Abstract
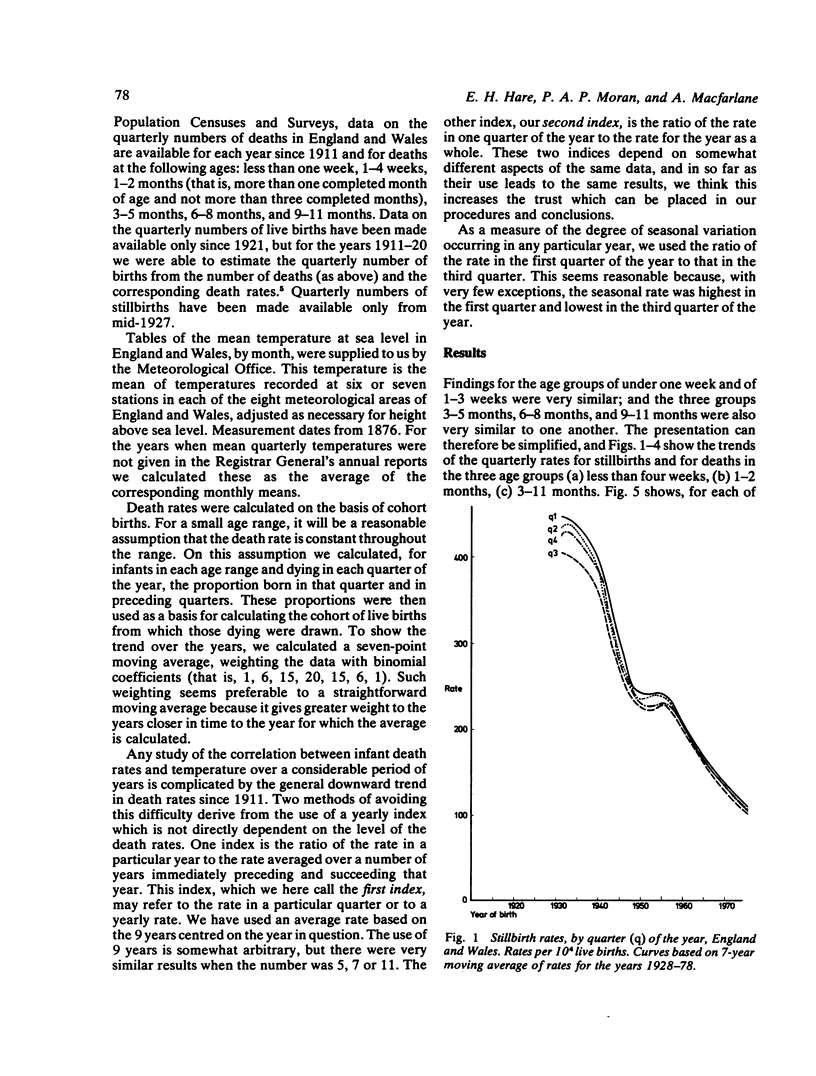
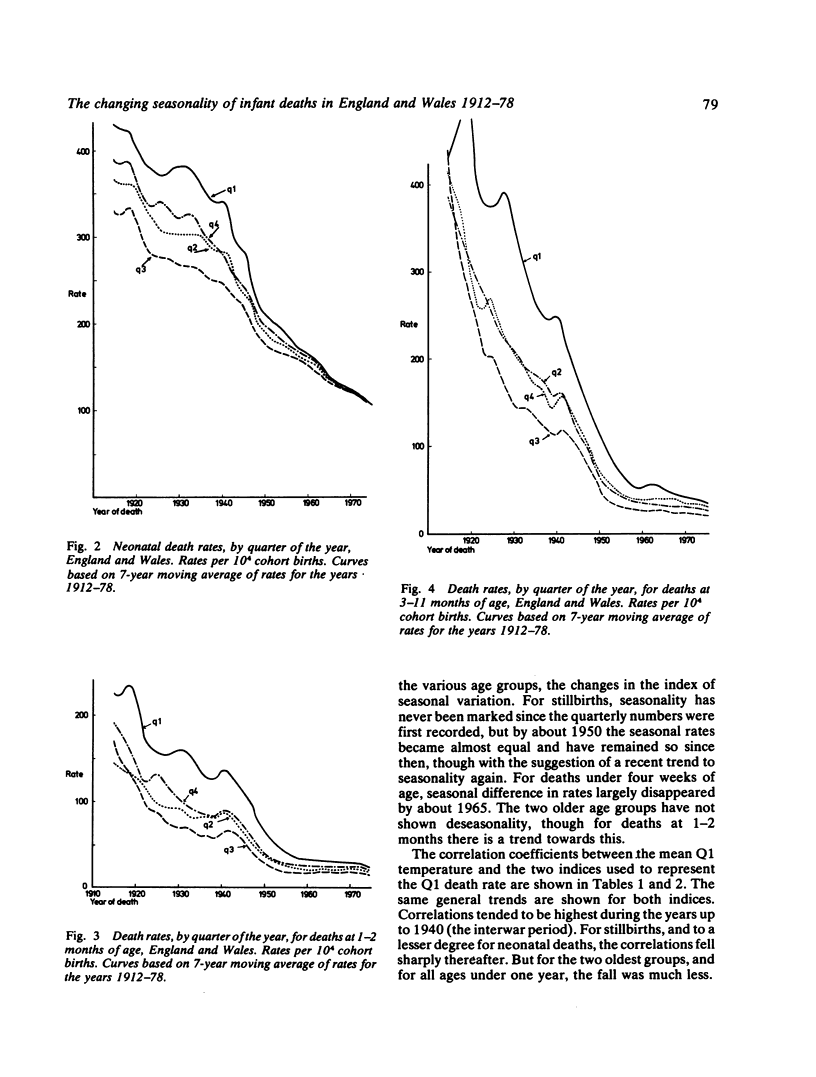
Seasonal variation in the rates of stillbirth, and of deaths under the age of one year, were studied for England and Wales in order to examine (a) changes in the seasonal variation over the years and (b) the correlation between seasonal rates and seasonal temperatures. The quarterly rates of stillbirths were studied for the period 1928-78; and of deaths under the age of one year, in six different age groups, for the period 1912-78. A disappearance of seasonal variation in rates ('deseasonality') occurrred from stillbirths in about 1950, and for neonatal deaths in about 1965. For deaths at 1-2 months a trend towards deseasonality has been apparent since 1955, but there has been no such trends for deaths at 3-11 months of age. In the period before deseasonality, and for the first quarter of the year, there was a high negative correlation between the neonatal death rate and the mean temperature in England and Wales but this correlation fell as the seasonal variation in rates fell. The findings suggest that seasonal variation in the neonatal death rate was closely related to winter temperatures during the period 1921-60. For deaths at 1-11 months old, there has been and still is a relation between temperature and seasonal variation in rates, but the relation was less close than for the neonatal death rate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD J. T. Climate, air pollution, and mortality. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1960 Jul;14:123–135. doi: 10.1136/jech.14.3.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D., Moore F., Sweetnam P. Temperature and deaths from ischaemic heart disease. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1977 Mar;31(1):49–53. doi: 10.1136/jech.31.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull G. M., Morton J. Environment, temperature and death rates. Age Ageing. 1978 Nov;7(4):210–224. doi: 10.1093/ageing/7.4.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane A. Daily mortality and environment in English conurbations. Air pollution, low temperature, and influenza in Greater London. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1977 Mar;31(1):54–61. doi: 10.1136/jech.31.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane A. Daily mortality and environment in English conurbations. II. Deaths during summer hot spells in greater London. Environ Res. 1978 Jun;15(3):332–341. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(78)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


