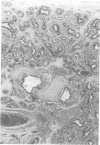
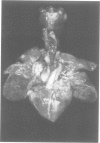
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boylan P., Howe A., Gearty J., O'Brien N. G. Familial pulmonary hypoplasia. Ir J Med Sci. 1977 Jun;146(6):179–180. doi: 10.1007/BF03030956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. M. Congenital acinar aplasia: an extreme form of pulmonary maldevelopment. Pathology. 1991 Jan;23(1):69–71. doi: 10.3109/00313029109061444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey B., Fleischhauer A., Gersbach M. Familial isolated pulmonary hypoplasia: a case report, suggesting autosomal recessive inheritance. Eur J Pediatr. 1994 Jun;153(6):460–463. doi: 10.1007/BF01983413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel B. C. Familial primary pulmonary hypoplasia. Eur J Pediatr. 1995 Apr;154(4):336–336. doi: 10.1007/BF01957378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Hara Y., Pineau T., Fernandez-Salguero P., Fox C. H., Ward J. M., Gonzalez F. J. The T/ebp null mouse: thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein is essential for the organogenesis of the thyroid, lung, ventral forebrain, and pituitary. Genes Dev. 1996 Jan 1;10(1):60–69. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer R., Kaufmann H. J. Primary (isolated) bilateral pulmonary hypoplasia: a comparative study of radiologic findings and autopsy results. Pediatr Radiol. 1986;16(3):175–179. doi: 10.1007/BF02456280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn G., Hutchins G. M. Primary pulmonary hypoplasia: report of a case with polyhydramnios. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Nov;131(11):1220–1223. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120240038008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutledge J. C., Jensen P. Acinar dysplasia: a new form of pulmonary maldevelopment. Hum Pathol. 1986 Dec;17(12):1290–1293. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80576-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spranger J., Benirschke K., Hall J. G., Lenz W., Lowry R. B., Opitz J. M., Pinsky L., Schwarzacher H. G., Smith D. W. Errors of morphogenesis: concepts and terms. Recommendations of an international working group. J Pediatr. 1982 Jan;100(1):160–165. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swischuk L. E., Richardson C. J., Nichols M. M., Ingman M. J. Primary pulmonary hypoplasia in the neonate. J Pediatr. 1979 Oct;95(4):573–577. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K. Mammalian lung development: interactions in formation and morphogenesis of tracheal buds. J Exp Zool. 1970 Dec;175(4):455–466. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401750405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigglesworth J. S. Pathology of the lung in the fetus and neonate, with particular reference to problems of growth and maturation. Histopathology. 1987 Jul;11(7):671–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb02682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]