Abstract
The fragile X syndrome, which often presents in childhood with overgrowth, may in some cases show some diagnostic overlap with classical Sotos syndrome. We describe four fragile X patients with general overgrowth, all of whom are from families with other affected relatives who show the classic Martin-Bell phenotype. Molecular studies of the FMR1 gene in all cases showed the typical full mutation as seen in males affected by the fragile X syndrome. Endocrine studies were unremarkable, except in one case where there were raised levels of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3)
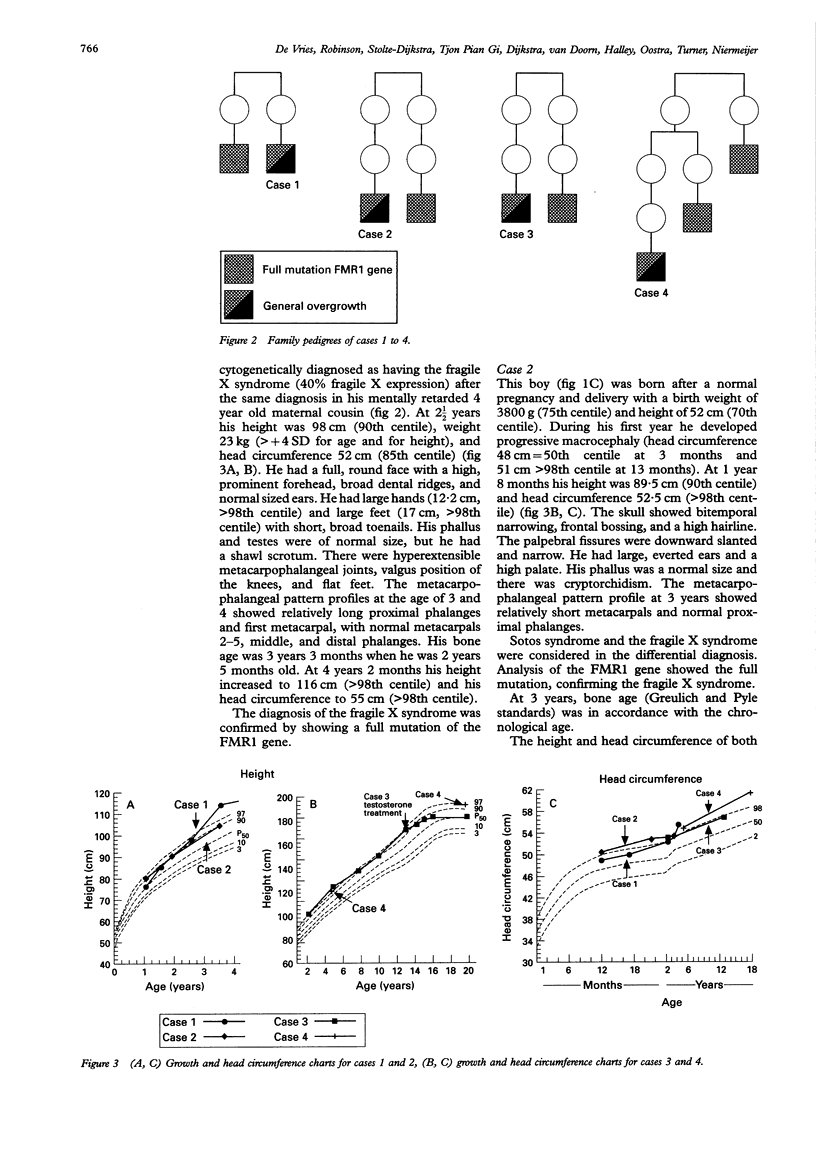
These cases illustrate the clinical variability of the fragile X syndrome and the necessity of performing analysis of the FMR1 gene in mentally retarded patients presenting with general overgrowth.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adashi E. Y., Resnick C. E., Hurwitz A., Ricciarellie E., Hernandez E. R., Roberts C. T., Leroith D., Rosenfeld R. The intra-ovarian IGF system. Growth Regul. 1992 Mar;2(1):10–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemer F. A., Veenema H., de Pater J. M. Cerebral gigantism (Sotos syndrome) in two patients with fra(X) chromosomes. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):221–226. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G., Allen G. A., Haynes J. L., Singh D. N., Watson M. S., Breg W. R. Anthropometric comparison of mentally retarded males with and without the fragile X syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Feb-Mar;38(2-3):260–268. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G., Brunschwig A., Miller L. K., Hagerman R. J. Standards for selected anthropometric measurements in males with the fragile X syndrome. Pediatrics. 1992 Jun;89(6 Pt 1):1059–1062. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G., Fletcher M., Gale D. D., Meaney F. J., McLeod D. R., Fagan J., Carpenter N. J. Metacarpophalangeal pattern profile analysis in fragile X syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Dec;31(4):767–773. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320310406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. R., Hughes H. E. Sotos syndrome: a study of the diagnostic criteria and natural history. J Med Genet. 1994 Jan;31(1):20–32. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra P. F. Cerebral gigantism (Sotos' syndrome). Metacarpophalangeal pattern profiles. Rofo. 1985 Aug;143(2):183–185. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Haspeslagh M., Dereymaeker A. M., Volcke P., Van den Berghe H. A peculiar subphenotype in the fra(X) syndrome: extreme obesity-short stature-stubby hands and feet-diffuse hyperpigmentation. Further evidence of disturbed hypothalamic function in the fra(X) syndrome? Clin Genet. 1987 Dec;32(6):388–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson K. H., Blomquist H. K., Holmgren G. Prevalence of the fragile-X syndrome in mentally retarded boys in a Swedish county. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):581–587. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isgaard J. Expression and regulation of IGF-I in cartilage and skeletal muscle. Growth Regul. 1992 Mar;2(1):16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J., van Buul-Offers S. C., Hoogerbrugge C. M., Van Den Brande J. L. Effects of a single cleavage in insulin-like growth factors I and II on binding to receptors, carrier proteins and antibodies. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):513–520. doi: 10.1042/bj2660513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellman B. Cerebral gigantism. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1965 Nov;54(6):603–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1965.tb06426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer E. J., Pritchard M., Lynch M., Yu S., Holman K., Baker E., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(CCG)n. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1711–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.1675488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch D. Z., Lafranchi M., Scott D. Anthropometry in Martin-Bell syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):149–164. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein from human plasma. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8754–8760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meryash D. L., Cronk C. E., Sachs B., Gerald P. S. An anthropometric study of males with the fragile-X syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):159–174. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Rousseau F., Heitz D., Kretz C., Devys D., Hanauer A., Boué J., Bertheas M. F., Mandel J. L. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1097–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oostra B. A., Verkerk A. J. The fragile X syndrome: isolation of the FMR-1 gene and characterization of the fragile X mutation. Chromosoma. 1992 Apr;101(7):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00582832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partington M. W. The fragile X syndrome II: preliminary data on growth and development in males. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):175–194. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOTOS J. F., DODGE P. R., MUIRHEAD D., CRAWFORD J. D., TALBOT N. B. CEREBRAL GIGANTISM IN CHILDHOOD. A SYNDROME OF EXCESSIVELY RAPID GROWTH AND ACROMEGALIC FEATURES AND A NONPROGRESSIVE NEUROLOGIC DISORDER. N Engl J Med. 1964 Jul 16;271:109–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196407162710301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano T., Yoshimitsu T., Tanabe A., Tanaka T., Kobayashi Y., Usui T., Takano K. Cerebral gigantism: a report of two cases with elevated serum somatomedin A levels and a review of the Japanese literature. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1977 Dec;26(4):311–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander-Stumpel C., Gerver W. J., Meyer H., Engelen J., Mulder H., Fryns J. P. Prader-Willi-like phenotype in fragile X syndrome. Clin Genet. 1994 Apr;45(4):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1994.tb04018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. E., Dean J., Howard-Peebles P. N., Bugge M., Mikkelsen M., Tommerup N., Hull C., Hagerman R., Holden J. J., Stevenson R. E. Obstetrical and gynecological complications in fragile X carriers: a multicenter study. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):400–402. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbergeld A., Litwin A., Bruchis S., Varsano I., Laron Z. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in healthy children, adolescents and adults as determined by a radioimmunoassay specific for the synthetic 53-70 peptide region. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Jul;25(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Ashforth P. L. X-linked mental retardation with macro-orchidism and the fragile site at Xq 27 or 28. Hum Genet. 1979 Apr 17;48(1):117–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00273283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Daniel A., Frost M. X-linked mental retardation, macro-orchidism, and the Xq27 fragile site. J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):837–841. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80552-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Daniel A., Frost M. X-linked mental retardation, macro-orchidism, and the Xq27 fragile site. J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):837–841. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80552-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Robinson H., Wake S., Martin N. Dizygous twinning and premature menopause in fragile X syndrome. Lancet. 1994 Nov 26;344(8935):1500–1500. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Reiner O., Richards S., Victoria M. F., Zhang F. P. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. P., Bundey S. E., Thake A. I., Todd J. Population incidence and segregation ratios in the Martin-Bell syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):573–580. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S., Pritchard M., Kremer E., Lynch M., Nancarrow J., Baker E., Holman K., Mulley J. C., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D. Fragile X genotype characterized by an unstable region of DNA. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavodny P. J., Petro M. E., Kumar C. C., Dailey S. H., Lonial H. K., Narula S. K., Leibowitz P. J. The nucleotide sequence of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain two. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1214–1214. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries B. B., Fryns J. P., Butler M. G., Canziani F., Wesby-van Swaay E., van Hemel J. O., Oostra B. A., Halley D. J., Niermeijer M. F. Clinical and molecular studies in fragile X patients with a Prader-Willi-like phenotype. J Med Genet. 1993 Sep;30(9):761–766. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.9.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]