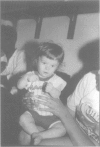Abstract
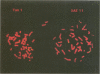
We report a case of an unbalanced cryptic telomeric translocation 46,XY,der(17),t(9;17)(q34.3;p13.3) in a boy with dysmorphic features and developmental delay. The proband had intrauterine growth retardation, postnatal short stature, and mild microcephaly. Magnetic resonance imaging showed incomplete myelination, but no evidence of lissencephaly. Cytogenetic analysis of the proband's peripheral blood showed an abnormal 17p. Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) with a Miller-Dieker cosmid probe did not detect a deletion for that area. Further analysis with a 17p telomere specific probe identified an unbalanced telomeric translocation. The same probe was used to determine the presence of an apparent balanced translocation t(9;17)(q34.3;p13.3) in the mother of the proband. The balanced translocation was confirmed with two cosmids that map distally on 9q34.3. Two phenotypically normal half sibs, a maternal aunt, a maternal uncle, and the maternal grandmother were found to be balanced translocation carriers as well. A subtle translocation carriers as well. A subtle translocation is one mechanism that can produce an abnormal phenotype in a patient who had a normal karyotype at lower band resolution levels.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aftimos S. F., Hoo J. J., Parslow M. I. Partial trisomy 9q due to maternal 9/17 translocation. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Sep;134(9):848–850. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130210032009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allderdice P. W., Eales B., Onyett H., Sprague W., Henderson K., Lefeuvre P. A., Pal G. Duplication 9q34 syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):1005–1019. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altherr M. R., Bengtsson U., Elder F. F., Ledbetter D. H., Wasmuth J. J., McDonald M. E., Gusella J. F., Greenberg F. Molecular confirmation of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome with a subtle translocation of chromosome 4. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1235–1242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado M., Bass H. N., Caldwell S., Jamehdor M., Miller A. A., Jacob P. Miller-Dieker syndrome. Detection of a cryptic chromosome translocation using in situ hybridization in a family with multiple affected offspring. Am J Dis Child. 1993 Dec;147(12):1291–1294. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1993.02160360033012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogen P. H., Daneshvar L., Metzger A. K., Duyk G., Edwards M. S., Sheffield V. C. Involvement of multiple chromosome 17p loci in medulloblastoma tumorigenesis. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):584–589. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisen L. W., Bird J., West D. C., Soreng A. L., Reynolds T. C., Smith S. D., Sklar J. TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):649–661. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90111-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeuchi T. Inhibitory effect of ethidium bromide on mitotic chromosome condensation and its application to high-resolution chromosome banding. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(1):56–61. doi: 10.1159/000132030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Ledbetter S. A., Dobyns W. B., Emanuel B. S., Ledbetter D. H. Detection of deletions and cryptic translocations in Miller-Dieker syndrome by in situ hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):707–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler A., Hain J., Müller U. Familial half cryptic translocation t(9;17). J Med Genet. 1994 Sep;31(9):712–714. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.9.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter S. A., Kuwano A., Dobyns W. B., Ledbetter D. H. Microdeletions of chromosome 17p13 as a cause of isolated lissencephaly. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;50(1):182–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter S. A., Wallace M. R., Collins F. S., Ledbetter D. H. Human chromosome 17 NotI linking clones and their use in long-range restriction mapping of the Miller-Dieker chromosome region (MDCR) in 17p13.3. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90549-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mewar R., Kline A. D., Jackson L., Overhauser J. Confirmation of a cryptic unbalanced translocation using whole chromosome fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Nov 1;44(4):477–481. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320440418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Barker D., Wright E., Skolnick M., Kondoleon S., Litt M., Lalouel J. M. A mapped set of DNA markers for human chromosome 17. Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overhauser J., Bengtsson U., McMahon J., Ulm J., Butler M. G., Santiago L., Wasmuth J. J. Prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of a cryptic translocation by using DNA markers from the short arm of chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):296–303. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltan H. C., Jung J. H., Pyatt Z., Singh R. P. Partial trisomy 9q resulting from a familial translocation t(9;16)(q32;q24). Clin Genet. 1984 May;25(5):449–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb02015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrt I., Janovský M., Jodl J. Partial trisomy 9q--chromosomal syndrome. Hum Genet. 1976 Oct 28;34(2):151–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00278883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten S. K., Chin Y. M., Tan S. K., Hassan K. Three cases of partial trisomy 9q in one generation due to maternal reciprocal t(6;8;9) translocation. Clin Genet. 1987 Jun;31(6):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb02824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turleau C., de Grouchy J., Chavin-Colin F., Roubin M., Brissaud P. E., Repessé G., Safar A., Borniche P. Partial trisomy 9q: a new syndrome. Humangenetik. 1975 Sep 23;29(3):233–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00297629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Raj A., Baker D. The phenotypic and cytogenetic spectrum of partial trisomy 9. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Feb;20(2):277–282. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]