Abstract
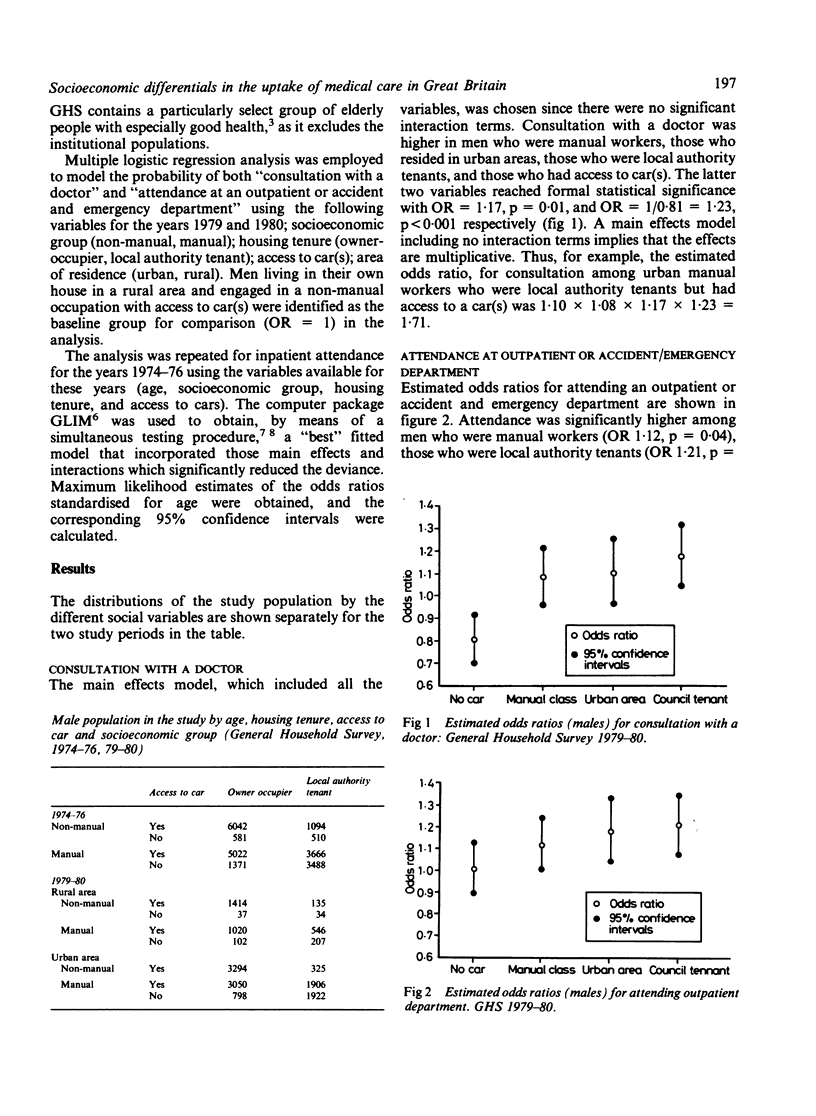
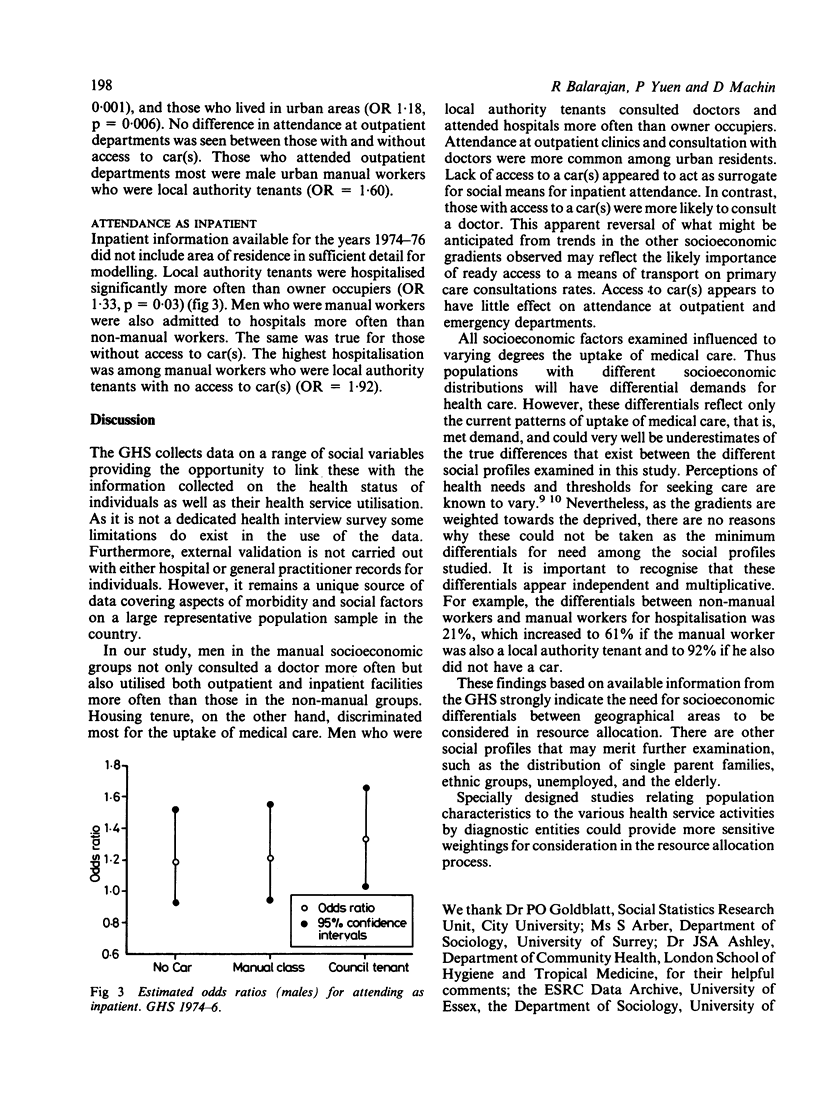
Socioeconomic differentials in the uptake of medical care in men were investigated using data from the General Household Survey (1974-76 and 1979-80). Hospitalisation, attendance at out patient clinics, and consultation with doctors were higher in local authority tenants than in owner occupiers. Men belonging to the manual socioeconomic groups also used services and consulted doctors more often than those in the non-manual groups. Hospitalisation among men was highest among manual workers living in local authority properties without access to car(s) (OR 1.92). Highest attendance at outpatient clinics (OR 1.60) was seen among local authority tenants in urban areas belonging to manual groups. However, consultation with doctors was highest among urban manual workers living in local authority properties but with access to car(s) (OR 1.72). The implications of these findings for resource allocation are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cameron A., Hinton J. Delay in seeking treatment for mammary tumors. Cancer. 1968 Jun;21(6):1121–1126. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196806)21:6<1121::aid-cncr2820210612>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


