovs followed from a management perspective, and the 2-grade classification system quantitatively classifies varix size into either small (< 5 mm) or large (≥ 5 mm).
Research motivation
The quantitative system is not widely used in clinical practice probably due to following limitations: Doubtful accuracy due to varix size assessment demanding high level of experience in specialized centers; lack of data on the interobserver agreement and reproducibility. We invented Endoscopic Ruler, a new endoscopic device to measure the size of varices in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
Research objectives
This study aims to assess the feasibility and safety of Endoscopic Ruler, and evaluate the agreement on identifying large OV between Endoscopic Ruler and the endoscopists, as well as the interobserver agreement on diagnosing large OV using Endoscopic Ruler.
Research methods
We prospectively and consecutively enrolled patients with cirrhosis from 11 hospitals, all of whom got EGD with Endoscopic Ruler. The primary study outcome was a successful measurement of the size of varices using Endoscopic Ruler. The secondary outcomes included adverse events, operation time, the agreement of identifying large OV between the objective measurement of Endoscopic Ruler and the empirical reading of endoscopists, together with the interobserver agreement on diagnosing large OV by Endoscopic Ruler.
Research results
From November 2020 to April 2022, a total of 120 eligible patients with cirrhosis were recruited and all of them underwent EGD examinations with Endoscopic Ruler successfully without any adverse event. The median operation time of Endoscopic Ruler was 3.00 min (IQR: 3.00 min). The kappa value between Endoscopic Ruler and the endoscopists while detecting large OV was 0.52, demonstrating a moderate agreement. The kappa value for diagnosing large OV using Endoscopic Ruler among the six independent observers was 0.77, demonstrating a substantial agreement.
Research conclusions
Endoscopic Ruler is feasible and safe for measuring the size of varices in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
Research perspectives
Endoscopic Ruler weakened the value of an experienced operator and it might improve the management of patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension in the non-tertiary hospitals without experienced endoscopist. Endoscopic Ruler might help to optimize the accuracy of the 2-grade classification system of OV followed from a management perspective. Endoscopic Ruler might normalize and promote development of novel non-invasive methods for OV screening.
Footnotes
Institutional review board statement: The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of principle research institutions.
Clinical trial registration statement: This study is registered at https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/. The registration identification number is NCT04639323.
Informed consent statement: All study participants or their legal guardian provided informed written consent about personal and medical data collection prior to study enrolment.
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declared no conflicts of interest related to this study.
CONSORT 2010 statement: The authors have read the CONSORT 2010 statement, and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the CONSORT 2010 statement.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Peer-review started: August 3, 2023
First decision: August 15, 2023
Article in press: September 1, 2023
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kumar R, India; Soldera J, Brazil S-Editor: Lin C L-Editor: A P-Editor: Cai YX
Contributor Information
Yi-Fei Huang, Institute of Portal Hypertension, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China.
Sheng-Juan Hu, Department of Gastroenterology, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Ningxia Medical University Affiliated People's Hospital of Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Yang Bu, Department of Gastroenterology, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Ningxia Medical University Affiliated People's Hospital of Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Yi-Ling Li, Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China.
Yan-Hong Deng, Department of Gastroenterology, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Ningxia Medical University Affiliated People's Hospital of Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Jian-Ping Hu, Department of Gastroenterology, Yinchuan First People's Hospital, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Shao-Qi Yang, Department of Gastroenterology, Ningxia Medical University General Hospital, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Qian Shen, Department of Gastroenterology, Yinchuan Second People's Hospital, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Mark McAlindon, Academic Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, AL 35660, Sheffield, United Kingdom.
Rui-Chun Shi, Department of Gastroenterology, Wuzhong People's Hospital, Wuzhong 751100, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Xiao-Qin Li, Department of Gastroenterology, The Fifth People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Shizuishan 753000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Tie-Ying Song, Department of Second Gastroenterology, The Sixth People’s Hospital of Shenyang, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China.
Hai-Long Qi, Department of Gastroenterology, Shizuishan Second People's Hospital, Shizuishan 753000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Tai-Wei Jiao, Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China.
Meng-Yuan Liu, Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China.
Fang He, Department of Gastroenterology, Ningxia Medical University General Hospital, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Jun Zhu, Department of Gastroenterology, The Fifth People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Shizuishan 753000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Bin Ma, Department of Gastroenterology, Yinchuan First People's Hospital, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Xiao-Bin Yu, Department of Gastroenterology, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Ningxia Medical University Affiliated People's Hospital of Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Jian-Yang Guo, Department of Gastroenterology, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Ningxia Medical University Affiliated People's Hospital of Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Yue-Hua Yu, Department of Gastroenterology, Yinchuan First People's Hospital, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Hai-Jiang Yong, Department of Gastroenterology, Wuzhong People's Hospital, Wuzhong 751100, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Wen-Tun Yao, Department of Gastroenterology, Yinchuan First People's Hospital, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Ting Ye, Department of Gastroenterology, Yinchuan First People's Hospital, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Hua Wang, Department of Gastroenterology, The Fifth People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Shizuishan 753000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Wen-Fu Dong, Department of Gastroenterology, The Fifth People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Shizuishan 753000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Jian-Guo Liu, Department of Gastroenterology, Zhongwei People's Hospital, Zhongwei 755000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Qiang Wei, Department of Gastroenterology, Zhongwei People's Hospital, Zhongwei 755000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Jing Tian, Department of Gastroenterology, Zhongwei People's Hospital, Zhongwei 755000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China.
Xiao-Guo Li, Institute of Portal Hypertension, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China.
Xavier Dray, Department of Hepato-Gastroenterology, ETIS, ENSEA, CNRS, Sorbonne Université & APHP, Hôpital Saint Antoine, Université Paris-Seine, Université de Cergy-Pontoise, Paris 75012, Sélectionner, France.
Xiao-Long Qi, Center of Portal Hypertension, Department of Radiology, Zhongda Hospital, Medical School, Southeast University, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China. qixiaolong@vip.163.com.
Data sharing statement
Deidentified individual participant data will not be shared. Researchers can apply for data by submitting a proposal to the corresponding author.
References
- 1.de Franchis R, Bosch J, Garcia-Tsao G, Reiberger T, Ripoll C Baveno VII Faculty. Baveno VII - Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2022;76:959–974. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Bosch J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology. 2017;65:310–335. doi: 10.1002/hep.28906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018;69:406–460. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Qi X, Berzigotti A, Cardenas A, Sarin SK. Emerging non-invasive approaches for diagnosis and monitoring of portal hypertension. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:708–719. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.North Italian Endoscopic Club for the Study and Treatment of Esophageal Varices. Prediction of the first variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis of the liver and esophageal varices. A prospective multicenter study. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:983–989. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810133191505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.de Franchis R, Pascal JP, Ancona E, Burroughs AK, Henderson M, Fleig W, Groszmann R, Bosch J, Sauerbruch T, Soederlund C. Definitions, methodology and therapeutic strategies in portal hypertension. A Consensus Development Workshop, Baveno, Lake Maggiore, Italy, April 5 and 6, 1990. J Hepatol. 1992;15:256–261. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90044-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Viera AJ, Garrett JM. Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Fam Med. 2005;37:360–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Qi X, Huang Y, Pavlides M, Rockey DC. A community of portal hypertension. Hepatol Int. 2021;15:575–578. doi: 10.1007/s12072-021-10192-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Margulies C, Krevsky B, Catalano MF. How accurate are endoscopic estimates of size? Gastrointest Endosc. 1994;40:174–177. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(94)70162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McMahon R. Error in estimates of size. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994;40:779–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fateen W, Ragunath K, White J, Khanna A, Coletta M, Samuel S, Ortiz J, James M, Wilkes E, Aithal GP, Guha IN, Sami SS. Validation of the AASLD recommendations for classification of oesophageal varices in clinical practice. Liver Int. 2020;40:905–912. doi: 10.1111/liv.14310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shimoda R, Akutagawa T, Tomonaga M, Murano T, Shinmura K, Yoshioka M, Teramura Y, Kiyomi F, Ikematsu H. Estimating colorectal polyp size with a virtual scale endoscope and visual estimation during colonoscopy: Prospective, preliminary comparison of accuracy. Dig Endosc. 2022;34:1471–1477. doi: 10.1111/den.14351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li ZQ, Linghu EQ, Hu M, Wang XD, Wang HB, Meng JY, Du H. Endoscopic measurement of variceal diameter. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:2140–2146. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i7.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sun JH, Zhao H, Zhang H, Li L, Örmeci N, Yu ZN, Li X, Li S, Yang X, Wei H, Zhu X, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Zhao Z, Mao J, Wu Q, Sun X, Xiang H, Jia K, Yang C, Wu W, Lin X, Yao H, Zuo C, Wang J, Zhang B, Zhang C, Wu X, Wang G, Yao S, Wang R, Zhou L, Huan H, Tu Q, Pu X, Zhang F, Yin Q, Zhang L, Guo Y, Kotani K, Uchida-Kobayashi S, Kawada N, Zhu H, Wang W, Zhang G, Yu L, Cui X, Zhu Q, Hu X, Ximenes RO, de Araújo AG, Gardenghi G, Zheng Y, Wu Z, Huang M, Chen X, Wu J, Xie F, Bo Y, Hu S, Ma L, Qi X. Tolerance and acceptance of hepatic venous pressure gradient measurement in cirrhosis (CHESS1904): An international multicenter study. Port Hypertens Cirrhos. 2022;1:7–14. [Google Scholar]
- 15.de Franchis R Baveno VI Faculty. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2015;63:743–752. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kim BK, Han KH, Park JY, Ahn SH, Kim JK, Paik YH, Lee KS, Chon CY, Kim DY. A liver stiffness measurement-based, noninvasive prediction model for high-risk esophageal varices in B-viral liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:1382–1390. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang S, Huang Y, Hu W, Mao H, McAlindon ME, Liu Y, Yang L, Zhang C, Xu M, He C, Dang T, Wu B, Ji D, Zhang L, Mao X, Liu C, Xu D, Li Y, Li G, Han J, Lv F, Liang X, Jin S, Zhang S, Tai FWD, Xu Q, Yang C, Wang G, Wang L, Li B, Yang H, Xie P, Deng L, Ren L, Chang Z, Wang X, Wang S, Gao X, Li J, Zhu L, Wang F, Zhang G, Jiang X, Pan J, Meng W, Li X, Hou J, Dray X, Liao Z, Qi X. Detachable string magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy for detecting high-risk varices in compensated advanced chronic liver disease (CHESS1801): A prospective multicenter study. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2021;6:100072. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2020.100072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huang Y, Huang F, Yang L, Hu W, Liu Y, Lin Z, Meng X, Zeng M, He C, Xu Q, Xie G, Liu C, Liang M, Li X, Kang N, Xu D, Wang J, Zhang L, Mao X, Yang C, Xu M, Qi X, Mao H. Development and validation of a radiomics signature as a non-invasive complementary predictor of gastroesophageal varices and high-risk varices in compensated advanced chronic liver disease: A multicenter study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36:1562–1570. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Li X, Kang N, Qi X, Huang Y. Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. J Med Ultrason (2001) 2022;49:371–379. doi: 10.1007/s10396-021-01153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Miao L, Targher G, Byrne CD, Valenti L, Qi X, Zheng MH. Portal hypertension in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Challenges and perspectives. Port Hypertens Cirrhos . 2022;1:57–65. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Deidentified individual participant data will not be shared. Researchers can apply for data by submitting a proposal to the corresponding author.