Abstract
A whole X chromosome study of families in which Rett syndrome had been diagnosed in more than one member indicated that the region between Xq27 and Xqter was the most likely region to harbour a gene which may be involved in the aetiology of the disease. Further, more detailed studies of Xq28 detected weak linkage and a higher than expected sharing of maternally inherited alleles. It is suggested that there may be more than one gene involved in the aetiology of this syndrome, particularly as the very rare families in which more than one girl is affected often show variable clinical symptoms.
Full text
PDF



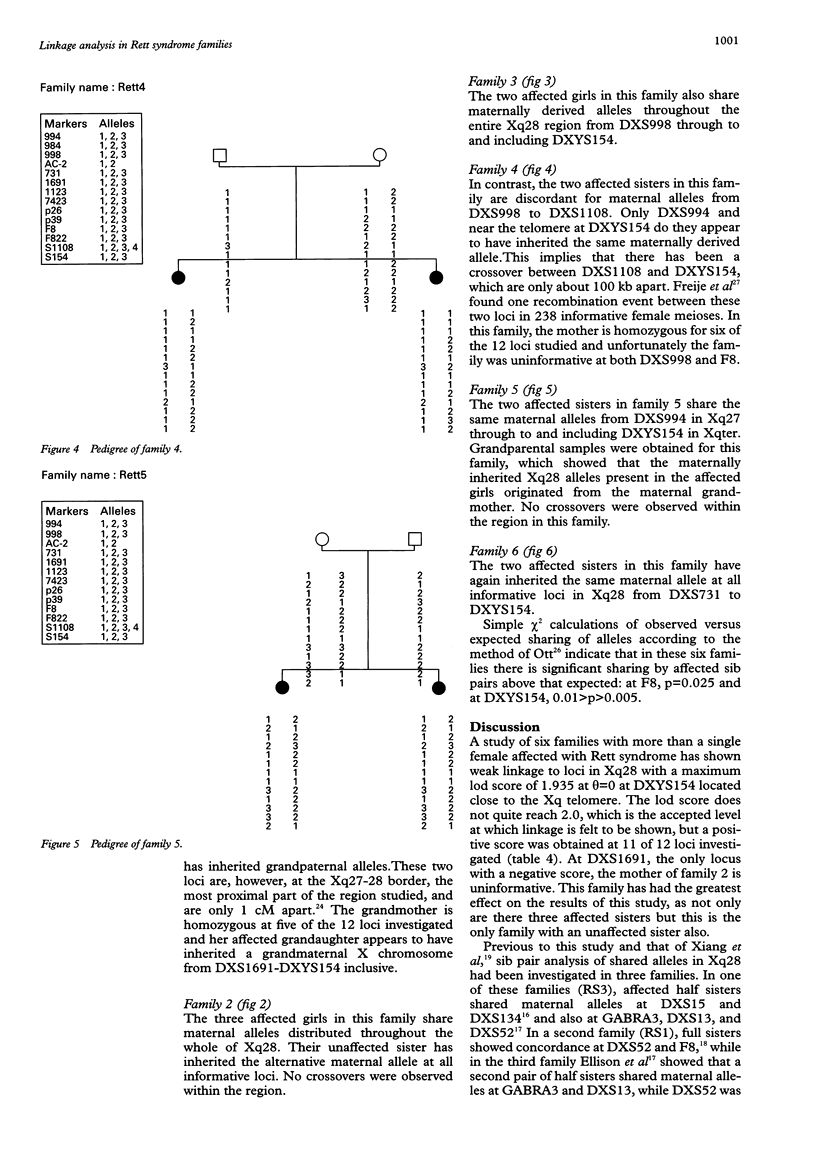


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akesson H. O., Hagberg B., Wahlström J. Rett syndrome, classical and atypical: genealogical support for common origin. J Med Genet. 1996 Sep;33(9):764–766. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.9.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anvret M., Wahlström J., Skogsberg P., Hagberg B. Segregation analysis of the X-chromosome in a family with Rett syndrome in two generations. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;37(1):31–35. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archidiacono N., Lerone M., Rocchi M., Anvret M., Ozcelik T., Francke U., Romeo G. Rett syndrome: exclusion mapping following the hypothesis of germinal mosaicism for new X-linked mutations. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):604–606. doi: 10.1007/BF00201549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Freimer N. F., Risch N., Lerer B., Alexander J. R., Straub R. E., Asokan S., Das K., Peterson A., Amos J. Diminished support for linkage between manic depressive illness and X-chromosome markers in three Israeli pedigrees. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):49–55. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus P., Abbadi N., Perrier M. C., Chéry M., Gilgenkrantz S. X chromosome inactivation in 30 girls with Rett syndrome: analysis using the probe. Hum Genet. 1996 Feb;97(2):247–250. doi: 10.1007/BF02265275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. Rett syndrome. J Med Genet. 1996 Aug;33(8):693–699. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.8.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis A. R., Headland S., Lindsay S., Thomas N. S., Boye E., Kamakari S., Roustan P., Anvret M., Wahlstrom J., McCarthy G. X chromosome linkage studies in familial Rett syndrome. Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;90(5):551–555. doi: 10.1007/BF00217457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly A., Kozman H., Gedeon A. K., Webb S., Lynch M., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I., Mulley J. C. A linkage map of microsatellite markers on the human X chromosome. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):363–370. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison K. A., Fill C. P., Terwilliger J., DeGennaro L. J., Martin-Gallardo A., Anvret M., Percy A. K., Ott J., Zoghbi H. Examination of X chromosome markers in Rett syndrome: exclusion mapping with a novel variation on multilocus linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Feb;50(2):278–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison K. A., Roth E. J., McCabe E. R., Chinault A. C., Zoghbi H. Y. Isolation of a yeast artificial chromosome contig spanning the X chromosomal translocation breakpoint in a patient with Rett syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Nov 15;47(7):1124–1134. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engerström I. W., Forslund M. Mother and daughter with Rett syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1992 Nov;34(11):1022–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain P. R., Kort E. N., Chance P. F., Nguyen K., Redd D. F., Econs M. J., Barker D. F. A 2D crossover-based map of the human X chromosome as a model for map integration. Nat Genet. 1995 Mar;9(3):261–266. doi: 10.1038/ng0395-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freije D., Helms C., Watson M. S., Donis-Keller H. Identification of a second pseudoautosomal region near the Xq and Yq telomeres. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1784–1787. doi: 10.1126/science.1465614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson T. J., Engelstein M., Lee M. K., Ho E. C., Rubenfield M. J., Adams C. P., Housman D. E., Dracopoli N. C. Isolation and chromosomal assignment of 100 highly informative human simple sequence repeat polymorphisms. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):622–629. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90133-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Journel H., Melki J., Turleau C., Munnich A., de Grouchy J. Rett phenotype with X/autosome translocation: possible mapping to the short arm of chromosome X. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jan;35(1):142–147. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Jouet M., Donnai D. X linked hydrocephalus and MASA syndrome. J Med Genet. 1996 Jan;33(1):59–65. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr A. M., Stephenson J. B. Rett's syndrome in the west of Scotland. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Aug 31;291(6495):579–582. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6495.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalloz M. R., McVey J. H., Pattinson J. K., Tuddenham E. G. Haemophilia A diagnosis by analysis of a hypervariable dinucleotide repeat within the factor VIII gene. Lancet. 1991 Jul 27;338(8761):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90348-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte J., Hu L. J., Kretz C., Mandel J. L., Kioschis P., Coy J. F., Klauck S. M., Poustka A., Dahl N. A gene mutated in X-linked myotubular myopathy defines a new putative tyrosine phosphatase family conserved in yeast. Nat Genet. 1996 Jun;13(2):175–182. doi: 10.1038/ng0696-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Splitt M., Edney S., Berney T. P., Knight S. J., Davies K. E., O'Brien O., Gale M., Burn J. PPM-X: a new X-linked mental retardation syndrome with psychosis, pyramidal signs, and macroorchidism maps to Xq28. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1120–1126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Dunn M. A., Thomas G., Schmeckpeper B. J., Naidu S. Studies of X inactivation and isodisomy in twins provide further evidence that the X chromosome is not involved in Rett syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):647–653. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Holman K., Kozman H., Kremer E., Lynch M., Pritchard M., Yu S., Mulley J., Sutherland G. R. Fragile X syndrome: genetic localisation by linkage mapping of two microsatellite repeats FRAXAC1 and FRAXAC2 which immediately flank the fragile site. J Med Genet. 1991 Dec;28(12):818–823. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.12.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger D., Little R. D., Freije D., Abidi F., Zucchi I., Porta G., Pilia G., Nagaraja R., Johnson S. K., Yoon J. Y. Yeast artificial chromosome-based genome mapping: some lessons from Xq24-q28. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90001-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H. High male:female ratio of germ-line mutations: an alternative explanation for postulated gestational lethality in males in X-linked dominant disorders. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1364–1368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Collins A., Lawrence S., Keats B. J., Morton N. E. Integration of gene maps: chromosome X. Genomics. 1994 Aug;22(3):590–604. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T., Watkiss E. A comparative study of X-inactivation in Rett syndrome probands and control subjects. Clin Genet. 1996 Apr;49(4):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1996.tb03285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehnert M., Reiner O., Caskey C. T. Four STR polymorphisms map to a 500 kb region between DXS15 and DXS134. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Sep;2(9):1503–1503. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.9.1503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Cremers F., Mandel J. L., Monaco A. P., Nelson D. L., Schlessinger D. Report and abstracts of the Fifth International Workshop on Human X Chromosome Mapping 1994. Heidelberg, Germany, April 24-27, 1994. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;67(4):295–358. doi: 10.1159/000133870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor S., Taylor S. A., Lillicrap D. Multiplex analysis of two intragenic microsatellite repeat polymorphisms in the genetic diagnosis of haemophilia A. Br J Haematol. 1994 Apr;86(4):810–815. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1994.tb04834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang F., Zhang Z., Clarke A., Joseluiz P., Sakkubai N., Sarojini B., Delozier-Blanchet C. D., Hansmann I., Edström L., Anvret M. Chromosome mapping of Rett syndrome: a likely candidate region on the telomere of Xq. J Med Genet. 1998 Apr;35(4):297–300. doi: 10.1136/jmg.35.4.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi H. Y., Ledbetter D. H., Schultz R., Percy A. K., Glaze D. G. A de novo X;3 translocation in Rett syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jan;35(1):148–151. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




