Abstract
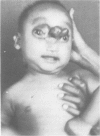
One hundred and thirty nine patients suffering from encephalomeningocoele and myelomeningocoele who had attended the neurosurgical outpatients department of the Rangoon People's Hospital were interviewed. A predominance of frontal encephalomeningocoele was found; a low proportion of these patients had been conceived in the cold season and an increased interval separated the index patients from the previous full term pregnancy of their mothers; no first degree relatives were affected. It is suggested that an environmental factor is implicated in the developmental aetiology.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Klerk D. J., De Villiers J. C. Frontal encephaloceles. S Afr Med J. 1973 Aug 4;47(30):1350–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedrick J. Anencephalus and maternal tea drinking: evidence for a possible association. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 May;67(5):356–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatz G. Fronto-ethmoidal encephalomeningoceles in the population of northern Thailand. Humangenetik. 1970;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00296297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIROUD A., TUCHMANN-DUPLESSIS H., MERCIER-PAROT L. [Observatios on the teratogenic repercussions of thalidomide in the mouse and rabbit]. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1962;156:765–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renwick J. H., Possamai A. M., Munday M. R. Potatoes and spina bifida. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 May;67(5):360–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanwela C. Geographical distribution of fronto-ethmoidal encephalomeningocele. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1972 Aug;26(3):193–198. doi: 10.1136/jech.26.3.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanwela C., Hongsaprabhas C. Fronto-ethmoidal encephalomeningocele. J Neurosurg. 1966 Aug;25(2):172–182. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.25.2.0172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. E., Knights P. J., Anderson J. R. Inheritance and morphology of exencephaly, a neonatal lethal recessive with partial penetrance, in the house mouse. Genet Res. 1978 Oct;32(2):135–149. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300018632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S., MacMahon B. Genetics of anencephaly and spina bifida? Lancet. 1968 Sep 14;2(7568):623–626. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90709-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]