Abstract
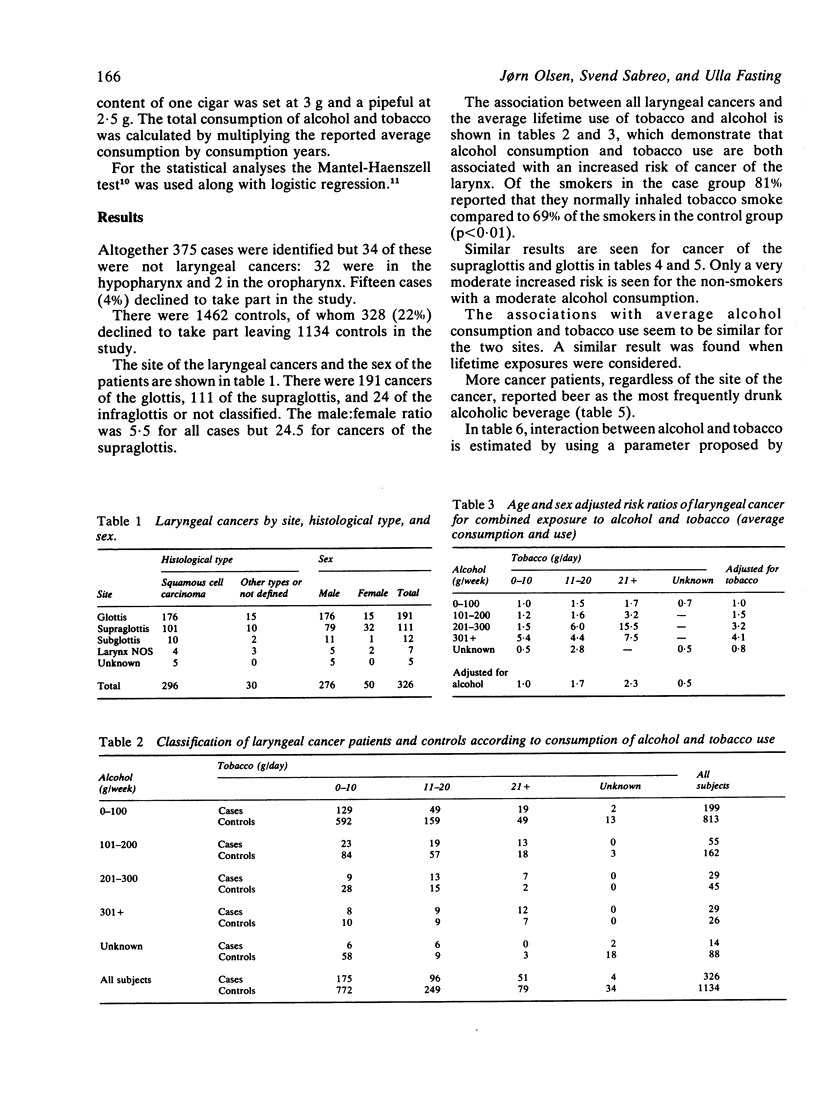
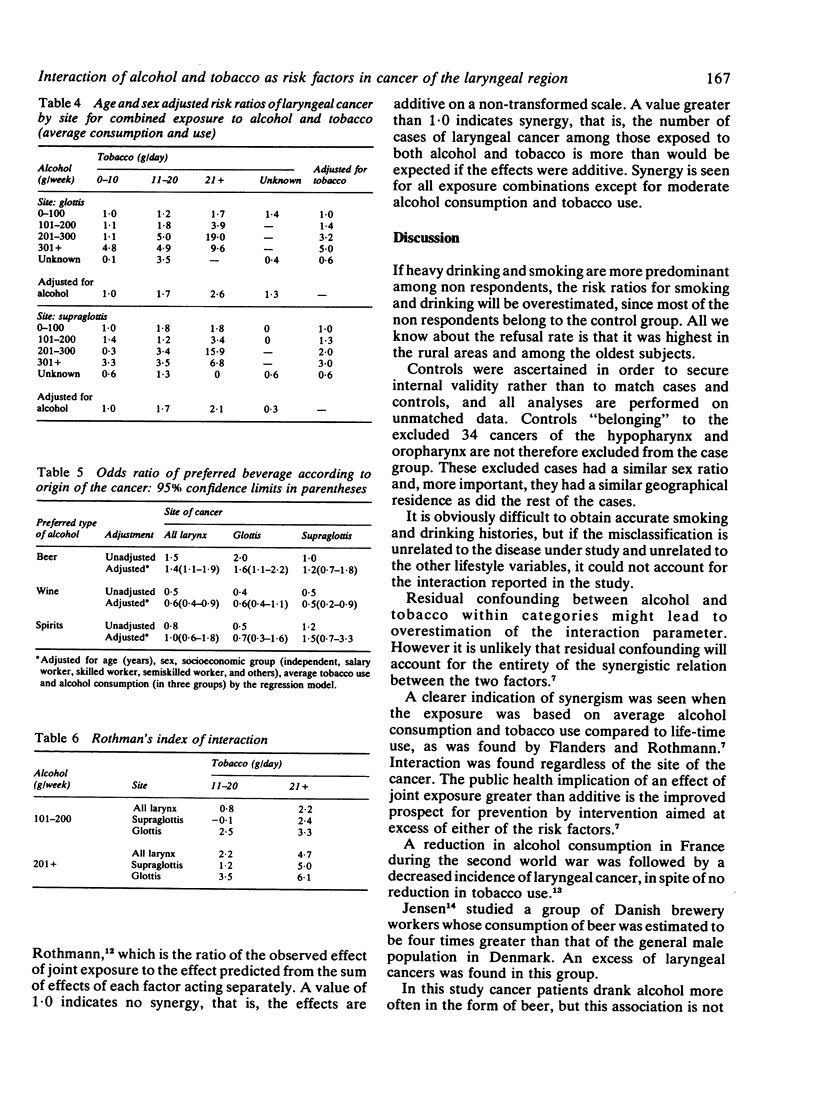
The aim of this study is to present risk assessments for the combined effect of alcohol and tobacco in cancer of the larynx. The case control study included all newly diagnosed laryngeal cancer patients under the age of 75 in Denmark during the years 1980-2. Four age and sex matched controls were selected using the municipal person registry in which the case was listed. Ninety six per cent of all cases and 78% of controls participated in the study, which is based on 326 cases and 1134 controls. Information on alcohol consumption and tobacco use was obtained by means of mailed questionnaires. For all laryngeal cancers as well as for the subgroups concerning cancer of the glottis and supraglottis alcohol consumption and tobacco use were found to be important risk factors. The effect of joint exposure was greater than the effect predicted from the sum of effects of each factor acting separately. Thus the combined effect follows a multiplicative rather than additive model.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Flanders W. D., Rothman K. J. Interaction of alcohol and tobacco in laryngeal cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Mar;115(3):371–379. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds M. W., Thomas D. B., O'Reilly H. P. Asbestos, dental X-rays, tobacco, and alcohol in the epidemiology of laryngeal cancer. Cancer. 1979 Sep;44(3):1114–1120. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197909)44:3<1114::aid-cncr2820440346>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J., Sabroe S., Lajer M. Welding and cancer of the larynx: a case-control study. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1984 May;20(5):639–643. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(84)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J., Sabroe S. Occupational causes of laryngeal cancer. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1984 Jun;38(2):117–121. doi: 10.1136/jech.38.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman K. J., Cann C. I., Flanders D., Fried M. P. Epidemiology of laryngeal cancer. Epidemiol Rev. 1980;2:195–209. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman K. J. The estimation of synergy or antagonism. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 May;103(5):506–511. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuyns A. J., Audigier J. C. Double wave cohort increase for oesophageal and laryngeal cancer in France in relation to reduced alcohol consumption during the second world war. Digestion. 1976;14(3):197–208. doi: 10.1159/000197932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYNDER E. L., BROSS I. J., DAY E. A study of environmental factors in cancer of the larynx. Cancer. 1956 Jan-Feb;9(1):86–110. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195601/02)9:1<86::aid-cncr2820090108>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Covey L. S., Mabuchi K., Mushinski M. Environmental factors in cancer of the larynx: a second look. Cancer. 1976 Oct;38(4):1591–1601. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197610)38:4<1591::aid-cncr2820380425>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


