Abstract
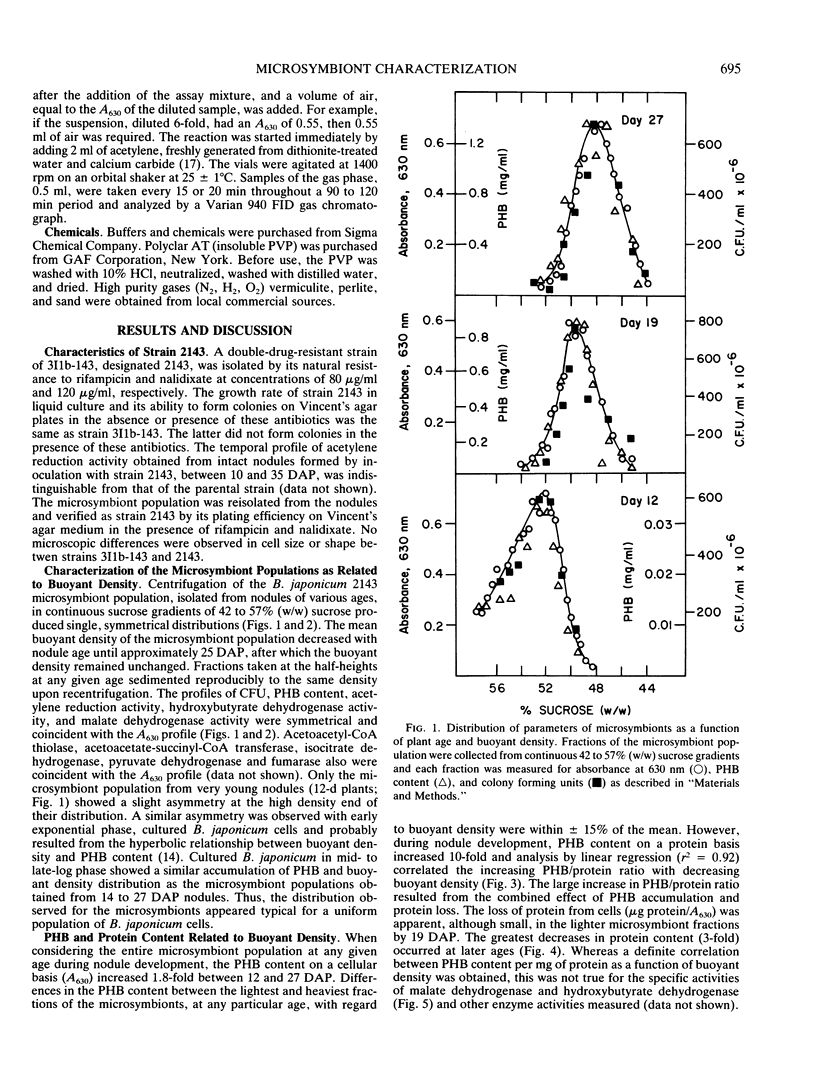
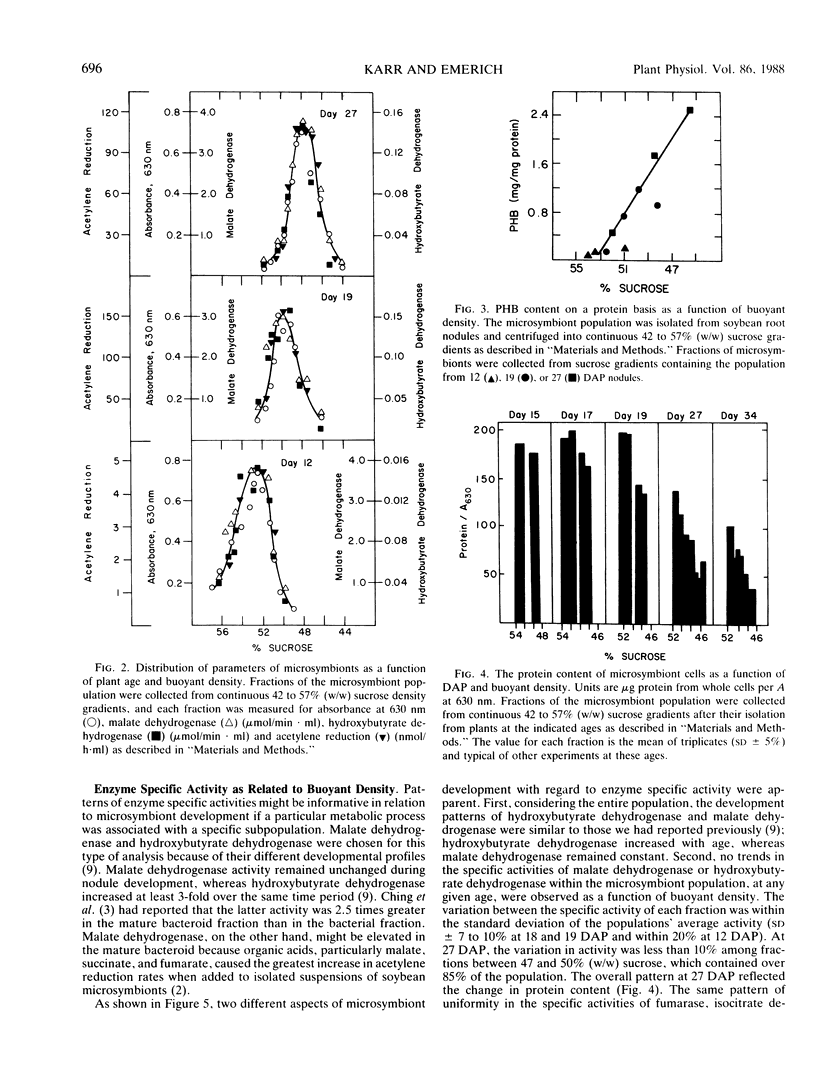
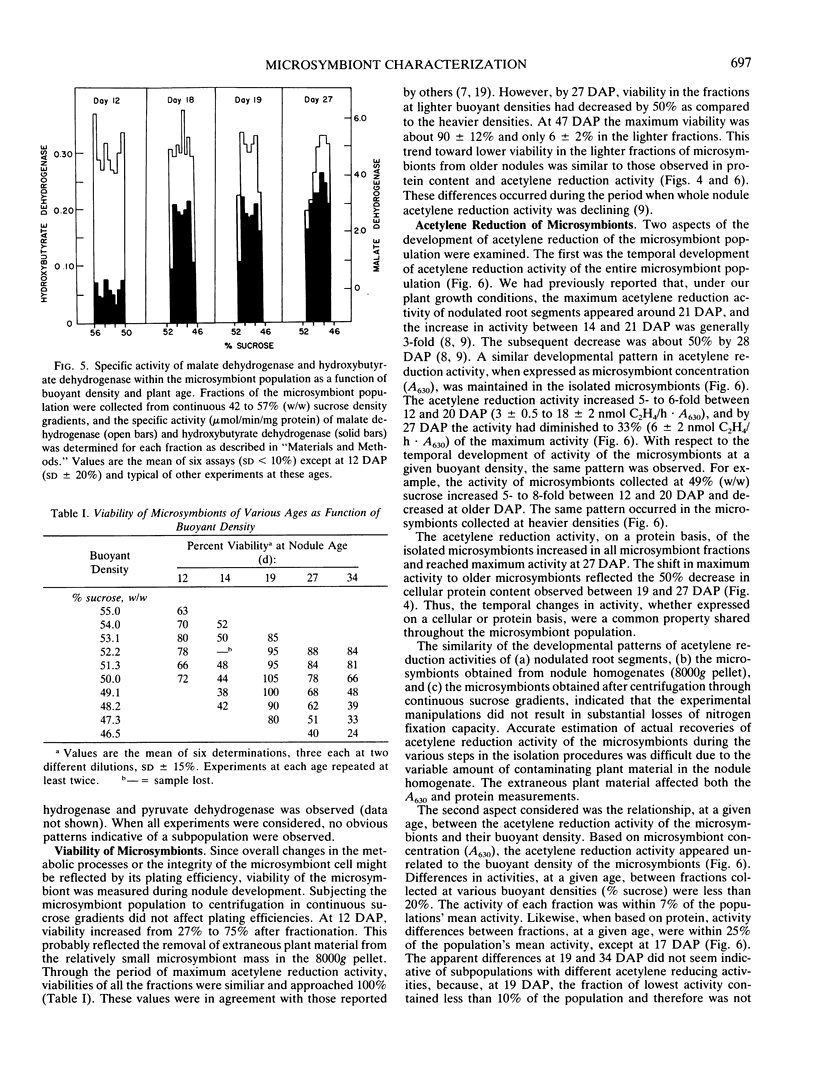
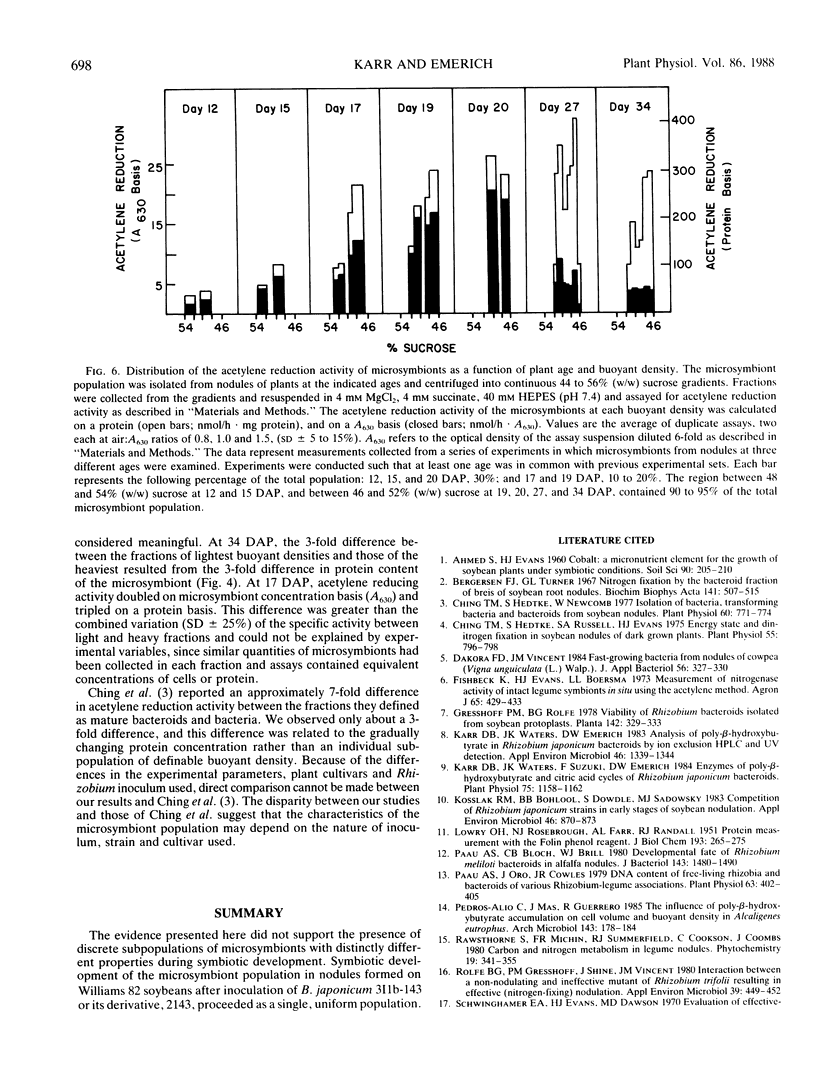
The microsymbiont population in soybean root nodules (Glycine max L. cv Williams 82 inoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum 2143) was characterized during symbiotic development to determine the extent of heterogeneity in this population. The microsymbiont population was isolated by centrifugation through a continuous sucrose gradient (44 to 57% weight to weight ratio) and appeared homogeneous at each age examined up to 26 days after planting based on the symmetrical distribution of the population, enzyme activities, poly-β-hydroxybutyrate contents, protein contents, and viabilities. Some differences in viability, protein content, and acetylene reduction activity were observed at later ages. The population migrated to progressively lighter buoyant densities with increasing age until a density equivalent to 48% sucrose was reached. The changing density correlated directly with the increasing poly-β-hydroxybutyrate to protein ratio. The acetylene reduction activity, based on microsymbiont concentration, followed the same developmental pattern as whole nodules. On a protein basis, the decline of acetylene reduction activity was later and reflected the decrease in protein content per cell. These results suggested that the microsymbiont population, which resulted from inoculation of B. japonicum 2143 onto Williams 82 cultivar of soybeans, developed as a homogeneous population.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergersen J. F., Turner G. L. Nitrogen fixation by the bacteroid fraction of breis of soybean root nodules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 29;141(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching T. M., Hedtke S. Isolation of bacteria, transforming bacteria, and bacteroids from soybean nodules. Plant Physiol. 1977 Nov;60(5):771–774. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.5.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching T. M., Hedtke S., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Energy State and Dinitrogen Fixation in Soybean Nodules of Dark-grown Plants. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):796–798. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr D. B., Waters J. K., Emerich D. W. Analysis of Poly-beta-Hydroxybutyrate in Rhizobium japonicum Bacteroids by Ion-Exclusion High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography and UV Detection. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Dec;46(6):1339–1344. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.6.1339-1344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr D. B., Waters J. K., Suzuki F., Emerich D. W. Enzymes of the Poly-beta-Hydroxybutyrate and Citric Acid Cycles of Rhizobium japonicum Bacteroids. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1158–1162. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bohlool B. B., Dowdle S., Sadowsky M. J. Competition of Rhizobium japonicum Strains in Early Stages of Soybean Nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):870–873. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.870-873.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Bloch C. B., Brill W. J. Developmental fate of Rhizobium meliloti bacteroids in alfalfa nodules. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1480–1490. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1480-1490.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Oro J., Cowles J. R. DNA content of free living rhizobia and bacteroids of various Rhizobium-legume associations. Plant Physiol. 1979 Feb;63(2):402–405. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.2.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe B. G., Gresshoff P. M., Shine J., Vincent J. M. Interaction Between a Non-Nodulating and an Ineffective Mutant of Rhizobium trifolli Resulting in Effective (Nitrogen-Fixing) Nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):449–452. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.449-452.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Cain P. S., Schmidt E. L. Viability of Rhizobium bacteroids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):854–856. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.854-856.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


