Abstract
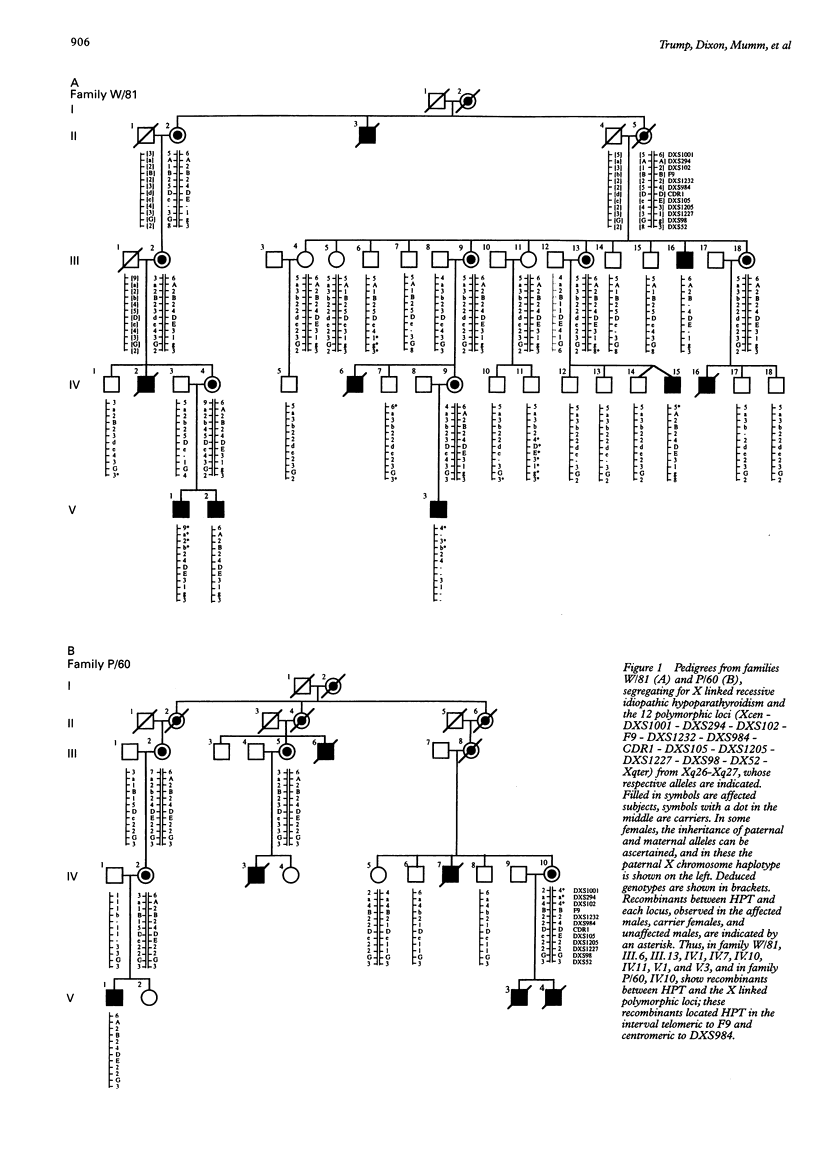
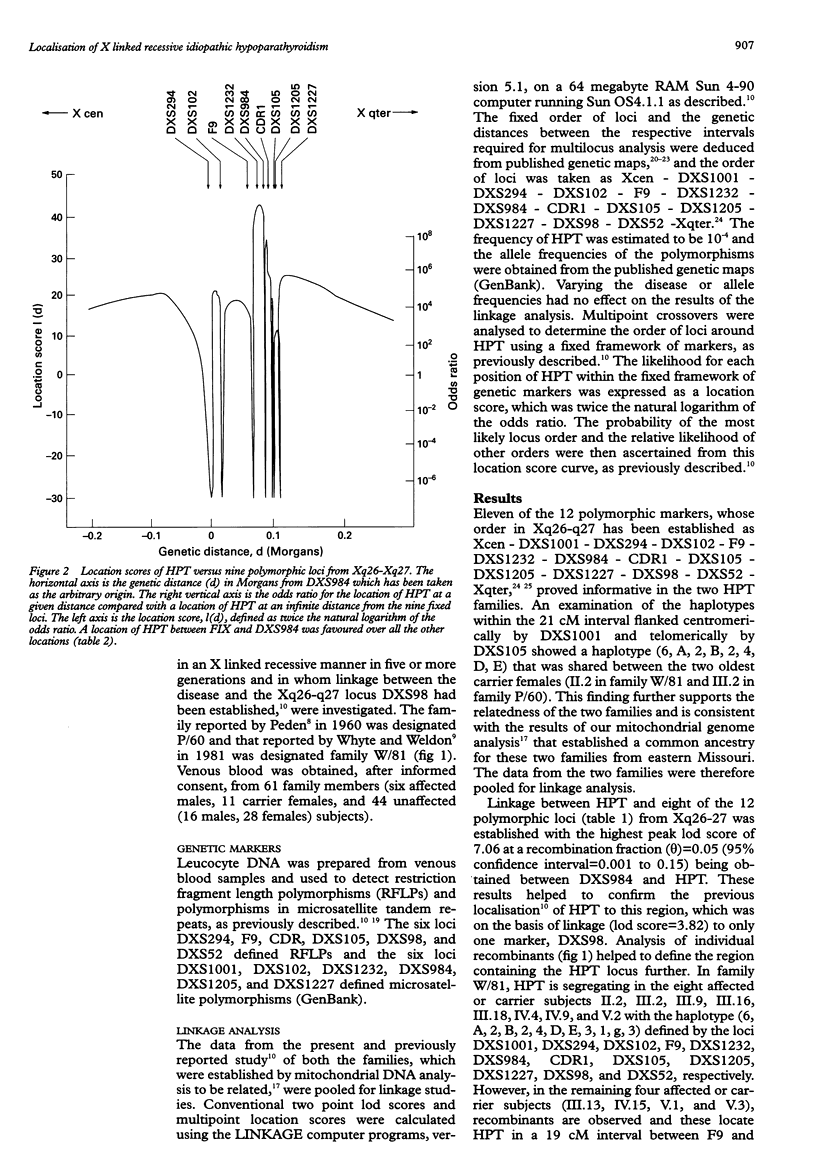
X linked recessive idiopathic hypoparathyroidism (HPT) has been observed in two kindreds from Missouri, USA. Affected subjects, who are males, suffer from infantile onset of epilepsy and hypocalcaemia, which appears to be the result of an isolated congenital defect of parathyroid gland development; females are not affected and are normocalcaemic. The gene causing HPT has been previously mapped to a 7 cM interval, flanked centromerically by F9 and telomerically by DXS98, in Xq26-q27, and an analysis of mitochondrial DNA has established a common ancestry for these two kindreds. In order to define further the map location of HPT and thereby facilitate its isolation, we have undertaken linkage studies using polymorphic loci whose order has been established as Xcen - DXS1001 - DXS294 - DXS102 - F9 - DXS1232 - DXS984 - CDR1 - DXS105 - DXS1205 - DXS1227 - DXS98 - DXS52 - Xqter, within this region. Our results established linkage (lod score > 3) between HPT and eight of these 12 loci and indicated that the most likely location of HPT was within a 1.5 Mb interval flanked centromerically by F9 and telomerically by DXS984. Thus, the results of this study have helped to refine the map location of HPT, and this will facilitate the identification of this putative developmental gene and its role in the embryological formation of the parathyroids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn T. G., Antonarakis S. E., Kronenberg H. M., Igarashi T., Levine M. A. Familial isolated hypoparathyroidism: a molecular genetic analysis of 8 families with 23 affected persons. Medicine (Baltimore) 1986 Mar;65(2):73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold A., Horst S. A., Gardella T. J., Baba H., Levine M. A., Kronenberg H. M. Mutation of the signal peptide-encoding region of the preproparathyroid hormone gene in familial isolated hypoparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1084–1087. doi: 10.1172/JCI114811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J., Winer K. K., Yanovski J. A., Cunningham A. W., Laue L., Zimmerman D., Cutler G. B., Jr Mutations in the Ca(2+)-sensing receptor gene cause autosomal dominant and sporadic hypoparathyroidism. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 May;5(5):601–606. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.5.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr D. G., Prader A., Esper U., Rampini S., Marrian V. J., Forfar J. O. Chronic hypoparathyroidism in two generations. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1971 Dec;26(5):507–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronsky D., Kiamko R. T., Waldstein S. S. Familial idiopathic hypoparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jan;28(1):61–65. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S. Positional cloning: let's not call it reverse anymore. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):3–6. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiwara K., Berson E. L., Dryja T. P. Digenic retinitis pigmentosa due to mutations at the unlinked peripherin/RDS and ROM1 loci. Science. 1994 Jun 10;264(5165):1604–1608. doi: 10.1126/science.8202715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagerström-Fermér M., Sundvall M., Johnsen E., Warne G. L., Forrest S. M., Zajac J. D., Rickards A., Ravine D., Landegren U., Pettersson U. X-linked recessive panhypopituitarism associated with a regional duplication in Xq25-q26. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Apr;60(4):910–916. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren H., Sundvall M., Dahl N., Gustavson K. H., Annerén G., Wadelius C., Steén-Bondeson M. L., Pettersson U. Linkage mapping of a severe X-linked mental retardation syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1046–1052. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer H., Breyel E., Bostock C., Schmidtke J. Assignment of the human parathyroid hormone gene to chromosome 11. Hum Genet. 1983;64(3):283–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00279412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumm S., Whyte M. P., Thakker R. V., Buetow K. H., Schlessinger D. mtDNA analysis shows common ancestry in two kindreds with X-linked recessive hypoparathyroidism and reveals a heteroplasmic silent mutation. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Jan;60(1):153–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumm S., Zucchi I., Pilia G. SOX3 gene maps near DXS984 in Xq27.1, within candidate regions for several X-linked disorders. Am J Med Genet. 1997 Oct 31;72(3):376–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang J. T., Lloyd S. E., Wooding C., Farren B., Pottinger B., Harding B., Leigh S. E., Pook M. A., Benham F. J., Gillett G. T. Genetic mapping studies of 40 loci and 23 cosmids in chromosome 11p13-11q13, and exclusion of mu-calpain as the multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 gene. Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;97(6):732–741. doi: 10.1007/BF02346182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson D. B., Thakker R. V. A donor splice site mutation in the parathyroid hormone gene is associated with autosomal recessive hypoparathyroidism. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):149–152. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce S. H., Williamson C., Kifor O., Bai M., Coulthard M. G., Davies M., Lewis-Barned N., McCredie D., Powell H., Kendall-Taylor P. A familial syndrome of hypocalcemia with hypercalciuria due to mutations in the calcium-sensing receptor. N Engl J Med. 1996 Oct 10;335(15):1115–1122. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199610103351505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilia G., MacMillan S., Nagaraja R., Mumm S., Weissenbach J., Schlessinger D. YAC/STS map of 9 Mb of Xq26 at 100-kb resolution, localizing 6 ESTs, 6 genes, and 32 genetic markers. Genomics. 1996 May 15;34(1):55–62. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak M. R., Brown E. M., Chou Y. H., Hebert S. C., Marx S. J., Steinmann B., Levi T., Seidman C. E., Seidman J. G. Mutations in the human Ca(2+)-sensing receptor gene cause familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia and neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1297–1303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90617-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A., Eva A. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human dbl proto-oncogene: evidence that its overexpression is sufficient to transform NIH/3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2465–2473. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey M., Graba Y., Scott M. P. Hox genes in evolution: protein surfaces and paralog groups. Trends Genet. 1997 Apr;13(4):145–151. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(97)01096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović M., Lovell-Badge R., Collignon J., Goodfellow P. N. SOX3 is an X-linked gene related to SRY. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2013–2018. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Oberlé I., Nancarrow J., Mulley J. C., Hyland V. J., Wilson P. J., McCure J., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J., Mandel J. L. Genetic mapping of new RFLPs at Xq27-q28. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Davies K. E., Whyte M. P., Wooding C., O'Riordan J. L. Mapping the gene causing X-linked recessive idiopathic hypoparathyroidism to Xq26-Xq27 by linkage studies. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):40–45. doi: 10.1172/JCI114712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. P., Kim G. S., Kosanovich M. Absence of parathyroid tissue in sex-linked recessive hypoparathyroidism. J Pediatr. 1986 Nov;109(5):915–915. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80741-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. P., Weldon V. V. Idiopathic hypoparathyroidism presenting with seizures during infancy: X-linked recessive inheritance in a large Missouri kindred. J Pediatr. 1981 Oct;99(4):608–611. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Cremers F., Mandel J. L., Monaco A. P., Nelson D. L., Schlessinger D. Report and abstracts of the Fifth International Workshop on Human X Chromosome Mapping 1994. Heidelberg, Germany, April 24-27, 1994. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;67(4):295–358. doi: 10.1159/000133870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucchi I., Mumm S., Pilia G., Macmillan S., Reinbold R., Susani L., Weissenbach J., Schlessinger D. YAC/STS map across 12 Mb of Xq27 at 25-kb resolution, merging Xq26-qter. Genomics. 1996 May 15;34(1):42–54. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


