Figure 7. Unifying model of DMN role in cognition.
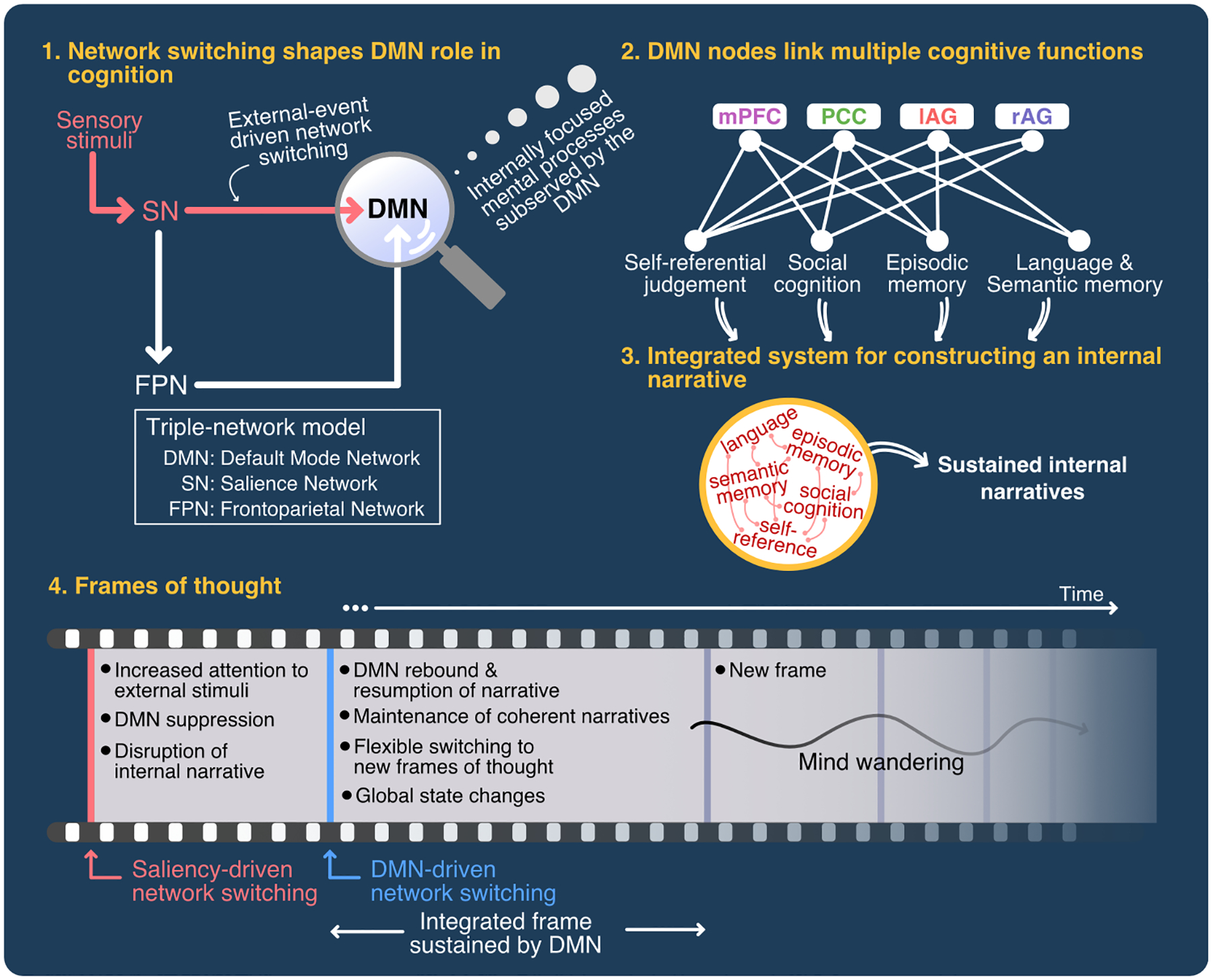
The model posits four key unifying themes that underlie DMN function: (1) Network switching shapes DMN role in cognition. Salient stimuli result in suppression of the DMN during attentionally-demanding tasks. This suppression is followed by a rebound and return to internally-focused mental processes. Multiple lines of evidence suggest that the anterior insula plays an important role in suppression and disengagement of the DMN. (2) DMN nodes link multiple cognitive functions associated with self-referential judgements, social cognition, language and semantic memory, and episodic memory operations. (3) The DMN integrates these cognitive operations to construct an “internal narrative”. (4) The DMN sustains frames of thought, and its hub properties facilitate network switching and global state changes. This dynamic process creates new frames of thought. Mind wandering, one of the cognitive functions ascribed to the DMN, is a natural outcome of this dynamical process.
