Abstract
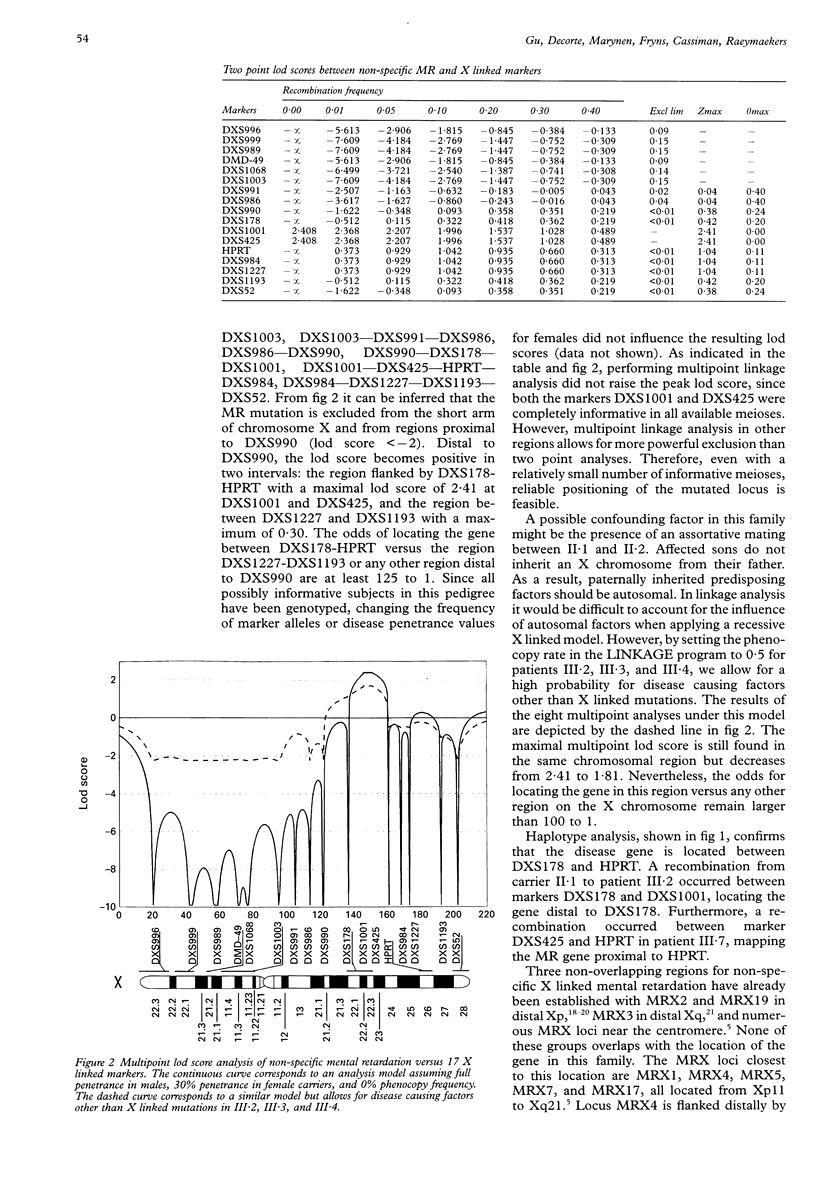
Non-specific mental retardation (MR) is a condition in which MR appears to be the only consistent manifestation. The X linked form (MRX) is genetically heterogeneous. We report clinical, cytogenetic, and linkage data on a family with X linked non-specific MR. Two point and multi-point linkage analysis with 18 polymorphic markers, covering the entire chromosome, showed close linkage to DXS1001 and DXS425 with a maximal lod score of 2.41 at 0% recombination. DXS178 and the gene for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl-transferase (HPRT), located in Xq22 and Xq26 respectively, flank the mutation. All other chromosomal regions could be excluded with odds of at least 100:1. To our knowledge there is currently no other non-specific MR gene mapped to this region. Therefore, the gene causing MR in this family can be considered to be a new, independent MRX locus (MRX35).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeliovich D., Dagan J., Kimchi-Sarfaty C., Zlotogora J. Paracentric inversion X(q21.2q24) associated with mental retardation in males and normal ovarian function in females. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Jan 30;55(3):359–362. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320550322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arveiler B., Alembik Y., Hanauer A., Jacobs P., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Puissant H., Piet L. L., Mandel J. L. Linkage analysis suggests at least two loci for X-linked non-specific mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):473–483. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetow K. H., Weber J. L., Ludwigsen S., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Duyk G. M., Sheffield V. C., Wang Z., Murray J. C. Integrated human genome-wide maps constructed using the CEPH reference panel. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):391–393. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundey S., Carter C. O. Recurrence risks in severe undiagnosed mental deficiency. J Ment Defic Res. 1974 Jun;18(2):115–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1974.tb01227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S., Chang S. Y., Gravitt P., Respess R. Long PCR. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):684–685. doi: 10.1038/369684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly A. J., Choo K. H., Kozman H. M., Gedeon A. K., Danks D. M., Mulley J. C. Regional localisation of a non-specific X-linked mental retardation gene (MRX19) to Xp22. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):581–585. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedeon A., Kerr B., Mulley J., Turner G. Localisation of the MRX3 gene for non-specific X linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1991 Jun;28(6):372–377. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.6.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedeon A., Kerr B., Mulley J., Turner G. Pericentromeric genes for non-specific X-linked mental retardation (MRX). Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):553–564. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass I. A. X linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1991 Jun;28(6):361–371. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.6.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L. J., Blumenfeld-Heyberger S., Hanauer A., Weissenbach J., Mandel J. L. Non-specific X-linked mental retardation: linkage analysis in MRX2 and MRX4 families revisited. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):569–574. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedele K. B., Michels V. V., Schaid D. J., Schowalter K. V., Thibodeau S. N. Linkage of nonspecific X-linked mental retardation to Xq21.31. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):436–442. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr B., Turner G., Mulley J., Gedeon A., Partington M. Non-specific X linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1991 Jun;28(6):378–382. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.6.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahey A. M., Charnas L. R., Nussbaum R. L. Nonsense mutations in the OCRL-1 gene in patients with the oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Apr;2(4):461–463. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):277–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L. Towards identification of X-linked mental retardation genes: a proposal. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):550–552. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Buetow K. H., Weber J. L., Ludwigsen S., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Manion F., Quillen J., Sheffield V. C., Sunden S., Duyk G. M. A comprehensive human linkage map with centimorgan density. Cooperative Human Linkage Center (CHLC). Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2049–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8091227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri G., Chiurazzi P., Arena J. F., Lubs H. A. XLMR genes: update 1994. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):542–549. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham-Dinh D., Boespflug-Tanguy O., Mimault C., Cavagna A., Giraud G., Leberre G., Lemarec B., Dautigny A. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: a frameshift deletion/insertion event in the myelin proteolipid gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Apr;2(4):465–467. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanns C., Albrecht R., Neugebauer M., Neri G., Gal A. Gene for non-specific X-linked mental retardation maps in the pericentromeric region. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Feb-Mar;38(2-3):224–227. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. E. X-linked mental retardation: in pursuit of a gene map. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1025–1031. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Oberlé I., Nancarrow J., Mulley J. C., Hyland V. J., Wilson P. J., McCure J., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J., Mandel J. L. Genetic mapping of new RFLPs at Xq27-q28. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Turner G., Mulley J. C. A non-syndromal form of X-linked mental retardation (XLMR) is linked to DXS14. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):485–491. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranebjaerg L., Schwartz C., Eriksen H., Andreasson S., Ponjavic V., Dahl A., Stevenson R. E., May M., Arena F., Barker D. A new X linked recessive deafness syndrome with blindness, dystonia, fractures, and mental deficiency is linked to Xq22. J Med Genet. 1995 Apr;32(4):257–263. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.4.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Collins A., Lawrence S., Keats B. J., Morton N. E. Integration of gene maps: chromosome X. Genomics. 1994 Aug;22(3):590–604. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


