Abstract
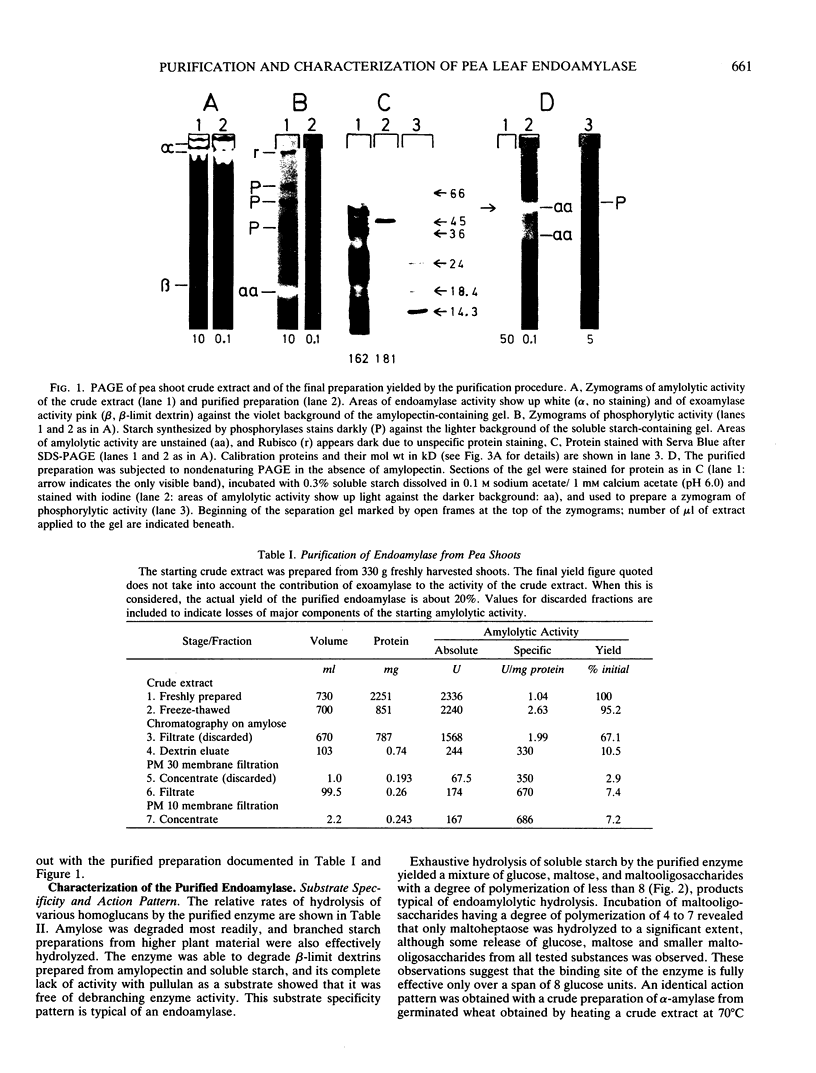
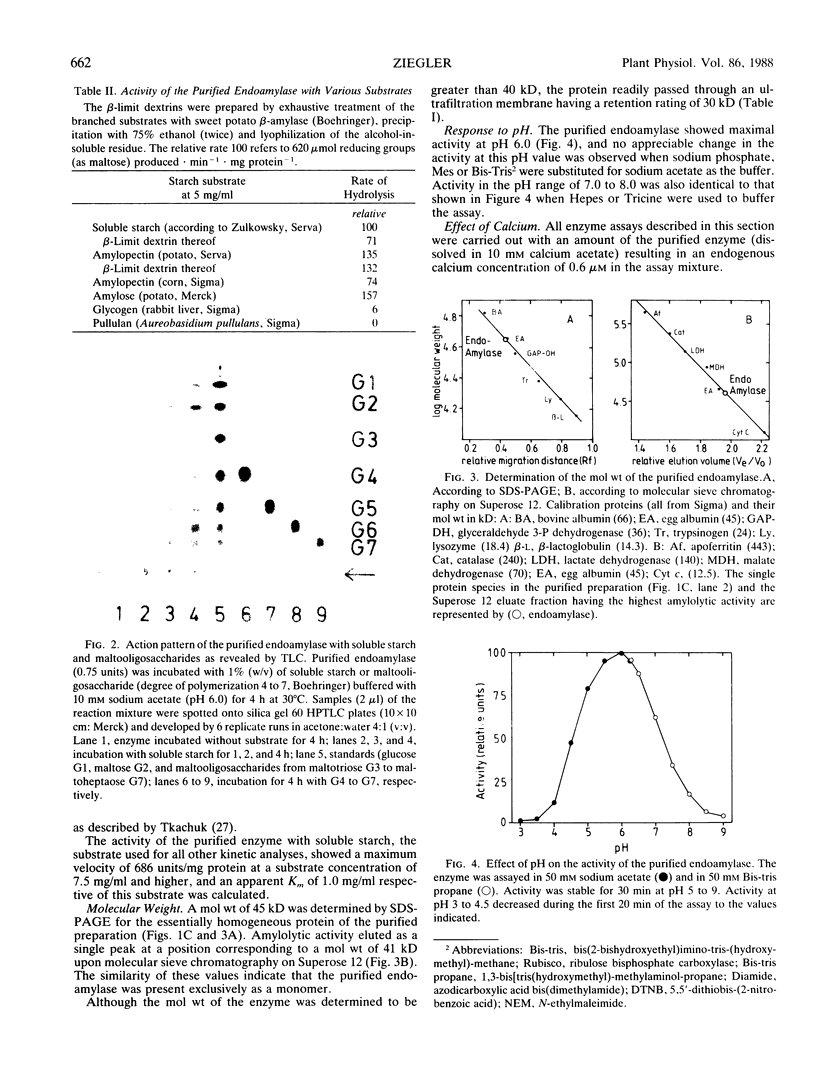
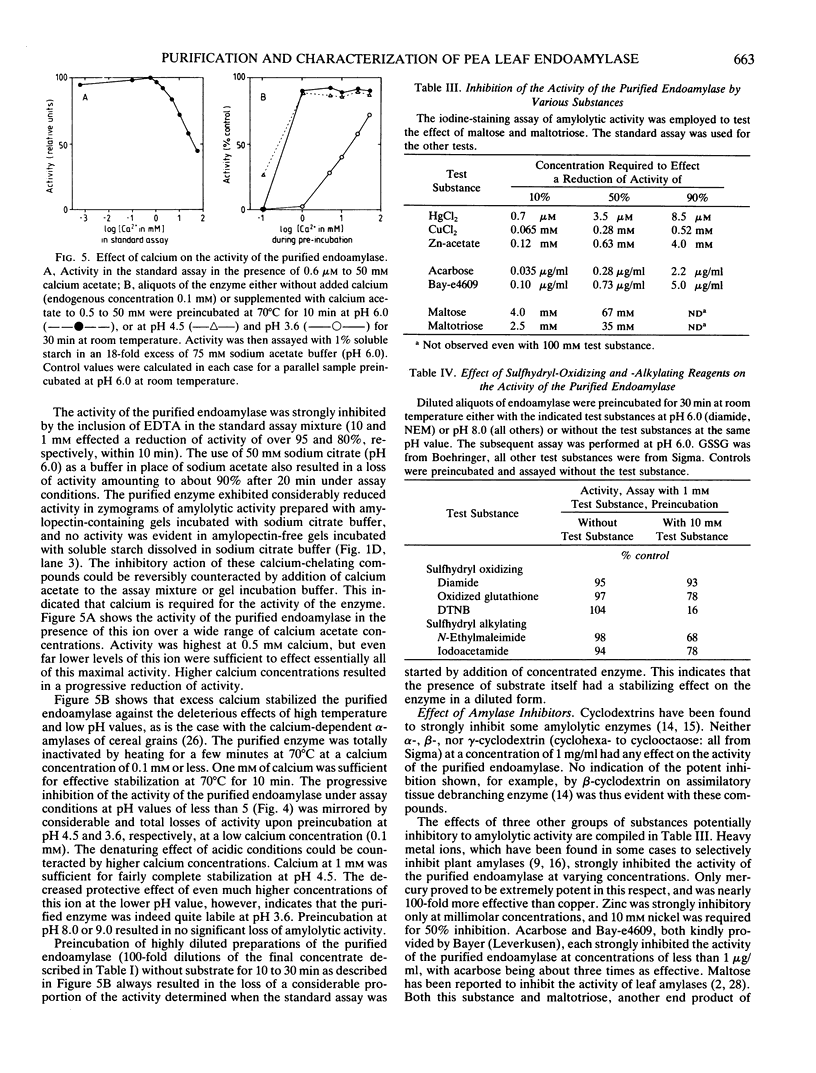
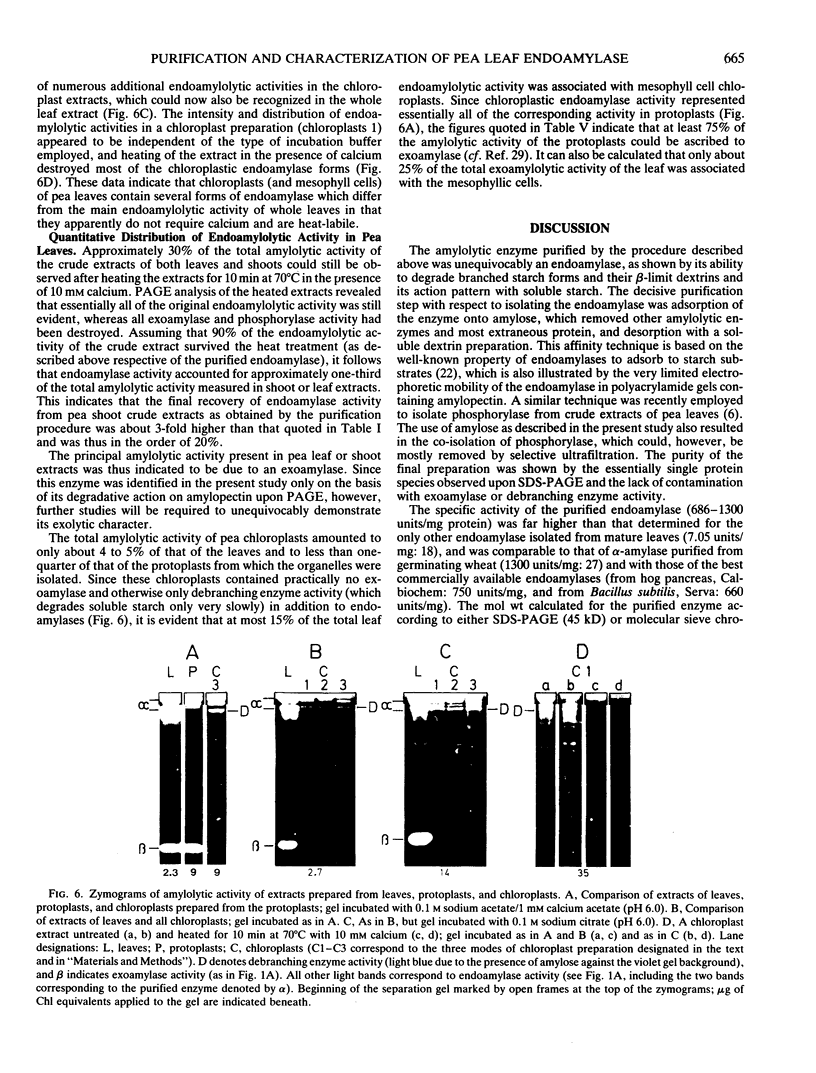
An endoamylase from leaves of pea (Pisum sativum) was purified to near homogeneity by affinity chromatography and ultrafiltration with a yield of about 20%. The purified protein had a specific activity of 686 to 1300 units per milligram protein. Molecular weights of 45 and 41 kilodalton were determined by SDS-PAGE and molecular sieve chromatography, respectively. The purified protein exhibited an action pattern commensurate with that of an endoamylase and exhibited properties indicating it to be very similar to cereal grain α-amylases (calcium requirement, stability to heat, lability to low pH-values, insensitivity to sulfhydryl reagents). Leaf frationation studies indicated that the enzyme was not primarily located in assimilatory mesophyll cells. Chloroplasts isolated from the leaves were found to contain endoamylases, but their activities represented only a small proportion of the total amylolytic potential of the leaf and reflected for the most part properties quite different from those exhibited by the purified enzyme.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapman G. W., Jr, Pallas J. E., Jr, Mendicino J. The hydrolysis of maltodextrins by a -amylase isolated from leaves of Vicia faba. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 28;276(2):491–507. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)91010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doehlert D. C., Duke S. H. Specific Determination of alpha-Amylase Activity in Crude Plant Extracts Containing beta-Amylase. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):229–234. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Hanson A. D., Chandler P. C. Water stress enhances expression of an alpha-amylase gene in barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):350–359. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Preiss J. Amylopectin degradation in pea chloroplast extracts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):218–220. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig I., Ziegler P., Beck E. Purification and properties of spinach leaf debranching enzyme. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):856–861. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. J. Inhibition of pullulanase by Schardinger dextrins. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80476-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Greenberg E., Kuhn D. N., Preiss J. Subcellular localization of the starch degradative and biosynthetic enzymes of spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):187–192. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Preiss J. Starch Degradation in Spinach Leaves: ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE AMYLASES AND R-ENZYME OF SPINACH LEAVES. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):870–876. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongratz P., Beck E. Diurnal oscillation of amylolytic activity in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Nov;62(5):687–689. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas E., Cardemil L. The Multiple Forms of alpha-Amylase Enzyme of the Araucaria Species of South America: A. araucana (Mol.) Koch and A. angustifolia (Bert.) O. Kutz : A Comparative Study. Plant Physiol. 1986 Aug;81(4):1062–1068. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.4.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Bulpin P. V., ap Rees T. Pathway of starch breakdown in photosynthetic tissues of Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 15;544(1):200–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkachuk R. Competitive affinity chromatography of wheat alpha-amylase. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 15;52(1):66–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80639-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler P., Beck E. Exoamylase activity in vacuoles isolated from pea and wheat leaf protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):1119–1121. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]