Abstract
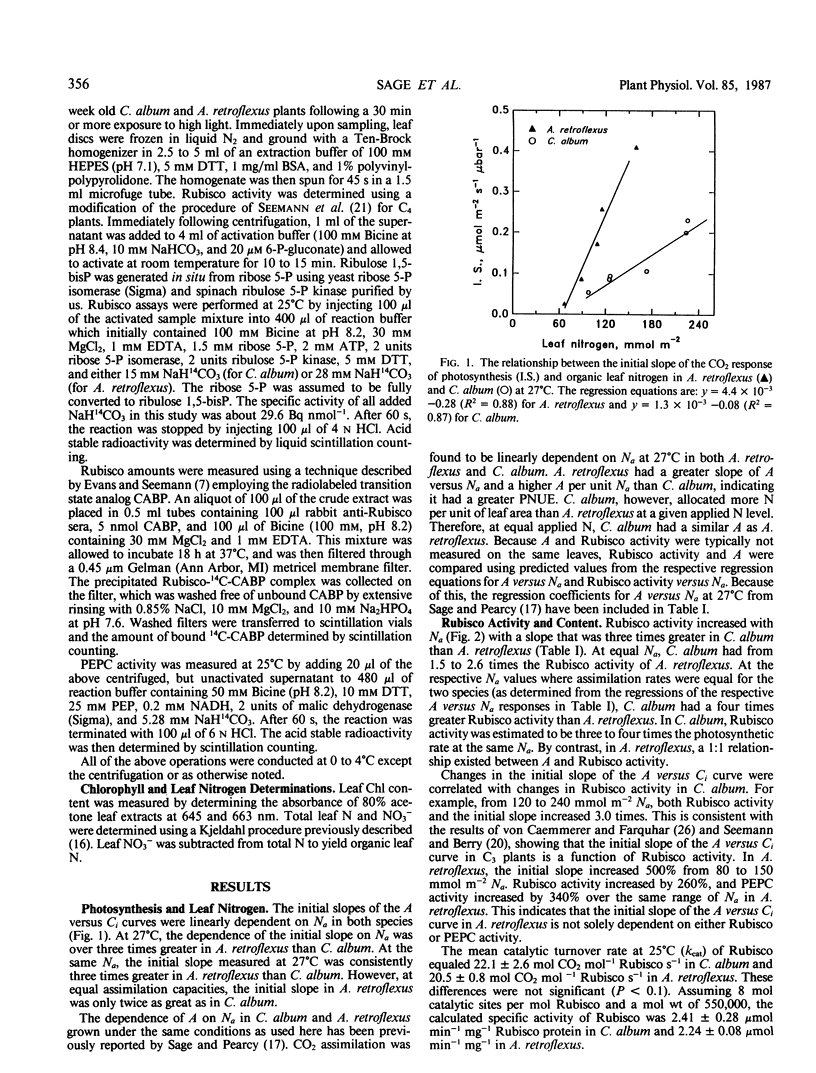
The relationships between leaf nitrogen content per unit area (Na) and (a) the initial slope of the photosynthetic CO2 response curve, (b) activity and amount of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC), and (c) chlorophyll content were studied in the ecologically similar weeds Chenopodium album (C3) and Amaranthus retroflexus (C4). In both species, all parameters were linearly dependent upon leaf Na. The dependence of the initial slope of the CO2 response of photosynthesis on Na was four times greater in A. retroflexus than in C. album. At equivalent leaf Na contents, C. album had 1.5 to 2.6 times more CO2 saturated Rubisco activity than A. retroflexus. At equal assimilation capacities, C. album had four times the Rubisco activity as A. retroflexus. In A. retroflexus, a one to one ratio between Rubisco activity and photosynthesis was observed, whereas in C. album, the CO2 saturated Rubisco activity was three to four times the corresponding photosynthetic rate. The ratio of PEPC to Rubisco activity in A. retroflexus ranged from four at low Na to seven at high Na. The fraction of organic N invested in carboxylation enzymes increased with increased Na in both species. The fraction of N invested in Rubisco ranged from 10 to 27% in C. album. In A. retroflexus, the fraction of Na invested in Rubisco ranged from 5 to 9% and the fraction invested in PEPC ranged from 2 to 5%.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton J. K., Brown R. H. Photosynthesis of Grass Species Differing in Carbon Dioxide Fixation Pathways: V. RESPONSE OF PANICUM MAXIMUM, PANICUM MILIOIDES, AND TALL FESCUE (FESTUCA ARUNDINACEA) TO NITROGEN NUTRITION. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jul;66(1):97–100. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. R. Nitrogen and Photosynthesis in the Flag Leaf of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol. 1983 Jun;72(2):297–302. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. R., Seemann J. R. Differences between Wheat Genotypes in Specific Activity of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase and the Relationship to Photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):759–765. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich J. W., Huffaker R. C. Photosynthesis, leaf resistances, and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase degradation in senescing barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jun;65(6):1103–1107. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.6.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino A., Mae T., Ohira K. Photosynthesis and Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase in Rice Leaves: Changes in Photosynthesis and Enzymes Involved in Carbon Assimilation from Leaf Development through Senescence. Plant Physiol. 1983 Dec;73(4):1002–1007. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.4.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearcy R. W. Acclimation of Photosynthetic and Respiratory Carbon Dioxide Exchange to Growth Temperature in Atriplex lentiformis (Torr.) Wats. Plant Physiol. 1977 May;59(5):795–799. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage R. F., Pearcy R. W. The Nitrogen Use Efficiency of C(3) and C(4) Plants: I. Leaf Nitrogen, Growth, and Biomass Partitioning in Chenopodium album (L.) and Amaranthus retroflexus (L.). Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):954–958. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage R. F., Pearcy R. W. The Nitrogen Use Efficiency of C(3) and C(4) Plants: II. Leaf Nitrogen Effects on the Gas Exchange Characteristics of Chenopodium album (L.) and Amaranthus retroflexus (L.). Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):959–963. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Badger M. R., Berry J. A. Variations in the Specific Activity of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase between Species Utilizing Differing Photosynthetic Pathways. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):791–794. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Sharkey T. D., Wang J., Osmond C. B. Environmental effects on photosynthesis, nitrogen-use efficiency, and metabolite pools in leaves of sun and shade plants. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):796–802. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Mizuno M., Hayashi M. Partitioning of Nitrogen among Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase, Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase, and Pyruvate Orthophosphate Dikinase as Related to Biomass Productivity in Maize Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):665–669. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uedan K., Sugiyama T. Purification and characterization of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from maize leaves. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jun;57(6):906–910. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.6.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenbach V. A. Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase and Proteolytic Activity in Wheat Leaves from Anthesis through Senescence. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):884–887. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



