Abstract
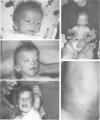
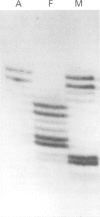
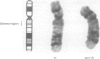
We report the first visible cytogenetic deletion involving the NF1 gene in a patient with sporadic neurofibromatosis, dysmorphic features, and marked developmental delay. The combined evidence of molecular and cytogenetic techniques based on dosage reduction, hemizygosity for microsatellite markers, high resolution G banding, and FISH analysis, predicts this deletion to be approximately 7 Mb in size. Our findings highlight the importance of conducting a detailed cytogenetic and FISH analysis in patients with NF1 who have additional dysmorphic features or particularly severe learning difficulties.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D., Wright E., Nguyen K., Cannon L., Fain P., Goldgar D., Bishop D. T., Carey J., Baty B., Kivlin J. Gene for von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis is in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1100–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.3107130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Weiss R., Xu G. F., Viskochil D., Culver M., Stevens J., Robertson M., Dunn D., Gesteland R., O'Connell P. A major segment of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and point mutations. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields C., Adams M. D., White O., Venter J. C. How many genes in the human genome? Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):345–346. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgar D. E., Green P., Parry D. M., Mulvihill J. J. Multipoint linkage analysis in neurofibromatosis type I: an international collaboration. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):6–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm T., Meng G., Liechti-Gallati S., Bettecken T., Müller C. R., Müller B. On the origin of deletions and point mutations in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: most deletions arise in oogenesis and most point mutations result from events in spermatogenesis. J Med Genet. 1994 Mar;31(3):183–186. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.3.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huson S. M., Compston D. A., Clark P., Harper P. S. A genetic study of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis in south east Wales. I. Prevalence, fitness, mutation rate, and effect of parental transmission on severity. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):704–711. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jadayel D., Fain P., Upadhyaya M., Ponder M. A., Huson S. M., Carey J., Fryer A., Mathew C. G., Barker D. F., Ponder B. A. Paternal origin of new mutations in von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):558–559. doi: 10.1038/343558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayes L. M., Burke W., Riccardi V. M., Bennett R., Ehrlich P., Rubenstein A., Stephens K. Deletions spanning the neurofibromatosis 1 gene: identification and phenotype of five patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Mar;54(3):424–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayes L. M., Riccardi V. M., Burke W., Bennett R. L., Stephens K. Large de novo DNA deletion in a patient with sporadic neurofibromatosis 1, mental retardation, and dysmorphism. J Med Genet. 1992 Oct;29(10):686–690. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.10.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterling R. P., Vielhaber E., Bottema C. D., Schaid D. J., Cohen M. P., Sexauer C. L., Sommer S. S. Germ-line origins of mutation in families with hemophilia B: the sex ratio varies with the type of mutation. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;52(1):152–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lázaro C., Gaona A., Xu G., Weiss R., Estivill X. A highly informative CA/GT repeat polymorphism in intron 38 of the human neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene. Hum Genet. 1993 Oct;92(4):429–430. doi: 10.1007/BF01247353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D. A., Tavakkol R., Wallace M. R., Brownstein B. H., Taillon-Miller P., Fong C. T., Legius E., Andersen L. B., Glover T. W., Collins F. S. A yeast artificial chromosome contig encompassing the type 1 neurofibromatosis gene. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):672–680. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90140-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E. Parameters of the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7474–7476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitzel H. A routine method for the establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):320–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00279094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purandare S. M., Lanyon W. G., Connor J. M. Characterisation of inherited and sporadic mutations in neurofibromatosis type-1. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jul;3(7):1109–1115. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.7.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenhiser D., Hovland K. A novel RsaI polymorphism within intron 39 of the neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene. Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;95(2):241–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00209414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Contiguous gene syndromes: a component of recognizable syndromes. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seizinger B. R., Rouleau G. A., Ozelius L. J., Lane A. H., Faryniarz A. G., Chao M. V., Huson S., Korf B. R., Parry D. M., Pericak-Vance M. A. Genetic linkage of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis to the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):589–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimmin L. C., Chang B. H., Li W. H. Male-driven evolution of DNA sequences. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):745–747. doi: 10.1038/362745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K., Kayes L., Riccardi V. M., Rising M., Sybert V. P., Pagon R. A. Preferential mutation of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene in paternally derived chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;88(3):279–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00197259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tint G. S., Irons M., Elias E. R., Batta A. K., Frieden R., Chen T. S., Salen G. Defective cholesterol biosynthesis associated with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 13;330(2):107–113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401133300205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Cheryson A., Broadhead W., Fryer A., Shaw D. J., Huson S., Wallace M. R., Andersen L. B., Marchuk D. A., Viskochil D. A 90 kb DNA deletion associated with neurofibromatosis type 1. J Med Genet. 1990 Dec;27(12):738–741. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.12.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Maynard J., Osborn M., Huson S. M., Ponder M., Ponder B. A., Harper P. S. Characterisation of germline mutations in the neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene. J Med Genet. 1995 Sep;32(9):706–710. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.9.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Sarfarazi M., Huson S. M., Broadhead W., Fryer A., Harper P. S. Close flanking markers for neurofibromatosis type I (NF1). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):41–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Molecular basis of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1): mutation analysis and polymorphisms in the NF1 gene. Hum Mutat. 1994;4(2):83–101. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380040202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Shen M., Cherryson A., Farnham J., Maynard J., Huson S. M., Harper P. S. Analysis of mutations at the neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):735–740. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Buchberg A. M., Xu G., Cawthon R. M., Stevens J., Wolff R. K., Culver M., Carey J. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Deletions and a translocation interrupt a cloned gene at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90252-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheater R. F., Roberts S. H. An improved lymphocyte culture technique: deoxycytidine release of a thymidine block and use of a constant humidity chamber for slide making. J Med Genet. 1987 Feb;24(2):113–114. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.2.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., Nelson L., O'Connell P., White R. An Alu polymorphism intragenic to the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene (NF1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3764–3764. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]