Abstract
Introduction
This review identified and examined the research literature on the effect of participating in physical and/or cognitive activities on older people’s quality of life, to establish whether the social relationships fostered by these activities can be a vector of better physical, mental and social quality of life.
Method
A systematic review of the literature was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. We searched four databases (MEDLINE, APA PsycArticles/PsycInfo, PubMed, and Web of Science) for articles published between 1975 and 2022 using search terms related to psychosocial, population, and intervention topics. Studies were eligible if they involved older adults, participation in at least one activity (physical or cognitive), and at least one quality of life related outcome measure.
Results
We selected 20 articles published between 1990 and 2021, the majority concerning studies conducted in English-speaking countries. Ten studies were interventional (introduction of program of activities), and 10 studies were observational (60% quantitative, 40% qualitative). Overall, results revealed a positive impact of the activities on every aspect of quality of life (i.e., cognitive, physical, social, psychological, and quality of life in general).
Conclusion
The present review confirmed the beneficial impact of practicing physical and/or cognitive group activities on older people’s quality of life, but the contribution of social factors and social relationships remains underestimated and not well defined in researches.
Keywords: social relations, quality of life, physical activities, cognitive activities, wellbeing, aging
Introduction
The world population is aging, and the number of people aged 60 years or over is expected to double by 2050 [World Health Organization (WHO), 2017]. Aging brings with it a gradual decline in sensory, physical and cognitive abilities. Cognitive decline has been identified as one of the main threats to the health and autonomy in aging (Reuter-Lorenz and Park, 2014). These negative effects raise many issues for older people, surrounding autonomy, aging in place and, more generally, quality of life. Successful or healthy aging, referred to as well-aging, which is defined in the literature as the maintenance of functional autonomy through the optimization of physical, mental and social wellbeing, is thus becoming a major societal challenge (Depp and Jeste, 2006; Gangbè and Ducharme, 2006). However, successful aging remains a complex concept that needs to be better defined in order to promote active, healthy aging for all older people (Estebsari et al., 2020). Well-being is a subjective phenomenon that involves both cognitive components (e.g., life satisfaction) and emotional components (e.g., the balance between positive and negative affect; Diener et al., 1999). The concept of well-being is strongly associated with the more integrative concept of quality of life. The World Health Organization [World Health Organization (WHO), 1994] defines quality of life as “a person’s perception of his/her position in life within the context of the culture and value systems in which he/she lives and in relation to his/her goals, expectations, standards, and concerns. It is a broad-ranging concept incorporating, in a complex way, the person’s physical health, psychological state, level of independence, social relationships, personal beliefs, and relationship to salient features of the environment” [World Health Organization (WHO), 1994, p. 29]. This definition highlights the essentially subjective and multidimensional (physical, psychological, social, etc.) concept of quality of life. According to the Ottawa Charter (WHO, 1986), health is defined as “a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being.” Quality of life is therefore a general concept that depends on health, although it is not limited to it. Indeed, some people whose health is considered degraded have a high quality of life, or vice versa (Rejeski and Mihalko, 2001).
Several studies have sought to identify factors that can contribute to successful aging by preserving cognitive health and improving the overall quality of life of older adults. So far, they have highlighted the beneficial effects of cognitive exercise (Kelly et al., 2014; Mewborn et al., 2017; Basak et al., 2020), physical activity (Colcombe et al., 2003; Mandolesi et al., 2018; Carta et al., 2021), training sessions combining cognitive and physical stimulation (Kraft, 2012; Zhu et al., 2016; Gheysen et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2020), and social interactions (Seeman et al., 2001; Pitkala et al., 2011; Kelly et al., 2017; Marsillas et al., 2017). The literature shows that an active and socially engaged lifestyle is linked to better cognitive function in aging, and self-esteem is an important characteristic of wellbeing arising from physical activity (Small et al., 2012; Litwin and Stoeckel, 2016; Yang et al., 2016).
However, although these different factors are beginning to be given greater salience in the literature as means of avoiding cognitive decline and improving quality of life, the health benefits of social relationships continue to be underplayed. Haslam et al. (2005, 2018) maintained that social support and social integration are both highly protective against mortality, and their importance is comparable or even superior to that of many behavioral risks such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress. There is considerable evidence that being cut off from social contact with friends, family and other social groups can have extremely negative health consequences, and even lead to premature death (Jetten et al., 2012). By contrast, belonging to and identifying with community groups have been shown to positively predict health and quality of life (McNamara et al., 2013; Haslam et al., 2018; Fong et al., 2019). This idea refers to the notion of social cure, which highlights the way in which a person’s social relationships, social networks, social support, and social identity contribute to health outcomes (Jetten et al., 2012; Haslam et al., 2014; Kellezi et al., 2019). This approach states that identification with and sense of belonging to social groups (family, community, sports group, etc.) have an impact on health, social life and wellbeing, leading to improvements in social life and quality of life through the reduction in loneliness, improvement in self-esteem, and perception of available social support (Greenaway et al., 2015; Sani et al., 2015; Kellezi et al., 2019).
The objective of the present literature review was to establish whether the social relationships fostered by some physical and/or cognitive activities can be a vector of better physical, cognitive, psychological and social quality of life for the older people.
Materials and methods
Information sources and research process
In order to answer this objective, we conducted a literature review, searching four databases (MEDLINE, APA PsycArticles/PsycInfo, PubMed, and Web of Science) for articles published between 1975 and 2022 Search terms covered the following four topics: (1) social relationships (psychosocial terms), (2) older people (population terms), (3) activity/leisure (intervention terms), and (4) quality of life (health terms).
The keyword search was based on the MEDLINE algorithm. We defined the following list of keywords: (social link or social relationships or social activities) AND (elderly or seniors or aging) AND (physical activities or cognitive activities or physical exercises) AND (well-being or quality of life or mental-physical-psychological health). We applied the same algorithm in the Web of Science, APA PsycArticles/PsycInfo, and PubMed databases. We also conducted a free search, consisting of additional manual searches were undertaken across the first pages of results from the generic web search engine Google Scholar. Moreover, additional searches were carried out by examining the references cited in the included studies and considered to be of interest. We merged these searches and included them in a library we created in Zotero. Duplicates were identified and deleted. In order to make our final selection of articles, we subjected the abstracts to detailed analysis, applying the eligibility criteria (inclusion and exclusion). We assessed point by point whether all the inclusion criteria had been met, and whether the abstracts did not present any exclusion criteria. Abstracts that did not meet all these criteria were excluded from the final selection of articles.
Eligibility criteria/study selection
The inclusion criteria were as follows:
Studies in which outcomes (i.e., the dependent variable, quality of life or well-being) are clearly defined will be included.
Studies in which the independent variable (social relationships) is present in the context of at least one physical and/or cognitive activity will be included.
The population is defined by the authors as a population of elderly or senior people.
The exclusion criteria were as follows:
Studies not written in English will be excluded
Studies that are not journal articles will be excluded (e.g., book chapter, editorial reviews, literature reviews, etc.)
Studies in which the dependent variable does not concern notion of quality of life or well-being will be excluded
Studies in which the independent variable (social relationships) is not present in the context of physical and/or cognitive activities will be excluded.
Studies of populations not defined by the authors as older people’s or elderly or seniors will be excluded.
Studies conducted on older people who do not live in the community will be excluded. Studies of older populations with pathologies (stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, etc.) will be excluded.
Studies concerning the evaluation of a measurement tool (e.g., validation of a test or questionnaire) will be excluded.
Data collection process
The review was not pre-registered, but followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) reporting guidelines (Moher et al., 2009), which ensure the transparent and complete reporting of systematic reviews. The articles were selected by the first author (TG) and this selection was then checked independently by all the other authors (DC, GB, CE). Any uncertainty and disagreement between evaluators were resolved by discussion and consensus within the author team (TG, DC, GB, and CE). The first author (TG) extracted the following information: first authors, year of publication, journal, study country, study population, study population size, method, data collection, dependent variables, summary of results.
Assessing the risk of bias
One of the review authors (TG) assessed independently the methodological quality of the studies included using the modified version of the Downs and Black checklist for assessing randomized controlled trials (RCT) and non-randomized controlled trials (NRCT; Downs and Black, 1998). It consists of 27 items distributed across five subscales: reporting (10 items), external validity (3 items), internal validity bias (7 items), internal validity confounding (6 items), and power (1 item). In the modified instrument, answers are scored 0 or 1, except for one item in the reporting subscale, which is scored 0 to 2. The total maximum score is 28 with higher scores indicating better study quality.
Results
Study selection
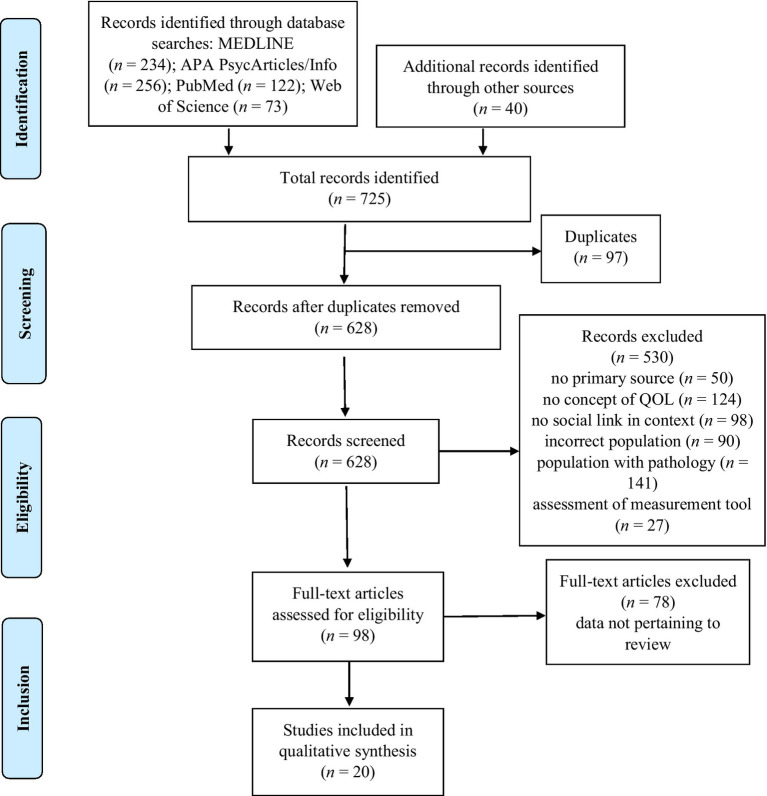
The study selection procedure is illustrated in Figure 1. The free search yielded 40 articles. The MEDLINE keyword search yielded 234 results. Keyword searching with the same algorithm yielded 256 results in APA PsycArticles/Info, 122 in PubMed, and 73 in Web of Science. After removing duplicates, 628 articles were removed based on the title and/or abstract because they did not meet criteria for inclusion, Finally, after reading and analyzing the 98 articles in their entirety according to the eligibility criteria, 20 studies were included in the review.
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram.
Study characteristics
The characteristics of the studies are set out in Table 1. All 20 selected articles were published between 1990 and 2022 (only one before 2000). Eleven articles concerned English-speaking countries (87.5% United States), five Asia, two Africa, and two Europe. The quality of life dimensions they assessed were general quality of life (23%), cognitive (19%), physical (28%), psychological (62%), and social (52%). The studies included have very large population criteria, ranging from 50 to 111 years of age, depending on the study. However, all the studies included in this review have a population whose mean age was over 60 (The lowest mean age was 64.62 in the study by Chang et al., 2014), despite their very large age samples, and according to the World Health Organization, 60 is the age at which people become elderly.
Table 1.
Characteristics of studies included in review.
| Authors | Journal | Study year | Country | Sample size | Mean age in years (SD) | % Women | Intervention | Duration of intervention | Quality score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aday et al. | Journal of Women & Aging | 2006 | United States | 415 women aged 50+ years, 274 living alone and 141 with a spouse | 74.4 | 100% | Multipurpose center for seniors (health, education, recreation, volunteering, social interaction, etc.) | ||
| Bailey & McLaren | Aging & Mental Health | 2005 | Australia | 194 seniors aged 60+ years | Men 69.59 (6.64) women 68.21 (7.78) |
55.1% | Physical activity alone or in a group | ||
| Camic et al. | Aging & Mental Health | 2014 | United Kingdom | 24 seniors aged 55+ years | 78.3 (8.8) | NA | Painting gallery (observation + creation of artworks) | 8 weekly 2-h sessions over 8 weeks | Total score: 12
|
| Chang et al. | Health Psychology | 2014 | United States | 2,965 seniors aged 50+ years | 64.62 (9.92) | 50.2% | Participation in social, mental, physical and productive activities | ||
| Dare et al. | Health and Social Care | 2018 | Australia | 35 seniors aged 60+ years | 71 | 71.4% | 2 physical activity groups / 1 painting group / 1 senior center group | ||
| Emery & Gatz | The Gerontologist | 1990 | United States | 48 seniors aged 60+ years | 72 (6) | 83.3% | Physical exercise program or social activity (card game, art activity, etc.) or waitlisted witness | 12-week intervention +12-week exercise program | Total score: 12
|
| Gagliardi et al. | Health and Social Care | 2019 | Italy | 73 seniors aged 65+ years | 72.88 (8.61) | 63% | Intergenerational events held at six farms | Every week for 1 year | Total score: 10
|
| Gyasi | Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics | 2019 | Kenya | 1,200 seniors aged 50+ years | 66 (11.6) | 63% | Frequency of participation in physical and social activities | ||
| Kamegaya et al. | Psychogeriatrics | 2014 | Japan | 43 seniors aged 65+ years | 74.9 (5.9) | 90% | Intervention = physical activity program (stretching, strength training, aerobics, balance) + leisure (cooking, crafts, competitive play) Control = no program |
12-week intervention with 2 h per week in a community center | Total score: 14
|
| Kanamori et al. | Scientific Reports | 2016 | Japan | 21,684 seniors aged 65+ years | 73.5 (6) | 52.1% | Physical activity alone or with others | ||
| Kim et al. | Health Care for Women International | 2015 | Korea | 11 women aged 68+ years | Range: 68–81 | 100% | Participation in activities at a senior center (yoga, recreational program, regular exercise, sports, traditional Korean games) | ||
| Kim et al. | International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being | 2014 | Korea | 10 seniors aged 65+ | 71 | 70% | Membership of a sports club for many years | ||
| Komatsu et al. | BMC Geriatrics | 2017 | Japan | 26 seniors aged 60+ years | 74.69 (range: 66–86) | 57% | Participation in regular group exercises in the community (Fujisawa+10 program) | ||
| Levinger et al. | BMC Geriatrics | 2020 | Australia | 80 seniors aged 60+ years | 73 (7.4) | 82.1% | Exercise program in an exercise park (strength, balance, coordination, etc.) | 12-week intervention 80 min twice a week, then 6 months unsupervised independent access to the park or access to supervised exercise sessions, but no group activity. | Total score: 12
|
| MacAulay et al. | Psychomusicology: Music, Mind, and Brain | 2019 | United States | 35 seniors aged 55+ years | 70 (5.12) | 98% | Music (recorder playing) project (Maine Understanding Sensory Integration and Cognition Project) | 12 1-h group sessions | Total score: 10
|
| McAuley et al. | Psychology and Health | 2000 | United States | 80 seniors aged 60–75 years | 65.5 | 77.5% | Aerobic physical activity (walking) program or stretching and toning program, practiced alone or in a group | Three 1-h sessions per week for 6 months | Total score: 15
|
| Meeks et al. | Aging and Mental Health | 2020 | United States | 42 seniors aged 60+ years | 66.13 (4.61) | 63.6% | Theatergoing (seven plays) | Seven plays over two consecutive seasons | Total score: 11
|
| Nadasen | Journal of Women & Aging | 2008 | South Africa | 30 seniors aged 60+ years | 69.6 (7.6) | 100% | Line dance program | 12 months | Total score: 9
|
| Pentikäinen | PLOS ONE | 2021 | Finland | 162 seniors aged 60+ years | High singer: 72.8 (5.7) Low singer: 69.2 (4.5) Control: 70.2 (6.5) |
High-level singer: 79.1% Low-level singer: 65.5% Control: 85.7% |
Follow-up of elderly choir singers and non-choir singers | ||
| Yuen et al. | Occupational Therapy International | 2011 | United States | 12 seniors aged 60+ years | 75.3 (8.5) | 91% | SAASY Program (theater instruction and experience) | Weekly 2-h sessions over 6 weeks + participation in five performances + giving four performances 2 months after the end of the 6 weeks | Total score: 10
|
NA: not available.
Methodologies
Of the 20 studies, 10 were interventional, involving a program of leisure, physical or cognitive activities, with a pre−/posttest analysis plan, and 10 were observational (60% quantitative, 40% qualitative). The quantitative studies were cross-sectional, and the qualitative studies were based on focus groups or interviews. Eight of the 20 studies compared the effects of activity according to group, while the other 12 studies assessed the effects of activity with no group comparison.
Study rigor and study quality
The summary of the quality scores is displayed in Table 1. The quality scoring descriptive statistics include a mean of 11,5. The quality assessment of the 10 interventional studies highlights that the majority of them were of low quality. The scores were very low in external validity, internal validity - confounding and statistical power. This indicates that the studies had the insufficient statistical power to detect important effects and none of the findings could be generalized to older population. Serious risk bias can be highlighted such as small samples, no comparison or control group, and lack of details regarding the intervention.
Outcomes
The results of the studies included in the review are set out in Table 2. More than half (52%) of the studies looked at the effects of participating in physical activities (sports clubs, aerobic activity programs, etc.) on quality of life, 42% were interested in the effects of participating in cognitive and/or social activities (day center for seniors, card games, social farm, etc.) and 38% looked at the impact of leisure activities (theater, musical training, etc.).
Table 2.
Results of Studies Included in Review.
| Author | Objective and method assessment times | Quality of life variable (cognitive, physical, psychological, social) | Data collection | Summary statistics | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aday et al. (2006) | Examine influences of late-life friendships and senior center activities on aging women’s health and wellbeing Quantitative: questionnaires |
|
|
|
|
| Bailey and McLaren (2005) | Determine whether physical activity alone or combined with other types of activity predicts depressive symptoms, which in turn predicts suicidal ideation Quantitative: questionnaires |
|
|
|
|
| Camic et al. (2014) | Examine possible impact of a longer intervention involving observation and art-making sessions in a gallery on social inclusion, quality of life, and activities of daily living among people with disabilities and their caregivers Mixed quantitative and qualitative: questionnaire + interview Pre- and postassessments |
|
|
|
|
| Chang et al. (2014) | Examine relationship between social relationships and health among seniors, looking at whether leisure plays a mediating role in the association between social relationships and health outcomes Quantitative: questionnaire + rating scale |
|
|
|
|
| Dare et al. (2018) | Identify the facilitators of and barriers to community participation, looking at whether they differ between those who regularly participate in community activities, those who participate only irregularly, and those who do not participate at all. Qualitative: focus group or individual interview |
|
|
|
|
| Emery and Gatz (1990) | Study the effects of a 12-week physical exercise program on measures of cognitive functioning and psychological wellbeing in community-dwelling older adults Quantitative: questionnaires + physical test Pre- and postintervention assessments |
|
|
|
|
| Gagliardi et al. (2019) | Assess a 1-year social farming program (horticultural and professional activities) aimed at older adults in good general health, conducted between 2014 and 2015 at six farms. Determine whether participating in social farming activities promotes quality of life, social relationships, leisure participation, and physical activity for older adults. Quantitative: questionnaires Pre- and postintervention assessments |
|
|
|
|
| Gyasi (2019) | Investigate the effects of regular physical activity, social support, and the interaction between the two on psychological distress outcomes in community-dwelling older adults Quantitative: questionnaires |
|
|
|
|
| Kamegaya et al. (2014) | Explore effectiveness of a comprehensive program of physical and recreational activities in preventing cognitive decline in older people Quantitative: questionnaires + tests Pre- and postintervention assessments |
|
|
|
|
| Kanamori et al. (2016) | Examine whether the association between subjective health status and exercise differs according to whether the exercise is performed alone and/or with others, adjusting for exercise frequency Quantitative: rating scale |
|
|
|
|
| Kim et al. (2015) | Explore benefits of social engagement in leisure activities among older Korean women Qualitative: semistructured interview |
|
|
|
|
| Kim et al. (2014) | Explore benefits of serious engagement in leisure activities at a sports club among older Korean adults Qualitative: interview |
|
|
|
|
| Komatsu et al. (2017) | Explore experiences of older adults engaging in regular group exercise and study their perceptions of the physical, mental, and social changes they experience as a result Qualitative: semistructured interview |
|
|
|
|
| Levinger et al. (2020) | Assess effects of supported physical activity program on physical, mental, social and health outcomes through use of Senior Exercise Park physical activity program for older adults Quantitative: questionnaires + self-reported measurements and physical tests Assessments at baseline, 3 months, and 9 months |
|
|
|
|
| MacAulay et al. (2019) | Study effect of music training on social, emotional and cognitive functions in older adults Mixed method: quantitative (cognitive test + questionnaires) and qualitative (semistructured interview) Pre- and postintervention assessments |
|
|
|
|
| McAuley et al. (2000) | Determine whether different exercise environments influence affective responses independently of the many effects of exercise intensity and duration Examine extent to which changes in exercise self-efficacy are associated with changes in affective responses to acute exercise independently of exercise dose Quantitative: questionnaires + physical tests Pre- and postintervention assessments |
|
|
|
|
| Meeks et al. (2020) | Follow a cohort of older theatergoers for two seasons to examine their experience during each play they attend Quantitative: questionnaires Pre- and postintervention assessments |
|
|
|
|
| Nadasen (2008) | Examine how participants in dance classes are directly affected by their line dancing activities Qualitative: interview and open-ended questions Pre- and postintervention assessments |
|
|
|
|
| Pentikäinen et al. (2021) | Explore whether active participation in choral singing is associated with cognitive, emotional and social wellbeing and quality of life in healthy older adults Quantitative: cognitive tests + questionnaires |
|
|
|
|
| Yuen et al. (2011) | Assess the impact of participation in the SAASY program on individuals’ psychological wellbeing and health-related quality of life Qualitative and quantitative: interview and questionnaire Pre- and postintervention assessments |
|
|
|
|
Presentation of results
All the results of the present literature review are presented in the same way: a brief description of the studies concerned, following by a paragraph on the interventional ones and a paragraph on the observational ones. In each case, we report any divergent results: first, the results confirming that physical and/or cognitive activities can be a vector of better physical, cognitive, psychological and social quality of life for the older people; then the results refuting (or at least not validating) this notion.
Physical quality of life
Six of the 20 studies examined the effects of various activities on physical quality of life. Four of them assessed the effects of an intervention program (Emery and Gatz, 1990; Yuen et al., 2011; Kamegaya et al., 2014; Levinger et al., 2020), and the other two (observational) studies looked at activities already performed by older adults and assessed the benefits of social engagement in terms of physical function (Chang et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2015).
Two of the four interventional studies showed an increase in self-reported physical activity after the intervention (Yuen et al., 2011; Levinger et al., 2020), as well as substantial improvements in all three objective measures of physical function (fall risk, endurance, strength; Levinger et al., 2020). Emery and Gatz (1990) and Kamegaya et al.’s (2014) studies found no improvement in physical function, as measured by an objective assessment of physical ability after participation in a 12-week intervention program.
The two observational studies assessing physical abilities subjectively, via questionnaires or interviews, found improvements in all the physical abilities that were assessed (e.g., muscle strength, flexibility, motor skills, coordination, mobility, pain reduction; Chang et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2015). Chang et al. (2014), highlighted direct links between social relationships and physical health, and between leisure activities and physical health.
Cognitive quality of life
Four of the 20 studies examined the effects of various activities on cognitive quality of life. Three of them assessed the effects of an intervention program (Emery and Gatz, 1990; Kamegaya et al., 2014; MacAulay et al., 2019), while the fourth (observational) study explored the effect of participating in leisure activities on cognitive functions (Pentikäinen et al., 2021).
One of the three interventional studies highlighted significant changes in global cognition, verbal fluency and visual memory performance after a music program, with improvements in executive attention, processing speed, and working memory (MacAulay et al., 2019). The second study found a significant increase in cognitive scores for the physical activity program and leisure intervention group compared with a control group on an animal naming task and analogy task (Kamegaya et al., 2014). However, there were no other differences on the other cognitive tasks probing executive function, attention, memory, and visuospatial function (Kamegaya et al., 2014). The third interventional study, which assessed the effect of physical exercise program or social activities on cognitive functions, found no effect of the program on any of the cognitive functions (e.g., verbal and working memory, processing speed) in either group in their study (Emery and Gatz, 1990).
The observational study by Pentikäinen et al. (2021) assessed the effects of choir membership on participants’ cognitive abilities. The authors highlighted the benefits of this social group activity on cognitive functions and in particular on the verbal flexibility subdomain of executive functions. However, although they highlighted a significant difference between choir and control groups on the subdomain of verbal flexibility, the groups did not differ on other cognitive domains such as memorization, episodic memory, processing speed, and inhibition (Pentikäinen et al., 2021).
Social quality of life
Eleven of the 20 studies examined the effects of various activities on the social dimension of quality of life. Six of them assessed the effects of an intervention program (musical training, physical activity program, etc.; McAuley et al., 2000; Nadasen, 2008; Yuen et al., 2011; Kamegaya et al., 2014; MacAulay et al., 2019; Levinger et al., 2020), while the other five (observational studies) explored the advantages and effects of participating in leisure activities on social quality of life (Aday et al., 2006; Chang et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2015; Dare et al., 2018; Pentikäinen et al., 2021).
For the interventional studies, the authors showed that taking part in leisure and social group programs is rewarded by social support (McAuley et al., 2000) and valuable socialization (MacAulay et al., 2019). Social empowerment provides the opportunity for social interactions or relationships (Yuen et al., 2011) that strengthen friendships, expressed through mutual emotional and social support (Nadasen, 2008). MacAulay et al. (2019) concluded that the learning, social engagement, and social support offered by these activities are the direct result of group participation. Moreover, McAuley et al. (2000) explained that the social component of the exercise environment can influence affective responses to exercise. However, although both Kamegaya et al. (2014) and Levinger et al. (2020) agreed that group exercise improves quality of life, they failed to observe any other differences in social support (Kamegaya et al., 2014) or changes in socialization and social isolation (Levinger et al., 2020) as a result of the program. Similarly, Yuen et al. (2011) found no significant improvement in social functioning scores.
The observational studies also reported positive effects of leisure or physical activity on quality of life at the social level. Leisure activities are a means of promoting social relationships (Kim et al., 2015), which in turn foster people’s engagement in these activities (Aday et al., 2006). Some authors have underlined the importance of the social context of practice regarding people’s engagement in these activities and the effects on health, notably at the social level, but also in a more general way. For example, Chang et al. (2014) suggested that there is a link between social relationships and leisure activities, and explained that better social relationships can enhance and motivate the adoption of health-promoting behavior. Dare et al. (2018, p. 879) stated that “While interest in an activity may motivate people to join a group, it is the sense of belonging and connection generated by the group that maintains participation and social engagement.” In Aday et al. (2006)’s study, women who found social support at the center were more likely to engage in center activities. By engaging in social activities, participants can increase their opportunities to interact with others, expand their social networks (Kim et al., 2015), and increase their perceived social wellbeing (Pentikäinen et al., 2021).
Participating in activities gives people an opportunity to develop close friendships and raise the level of perceived social support (Aday et al., 2006). Moreover, Dare et al. (2018) found that respondents lent more importance to the opportunity to socialize with others and the enjoyment of their interactions than to the activity itself. The ability to connect with others was particularly important for people living alone. However, when Aday et al. (2006) examined the influence of friendship at the end of life and participation in center activities on health by comparing single women and women in couples, they found little difference between the two groups in terms of friendship development, perceived social support, and depth of friendships. In general, there was no difference between single women and women in couples in terms of self-rated health (Aday et al., 2006). Finally, Dare et al. (2018) mentioned barriers to social participation such as lack of availability or accessibility, and problems of social integration, citing the testimony of a participant who said she was “alone in a crowd.”
Psychological quality of life
Thirteen of the 20 studies examined the effects of various activities on psychological quality of life. Seven (Emery and Gatz, 1990; McAuley et al., 2000; Yuen et al., 2011; Kamegaya et al., 2014; MacAulay et al., 2019; Levinger et al., 2020; Meeks et al., 2020) of them assessed the effects of an intervention program (musical training, physical activity program, theater, etc.), while the other six (Bailey and McLaren, 2005; Aday et al., 2006; Chang et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2015; Gyasi, 2019; Pentikäinen et al., 2021) observational studies explored the effects of taking part in social, sports and leisure activities on the psychological dimension of quality of life.
The interventional studies showed that participating in leisure, physical and social group programs improves quality of life in general (Emery and Gatz, 1990; McAuley et al., 2000; Yuen et al., 2011; Kamegaya et al., 2014), and more specifically reduces depressive symptoms and enhance sense of belonging, self-esteem, and self-confidence (McAuley et al., 2000; Yuen et al., 2011; Levinger et al., 2020). McAuley et al. (2000) found a reduction in stress and an improvement in emotional wellbeing after a music training intervention. Meeks et al. (2020) concluded that social engagement, enjoyment, knowledge, and perceived sense of belonging contributed significantly to positive affect. These authors claimed that belonging and social engagement have only indirect effects on quality of life, through their impact on positive affect. McAuley et al. (2000) agreed with Meeks et al. (2020), reporting that changes in self-efficacy during the program were significantly related to changes in positive quality of life, psychological distress, and fatigue. These authors explained that a greater increase in self-efficacy was associated with better quality of life and less psychological distress (McAuley et al., 2000). However, Kamegaya et al. (2014) and Emery and Gatz (1990) reported no difference between their groups and no improvement in depressive symptoms or anxiety. Emery and Gatz (1990) reported in particular that the exercise program did not appear to contribute overall to improvements in psychological wellbeing. Yuen et al. (2011) and Levinger et al. (2020), found no improvement in emotional role scores and no change in self-efficacy for exercise outcomes.
Observational studies explored the effects of participating in various activities on psychological quality of life. Kim et al. (2015) and Pentikäinen et al. (2021) showed that participating in singing or social engagement activities reduces negative feelings and emotions, whilst increasing self-esteem and self-confidence, which ultimately improves quality of life. Pentikäinen et al. (2021) added that general health scores were higher for low-activity singers than for high-activity singers. Three of the six studies found associations between activity and psychological wellbeing. Gyasi (2019) highlighted the links between physical activity, social support, and psychological distress: physical activity and social support were both negatively associated with psychological distress, while social support moderated the relationship between physical activity and psychological distress (i.e., the greater the social support, the stronger the negative association between physical activity and psychological distress). Bailey and McLaren (2005) highlighted the relationship between physical activity and depressive symptoms, reporting that more hours of group physical activity were associated with fewer depressive symptoms. Higher scores on sense of belonging and psychological status were also associated with more hours of group physical activity. These higher levels of sense of belonging were associated with lower levels of depressive symptoms and suicidal ideation (Bailey and McLaren, 2005). Chang et al. (2014) found a direct relation between social relationships and psychological wellbeing, and a direct effect of leisure activities on psychological wellbeing. They showed that the links between social relationships and physical health or psychological wellbeing were strengthened by leisure activity (Chang et al., 2014). For their part, Aday et al. (2006) observed that single women were more likely to feel less lonely, laugh more, worry less about the future, have more energy, and handle stress better as a result of attending a center. However, Pentikäinen et al. (2021) found no effect of song participation on depressive symptoms.
General quality of life
Five of the 20 studies examined the effects of various activities on general quality of life. Two (Camic et al., 2014; Gagliardi et al., 2019) of them assessed the effects of an intervention program (agricultural or cultural). The other three (observational) studies examined the benefits of engaging in a club’s leisure activities (Kim et al., 2014), as well as changes in participants’ health status following regular group leisure activity (Komatsu et al., 2017), or in comparison with single or group modes of practice (Kanamori et al., 2016).
For the interventional studies, Camic et al. (2014) and Gagliardi et al. (2019) reported an improvement in the level of cognitive engagement (Camic et al., 2014), as well as benefits at the social level. They showed that the intervention setting (art gallery or farm) increased social participation, with increases in participants’ contacts with family or friends, and in the number of leisure activities. In general, they reported that in both settings, the interventions led to the expansion of social networks and a sense of solidarity (Gagliardi et al., 2019), and helped people feel active members of society, socially active, and valued as individuals (Camic et al., 2014). However, the authors found no significant difference between general quality of life scores before and after the program, reporting that self-reported quality of life remained stable across the intervention (Camic et al., 2014; Gagliardi et al., 2019).
For the observational studies, Kim et al. (2014) did not examine changes in quality of life, but rather the perceived benefits of serious engagement in leisure activities. They highlighted three main benefits of this engagement, namely (1) a psychological benefit, with the development of a positive sense of pleasure, improved confidence, and self-esteem, (2) a social benefit, with the creation of social support, the development of positive social interaction fostered in these activities, and the development of a sense of friendship, and (3) a physical benefit, with an improvement in physical health due to the increase in physical strength and endurance (Kim et al., 2014). Kanamori et al. (2016) and Komatsu et al. (2017) were interested in the perception of changes in health according to the context of single or group practice. Kanamori et al. (2016) found that engaging in group physical activity increased self-reported health, as self-reported poor health was significantly lower for all exercise groups, compared with participants who exercised alone. The authors suggested that social relationships are behind the health benefits of group exercise, and regular group exercise has important health benefits. These results are consistent with those of Komatsu et al. (2017), who showed that group exercise contributes to individuals’ physical, mental and social quality of life, by helping them to improve or maintain their functional health, socialize, and enjoy life. They reported the social effects of group exercise, noting that participation in group exercise resulted in interactions with others, prevented isolation through socialization, and stimulated their daily lives (Komatsu et al., 2017).
Discussion
This review, conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines, was designed to establish whether the social relationships fostered by some activities (physical, leisure, cognitive) can be a vector of better physical, mental and social quality of life and a better quality of life for the older people. We begin by discussing our results on the effects of these social relationships on the physical, cognitive, social and psychological dimensions of quality of life, as well as quality of life in general. We then discuss the difficulty of grasping the dimensions of the social relationships fostered by group activities and understanding exactly how they are related to the different dimensions of quality of life. Finally, we discuss the importance of grasping these dimensions for future research and the challenges we have identified as a result of this review.
First, the present review highlighted the benefits of practicing various group activities in terms of improving or preserving older people’s quality of life. Most of the studies included in this review reported improvements in the physical, cognitive, social and psychological dimensions of quality of life. At the physical level, there was an improvement in physical condition (flexibility, coordination, endurance, etc.; Yuen et al., 2011; Chang et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2015; Levinger et al., 2020), as well as an increase in practice time (Levinger et al., 2020), bringing an improvement in functional autonomy. At the cognitive level, there were improvements in executive attention, processing speed, global cognition, verbal fluency, and memory (Kamegaya et al., 2014; MacAulay et al., 2019). These results are in line with the literature, which shows that the practice of physical and/or cognitive activity is beneficial for the cognitive health of Colcombe et al. (2003); Gheysen et al. (2018) and Guo et al. (2020). Our review also showed that physical activity can benefit the social and psychological dimensions of quality of life, reporting the development of social support, the reinforcement of autonomy, social interactions, and an increase in perceived quality of life (Nadasen, 2008; Yuen et al., 2011; MacAulay et al., 2019), as well as the development of a sense of belonging, and the strengthening of self-esteem and confidence (McAuley et al., 2000; Yuen et al., 2011; Levinger et al., 2020). The studies in this review all confirmed the beneficial effects of practicing diverse activities on the different dimensions of quality of life, as well as on general quality of life. Several studies investigating the effects on quality of life in general showed that group activities have beneficial effects on physical, mental and social health, and contribute to the maintenance of functional health in Camic et al. (2014); Kanamori et al. (2016) and Gagliardi et al. (2019). However, some of the studies included in this review failed to find any beneficial effect of group activity in some domains, simply observing the maintenance of basic physical (Emery and Gatz, 1990; Kamegaya et al., 2014), cognitive (Emery and Gatz, 1990; Kamegaya et al., 2014; Pentikäinen et al., 2021) and social (Aday et al., 2006) abilities. Failure to find significant relationships with certain dimensions or subdimensions of quality of life can be explained by the fact that some of the studies included in this review had sample sizes that were too small to allow relationships between activity and health to be identified in older people. Moreover, we included both interventional and observational studies, which did not all use the same assessment procedures (pre- and postintervention assessments, assessment of the effect of an intervention program, group comparisons, comparisons of solitary versus group mode of practice, quantitative and/or qualitative assessments), potentially leading to a methodological bias, with the resulting diversity and heterogeneity of results.
Although the studies included in this review yielded important and interesting results, and tended to agree with the rest of the literature on the beneficial effects of practicing different types of activity on older people’s cognitive functions and quality of life (Kelly et al., 2017; Marsillas et al., 2017; Guo et al., 2020), they had several limitations. In particular, there was difficulty grasping the dimensions of the social relationships fostered by group activities. The studies included in this review highlighted the beneficial effects of practicing group activities on the different physical, cognitive, social, and psychological dimensions of quality of life, but the actual role of the social relationships and the ways in which they influenced quality of life were not explained. As their dimensions were only very weakly defined in these studies, if at all, these relationships were treated as contextual data, rather than processes. We are therefore not in a position to say how and under what conditions the social relationships fostered by group activities affect older people’s quality of life and describe its direct impact on the specific dimensions of quality of life. The same observation was made by Haslam, who argued that the contribution of social factors to health remains underestimated and underemphasized in the literature (Haslam et al., 2018). The present review did not enable us to shed any further light on the contribution of social factors to the physical, cognitive and psychological components of quality of life.
Wakefield et al. (2019) recently stressed that improving quality of life involves addressing the complex interaction between people’s health and their social worlds. According to the notion of social cure, membership of a social group can improve quality of life, but only if members identify with the group (subjective sense of belonging to the group in question; Haslam et al., 2014, 2018). This social cure notion suggests that social identities can provide psychological resources, including a sense of connection among group members that engenders a sense of trust, meaning and purpose in life, as well as social support from other group members to help cope with life’s stresses and strains (Haslam et al., 2005; Greenaway et al., 2015; Wakefield et al., 2019). It is therefore important to explore this notion in depth, in order to define the impact of social factors and their relationships with the physical, cognitive, social, and psychological dimensions of quality of life, in order to act effectively on the quality of life of older people and promote healthy aging.
Future research must demonstrate the importance of social factors for health and identify the precise relationships and interactions between social relationships and quality of life dimensions. We see at least two main challenges in this area.
Challenge 1: relationship between practice environment, cognitive abilities, and perceived benefits of practice
We suspect that the positive effects of combined activities (simultaneously practicing physical and cognitive activities) on cognitive and general quality of life are influenced by the environment in which these activities are performed. We suspect that group practice and practice environments fostering social relationships and strong social interactions have positive benefits for older people’s general and cognitive health. This concerns the notion of environmental enrichment, namely, the stimulation of the brain by the physical, cognitive and social environment. We would expect older people to perform better on the various physical, cognitive and psychosocial assessments in conditions of group practice, as well as in an enriched environment favoring social relationships.
This hypothesis could be tested with a population of older people in three different practice environments: (1) combined (physical and cognitive) activity program at home; (2) combined activity program in a traditional group environment (gymnasium); and (3) combined group activity program in an enriched environment promoting social relationships and social interactions. The programs and the assessments would have to be identical across these three conditions, in order to test this hypothesis.
Challenge 2: psychosocial factors as mediators of the relationship
A second challenge would be to identify some of the key psychosocial factors that make older people’s cognitive quality of life more or less sensitive to the effects of combined activity practice, as a function of the practice environment. We suspect that it is the fluctuation of social factors (e.g., self-esteem, perceived social support) involved during practice that mediate the relationship between practice environment and older people’s cognitive abilities and their perceived quality of life. The feeling of belonging to a group and the relationships developed during group activities may enhance social factors such as perceived self-esteem or perceived social support, which then positively mediate the relationship between practice environment and participants’ cognitive abilities and perceived quality of life.
These measures of psychosocial factors could be used as potential mediators in statistical analyses to test whether older adults who engage in combined activity in a habitual group environment and in an enriched environment where social relationships are fostered benefit more in terms of cognitive ability and are more likely to have better perceived quality of life.
Conclusion
Although the present review confirmed the benefits of physical and/or cognitive group activity for older people, in general quality of life, the contribution of social factors to this relationship remains unknown. The contribution of this review is, however, to have highlighted the complexity of objectifying the contribution of these social relationships and the mechanisms that come into play during the practice of these activities and their benefit on quality of life. Further studies assessing the relationships and interactions between these social factors and cognitive ability and quality of life could help to expand on these findings and identify new ways of promoting healthy aging.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
This study was initially drafted by TG. Subsequent version was reviewed by DC, GB, and CE. Revision were made by TG. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine grant number [AAPR2021-2020-12021410].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1166072/full#supplementary-material
References
- Aday R. H., Kehoe G. C., Farney L. A. (2006). Impact of senior center friendships on aging women who live alone. J. Women Aging 18, 57–73. doi: 10.1300/J074v18n01_05, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey M., McLaren S. (2005). Physical activity alone and with others as predictors of sense of belonging and mental health in retirees. Aging Ment. Health 9, 82–90. doi: 10.1080/13607860512331334031, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basak C., Qin S., O’Connell M. A. (2020). Differential effects of cognitive training modules in healthy aging and mild cognitive impairment: a comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Psychol. Aging 35, 220–249. doi: 10.1037/pag0000442, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camic P. M., Tischler V., Pearman C. H. (2014). Viewing and making art together: a multi-session art-gallery-based intervention for people with dementia and their carers. Aging Ment. Health 18, 161–168. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2013.818101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carta M. G., Cossu G., Pintus E., Zaccheddu R., Callia O., Conti G., et al. (2021). Moderate exercise improves cognitive function in healthy elderly people: results of a randomized controlled trial. CPEMH 17, 75–80. doi: 10.2174/1745017902117010075, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P.-J., Wray L., Lin Y. (2014). Social relationships, leisure activity, and health in older adults. Health Psychol. 33, 516–523. doi: 10.1037/hea0000051, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colcombe S. J., Erickson K. I., Raz N., Webb A. G., Cohen N. J., McAuley E., et al. (2003). Aerobic fitness reduces brain tissue loss in aging humans. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Med. Sci. 58, M176–M180. doi: 10.1093/gerona/58.2.M176, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dare J., Wilkinson C., Marquis R., Donovan R. J. (2018). “The people make it fun, the activities we do just make sure we turn up on time.” factors influencing older adults participation in community-based group programmes in Perth, Western Australia. Health Soc. Care Community 26, 871–881. doi: 10.1111/hsc.12600, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depp C. A., Jeste D. V. (2006). Definitions and predictors of successful aging: a comprehensive review of larger quantitative studies. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 14, 6–20. doi: 10.1097/01.JGP.0000192501.03069.bc, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener E., Suh E., Lucas R., Smith H. (1999). Subjective well-being: three decades of progress. Psychol. Bull. 125, 276–302. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.125.2.276, PMID: 37210151 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Downs S. H., Black N. (1998). The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 52, 377–384. doi: 10.1136/jech.52.6.377, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery C. F., Gatz M. (1990). Psychological and cognitive effects of an exercise program for community-residing older Adults1. The Gerontologist 30, 184–188. doi: 10.1093/geront/30.2.184, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estebsari F., Dastoorpoor M., Khalifehkandi Z. R., Nouri A., Mostafaei D., Hosseini M., et al. (2020). The concept of successful aging: a review article. CAS 13, 4–10. doi: 10.2174/1874609812666191023130117, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong P., Cruwys T., Haslam C., Haslam S. A. (2019). Neighbourhood identification buffers the effects of (de-)gentrification and personal socioeconomic position on mental health. Health Place 57, 247–256. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2019.05.013, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardi C., Santini S., Piccinini F., Fabbietti P., di Rosa M. (2019). A pilot programme evaluation of social farming horticultural and occupational activities for older people in Italy. Health Soc. Care Community 27, 207–214. doi: 10.1111/hsc.12641 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangbè M., Ducharme F. (2006). Le « bien vieillir »: concepts et modèles. Med. Sci. (Paris) 22, 297–300. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2006223297, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen F., Poppe L., DeSmet A., Swinnen S., Cardon G., De Bourdeaudhuij I., et al. (2018). Physical activity to improve cognition in older adults: can physical activity programs enriched with cognitive challenges enhance the effects? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 15:63. doi: 10.1186/s12966-018-0697-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenaway K. H., Haslam S. A., Cruwys T., Branscombe N. R., Ysseldyk R., Heldreth C. (2015). From “we” to “me”: group identification enhances perceived personal control with consequences for health and well-being. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 109, 53–74. doi: 10.1037/pspi0000019, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W., Zang M., Klich S., Kawczyński A., Smoter M., Wang B. (2020). Effect of combined physical and cognitive interventions on executive functions in older adults: a meta-analysis of outcomes. IJERPH 17:6166. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176166, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyasi R. M. (2019). Social support, physical activity and psychological distress among community-dwelling older Ghanaians. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 81, 142–148. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2018.11.016, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam C., Cruwys T., Haslam S. A. (2014). “The we’s have it”: evidence for the distinctive benefits of group engagement in enhancing cognitive health in aging. Soc. Sci. Med. 120, 57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2014.08.037, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam S. A., McMahon C., Cruwys T., Haslam C., Jetten J., Steffens N. K. (2018). Social cure, what social cure? The propensity to underestimate the importance of social factors for health. Soc. Sci. Med. 198, 14–21. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.12.020, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam S. A., O’Brien A., Jetten J., Vormedal K., Penna S. (2005). Taking the strain: social identity, social support, and the experience of stress. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 44, 355–370. doi: 10.1348/014466605X37468, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingrisch D. (1995). Conformity and resistance as women age. In Connecting gender ageing: A sociological approach. (Eds.) Arber S., Ginn J., (Buckingham: Open University Press; ), 42–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jetten J., Haslam C., Haslam S. A. (2012). The social cure: Identity, health and well-being. Hove; New York: Psychology Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kamegaya T., Araki Y., Kigure H., Long-Term-Care Prevention Team of Maebashi City. Yamaguchi H. (2014). Twelve-week physical and leisure activity programme improved cognitive function in community-dwelling elderly subjects: a randomized controlled trial: preventing cognitive decline. Psychogeriatrics 14, 47–54. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12038, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori S., Takamiya T., Inoue S., Kai Y., Kawachi I., Kondo K. (2016). Exercising alone versus with others and associations with subjective health status in older Japanese: the JAGES cohort study. Sci. Rep. 6:39151. doi: 10.1038/srep39151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellezi B., Wakefield J. R. H., Stevenson C., McNamara N., Mair E., Bowe M., et al. (2019). The social cure of social prescribing: a mixed-methods study on the benefits of social connectedness on quality and effectiveness of care provision. BMJ Open 9:e033137. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033137, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. E., Duff H., Kelly S., McHugh Power J. E., Brennan S., Lawlor B. A., et al. (2017). The impact of social activities, social networks, social support and social relationships on the cognitive functioning of healthy older adults: a systematic review. Syst. Rev. 6:259. doi: 10.1186/s13643-017-0632-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. E., Loughrey D., Lawlor B. A., Robertson I. H., Walsh C., Brennan S. (2014). The impact of cognitive training and mental stimulation on cognitive and everyday functioning of healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 15, 28–43. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2014.02.004, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Irwin L., Kim M., Chin S., Kim J. (2015). The role of leisure engagement for health benefits among Korean older women. Health Care Women Int. 36, 1357–1374. doi: 10.1080/07399332.2015.1077843, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Yamada N., Heo J., Han A. (2014). Health benefits of serious involvement in leisure activities among older Korean adults. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well-Being 9:24616. doi: 10.3402/qhw.v9.24616, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu H., Yagasaki K., Saito Y., Oguma Y. (2017). Regular group exercise contributes to balanced health in older adults in Japan: a qualitative study. BMC Geriatr. 17:190. doi: 10.1186/s12877-017-0584-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft E. (2012). Cognitive function, physical activity, and aging: possible biological links and implications for multimodal interventions. Aging Neuropsychol. Cognit. 19, 248–263. doi: 10.1080/13825585.2011.645010, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger P., Panisset M., Dunn J., Haines T., Dow B., Batchelor F., et al. (2020). Exercise interveNtion outdoor proJect in the cOmmunitY for older people – results from the ENJOY seniors Exercise Park project translation research in the community. BMC Geriatr. 20:446. doi: 10.1186/s12877-020-01824-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin H., Stoeckel K. J. (2016). Social network, activity participation, and cognition: a complex relationship. Res. Aging 38, 76–97. doi: 10.1177/0164027515581422, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacAulay R. K., Edelman P., Boeve A., Sprangers N., Halpin A. (2019). Group music training as a multimodal cognitive intervention for older adults. Psychomusicol. Music Mind Brain 29, 180–187. doi: 10.1037/pmu0000239, PMID: 36327345 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mandolesi L., Polverino A., Montuori S., Foti F., Ferraioli G., Sorrentino P., et al. (2018). Effects of physical exercise on cognitive functioning and wellbeing: biological and psychological benefits. Front. Psychol. 9:509. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00509 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsillas S., De Donder L., Kardol T., van Regenmortel S., Dury S., Brosens D., et al. (2017). Does active ageing contribute to life satisfaction for older people? Testing a new model of active ageing. Eur. J. Ageing 14, 295–310. doi: 10.1007/s10433-017-0413-8, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAuley E., Blissmer B., Katula J., Duncan T. E. (2000). Exercise environment, self-efficacy, and affective responses to acute exercise in older adults. Psychol. Health 15, 341–355. doi: 10.1080/08870440008401997 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara N., Stevenson C., Muldoon O. T. (2013). Community identity as resource and context: a mixed method investigation of coping and collective action in a disadvantaged community: community identity as resource and context. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 43, 393–403. doi: 10.1002/ejsp.1953 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks S., Vandenbroucke R. J., Shryock S. K. (2020). Psychological benefits of attending the theatre associated with positive affect and well-being for subscribers over age 60. Aging Ment. Health 24, 333–340. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2018.1534082, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merriam S. B. (1998). Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education. Revised and Expanded from Case Study Research in Education. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Mewborn C. M., Lindbergh C. A., Stephen Miller L. (2017). Cognitive interventions for cognitively healthy, mildly impaired, and mixed samples of older adults: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Neuropsychol. Rev. 27, 403–439. doi: 10.1007/s11065-017-9350-8, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moher D., Liberati A., Tetzlaff J., Altman D. G., for the PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadasen K. (2008). “Life without line dancing and the other activities would be too dreadful to imagine”: an increase in social activity for older women. J. Women Aging 20, 329–342. doi: 10.1080/08952840801985060, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentikäinen E., Pitkäniemi A., Siponkoski S.-T., Jansson M., Louhivuori J., Johnson J. K., et al. (2021). Beneficial effects of choir singing on cognition and well-being of older adults: evidence from a cross-sectional study. PLoS One 16:e0245666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245666, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitkala K. H., Routasalo P., Kautiainen H., Sintonen H., Tilvis R. S. (2011). Effects of socially stimulating group intervention on lonely, older People’s cognition: a randomized, controlled trial. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 19, 654–663. doi: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e3181f7d8b0, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rejeski W. J., Mihalko S. L. (2001). Physical activity and quality of life in older adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 56, 23–35. doi: 10.1093/gerona/56.suppl_2.23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter-Lorenz P. A., Park D. C. (2014). How does it STAC up? Revisiting the scaffolding theory of aging and cognition. Neuropsychol. Rev. 24, 355–370. doi: 10.1007/s11065-014-9270-9, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sani F., Madhok V., Norbury M., Dugard P., Wakefield J. R. H. (2015). Greater number of group identifications is associated with healthier behaviour: evidence from a Scottish community sample. Br. J. Health Psychol. 20, 466–481. doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12119, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman T. E., Lusignolo T. M., Albert M., Berkman L. (2001). Social relationships, social support, and patterns of cognitive aging in healthy, high-functioning older adults: MacArthur studies of successful aging. Health Psychol. 20, 243–255. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.20.4.243, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small B. J., Dixon R. A., McArdle J. J., Grimm K. J. (2012). Do changes in lifestyle engagement moderate cognitive decline in normal aging? Evidence from the Victoria longitudinal study. Neuropsychology 26, 144–155. doi: 10.1037/a0026579, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield J. R. H., Bowe M., Kellezi B., McNamara N., Stevenson C. (2019). When groups help and when groups harm: origins, developments, and future directions of the “social cure” perspective of group dynamics. Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass 13:e12440. doi: 10.1111/spc3.12440 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- WHO (1986). PROMOTION DE LA SANTE - Charte d’OTTAWA.
- World Health Organization (WHO) (1994). Development of the WHOQOL: rationale and current status. Int. J. Ment. Health 23, 24–56. doi: 10.1080/00207411.1994.11449286 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2017). Global strategy and action plan on ageing and health.
- Yang Y. C., Boen C., Gerken K., Li T., Schorpp K., Harris K. M. (2016). Social relationships and physiological determinants of longevity across the human life span. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113, 578–583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1511085112, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen H. K., Mueller K., Mayor E., Azuero A. (2011). Impact of participation in a theatre programme on quality of life among older adults with chronic conditions: a pilot study: impact of theatre programme participation. Occup. Ther. Int. 18, 201–208. doi: 10.1002/oti.327, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X., Yin S., Lang M., He R., Li J. (2016). The more the better? A meta-analysis on effects of combined cognitive and physical intervention on cognition in healthy older adults. Ageing Res. Rev. 31, 67–79. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.07.003, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.