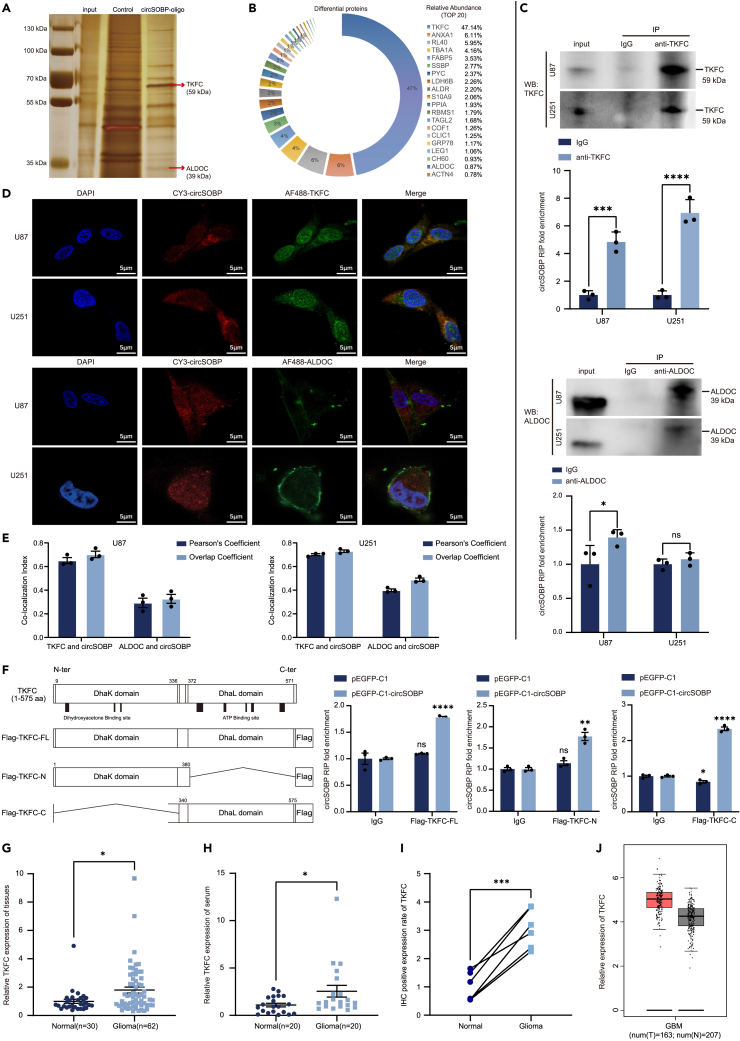
Figure 4.
Identification of TKFC as a binding protein for circSOBP
(A) Potential circSOBP-associated proteins were identified by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. Red arrows indicate bands identified by mass spectrometry as TKFC and ALDOC.
(B) Mass spectrometry (MS) to identify the relative abundance of proteins in specific bands (top 20 shown). The full list of proteins is shown in Table S3.
(C) Anti-TKFC and Anti-ALDOC antibody was used to pull down circSOBP in RIP. Western blotting showed effective pull down of TKFC and ALDOC in U87 and U251 cells. RT-qPCR determined the enrichment efficiency of circSOBP in TKFC and ALDOC pulldown samples, using IgG as a negative control.
(D) RNA in situ hybridization (FISH) and immunofluorescence (IF) double staining were performed to detect the co-localization of circSOBP with TKFC or ALDOC in U87 and U251 cells. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(E) ImageJ analysis of the intracellular distribution of circSOBP with TKFC or ALDOC. Pearson’s Coefficient >0.5 and Overlap Coefficient >0.6 indicate co-localization.
(F) Schematic diagram showing full-length TKFC and multiple truncated forms of TKFC. RT-qPCR analysis of enrichment levels of circSOBP in pulldown experiments of exogenously expressed full-length TKFC and multiple truncated forms. Using IgG as a negative control.
(G) The expression levels of TKFC in 30 normal brain tissues and 62 glioma tissues were detected by RT-qPCR.
(H) The expression levels of TKFC in 20 normal serum cases and 20 glioma serum cases were detected by RT-qPCR.
(I) Positive rate statistics of TKFC in normal brain tissue (n = 6) and glioma tissue (n = 6) by IHC staining.
(J) Expression levels of TKFC in gliomas were sourced from the GEPIA database. Red represents the glioma group (T) and gray represents the normal group (N). All statistics of error bars, S.E.M. from three independent experiments. NS, not significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by two-tailed Student’s t test.