Abstract
A family is described with six members affected by a syndrome of epilepsy, dementia, and amelogenesis imperfecta (Kohlschütter's syndrome). An autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance is established for this disorder.
Full text
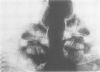
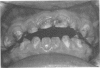
PDF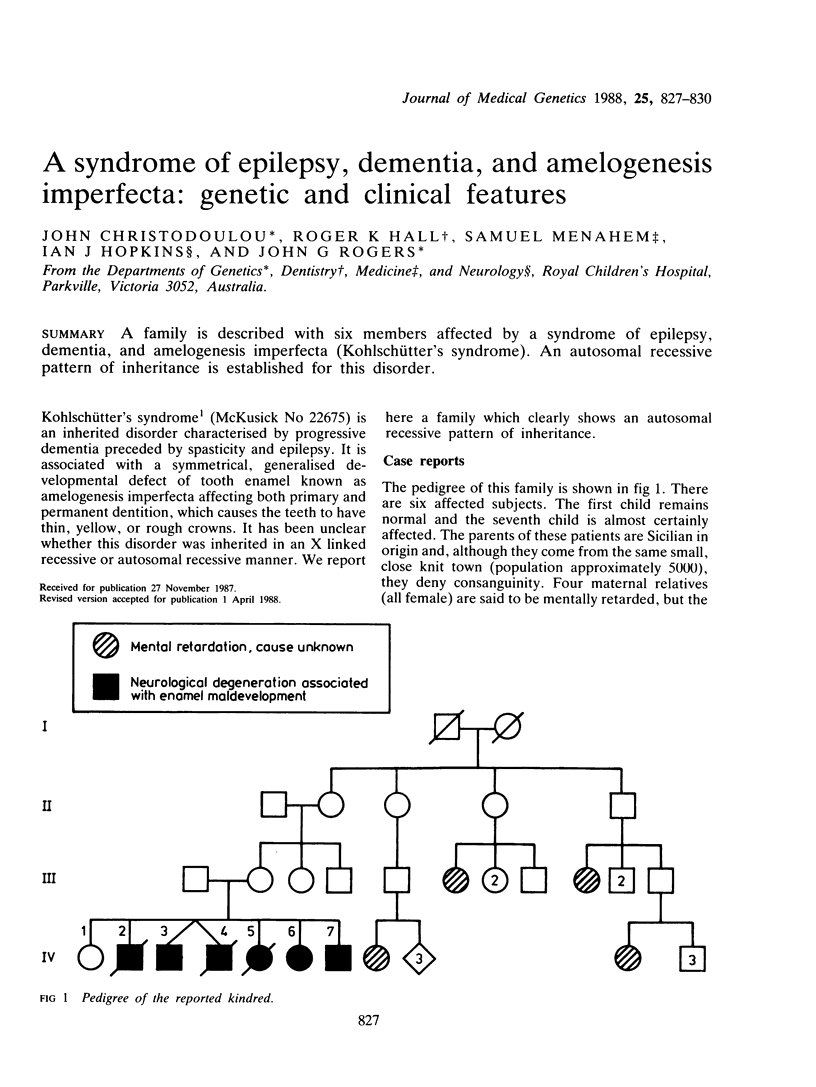

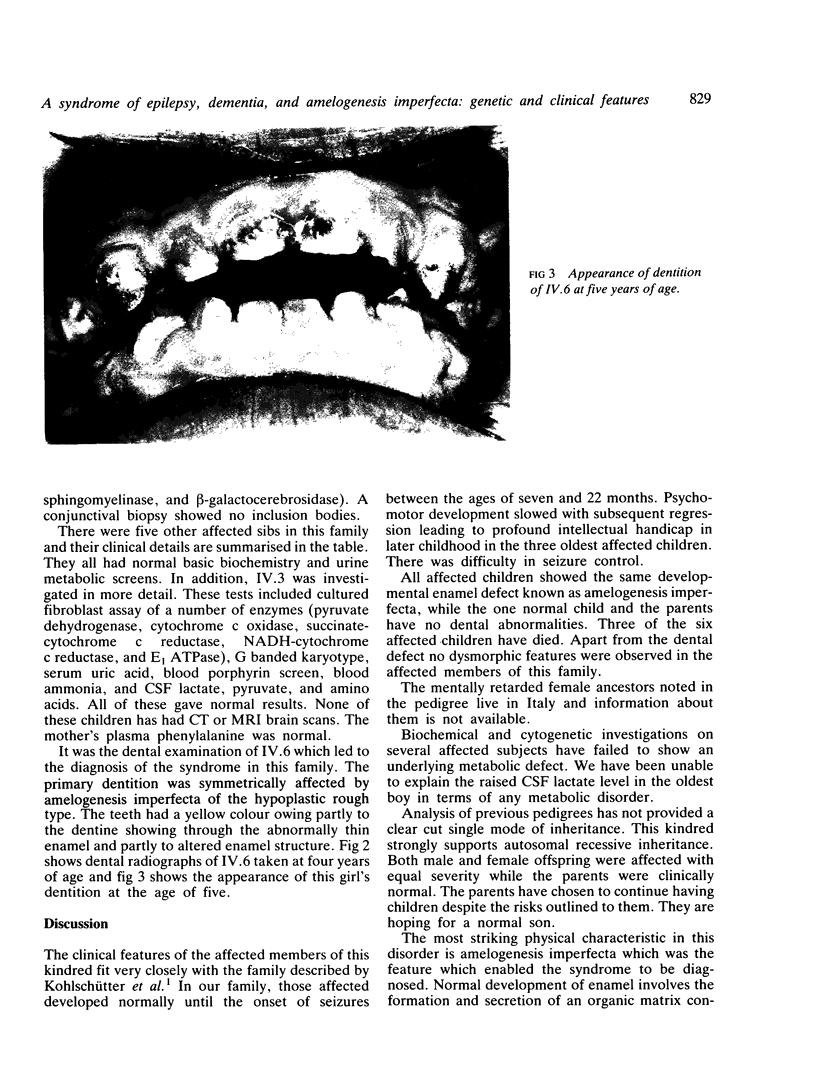

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kohlschütter A., Chappuis D., Meier C., Tönz O., Vassella F., Herschkowitz N. Familial epilepsy and yellow teeth--a disease of the CNS associated with enamel hypoplasia. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1974 Oct;29(4):283–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menanteau J., Mitre D., Raher S. An in-vitro study of enamel protein degradation in developing bovine enamel. Arch Oral Biol. 1986;31(12):807–810. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(86)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundell S., Koch G. Hereditary amelogenesis imperfecta. I. Epidemiology and clinical classification in a Swedish child population. Swed Dent J. 1985;9(4):157–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. T. Analysis of a kindred with amelogenesis imperfecta. J Oral Pathol. 1985 May;14(5):366–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1985.tb00507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]