Al Kury LT, Zeb A, Abidin ZU, et al. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:2715–2727.
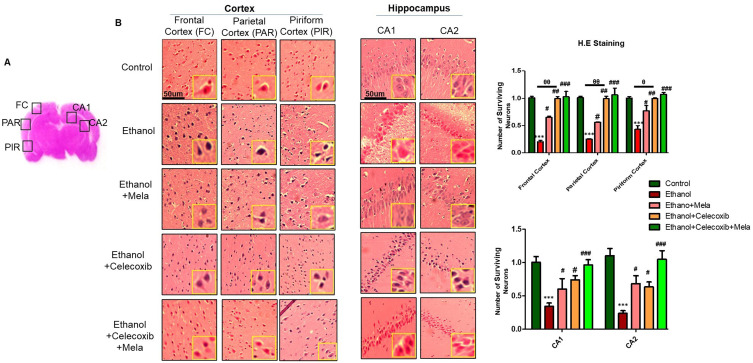
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 4B on page 2723. The image for Ethanol+celecoxib+mela (Piriform-PIR) was used mistakenly leading to a duplication with the Control (Piriform-PIR) images. A new image for Ethanol+celecoxib+mela (Piriform-PIR) was found from the original data and used as a replacement. The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the quality and scientific conclusions of the article.
The correct Figure 4 is as follows.
Figure 4.
Effect of melatonin and celecoxib on neuronal cell death.
Notes: (A) Regions of interest analyzed; (B) H&E staining showing the extent of surviving neurons in the cortex and hippocampus. Bar 50 μm, magnification 20×, n=5/group. Surviving neurons were marked by cytoplasmic swelling, scalloped neurons with intense cytoplasmic eosinophilia, and nuclear basophilia. These changes resulted from neuronal necrosis. Some cells had a shrunken appearance, along with pyknotic nuclei. Intensive neuropil vacuolation can be seen in the ethanol-only group. *Significant difference relative to control; #Significant difference relative to ethanol group; θSignificant difference relative to ethanol + melatonin. Data presented as means ± SEM. Data analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison using GraphPad Prism 5 software. ***P<0.001; #/θP<0.05; ##/θθP<0.01.