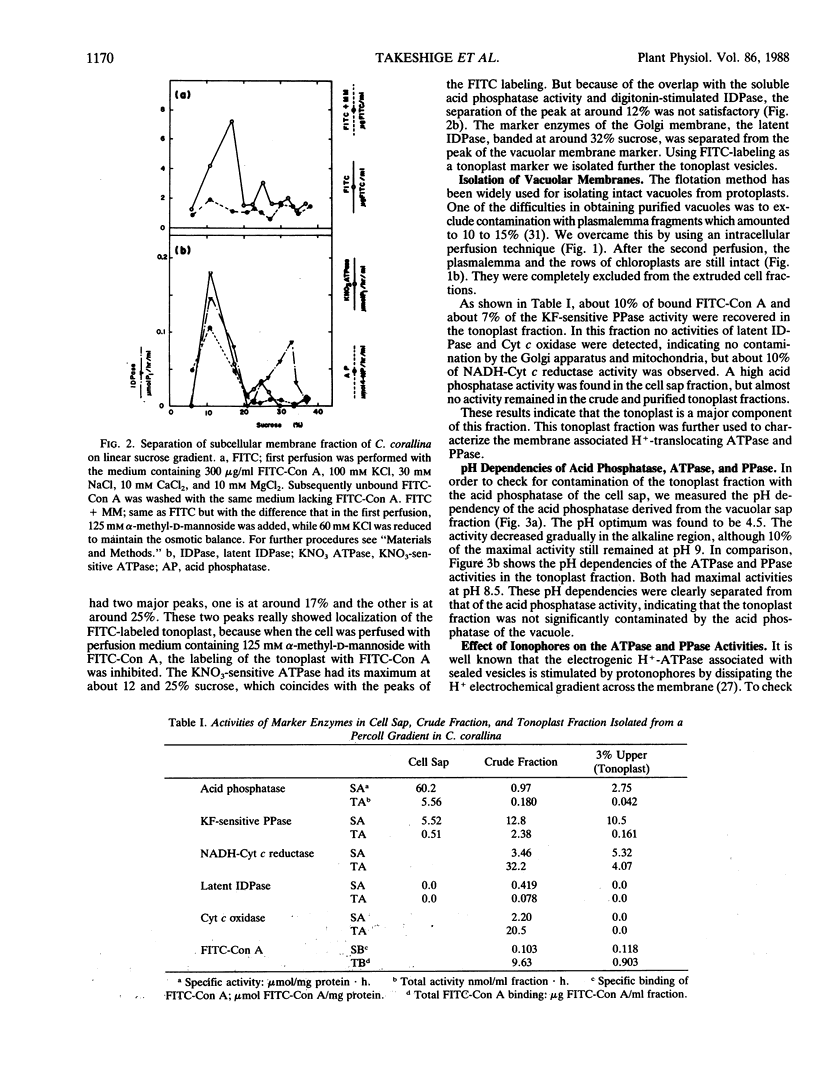
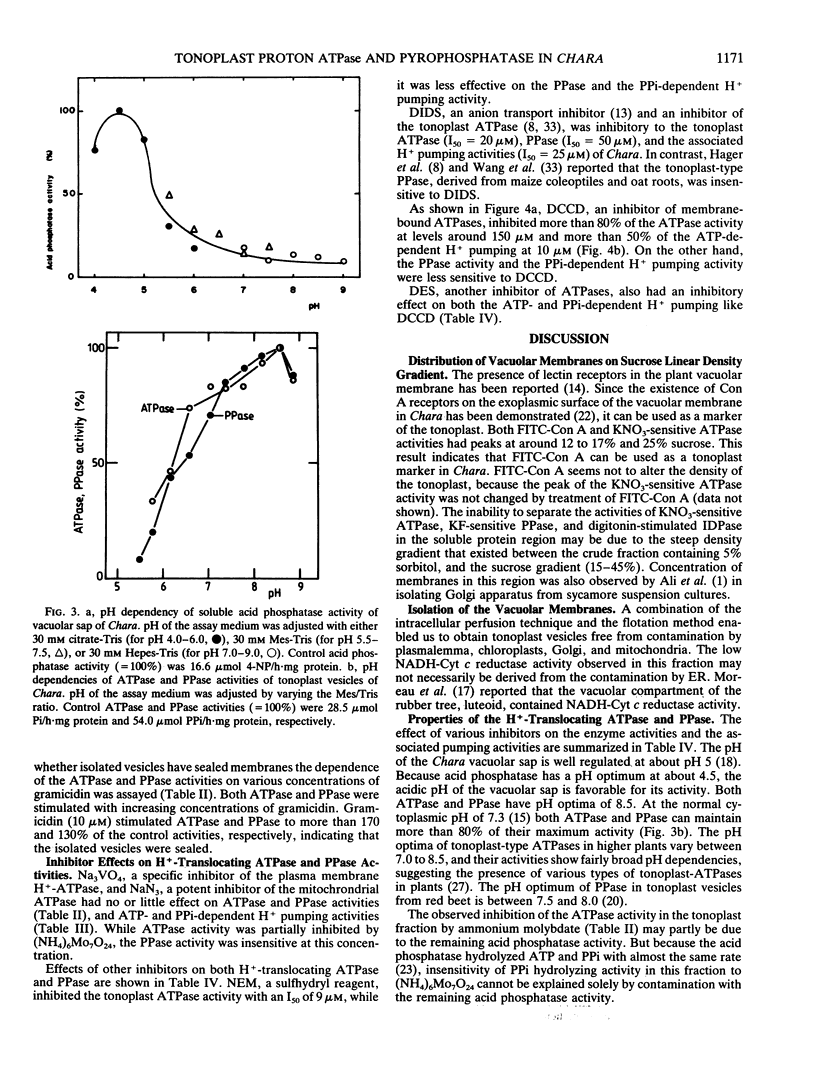
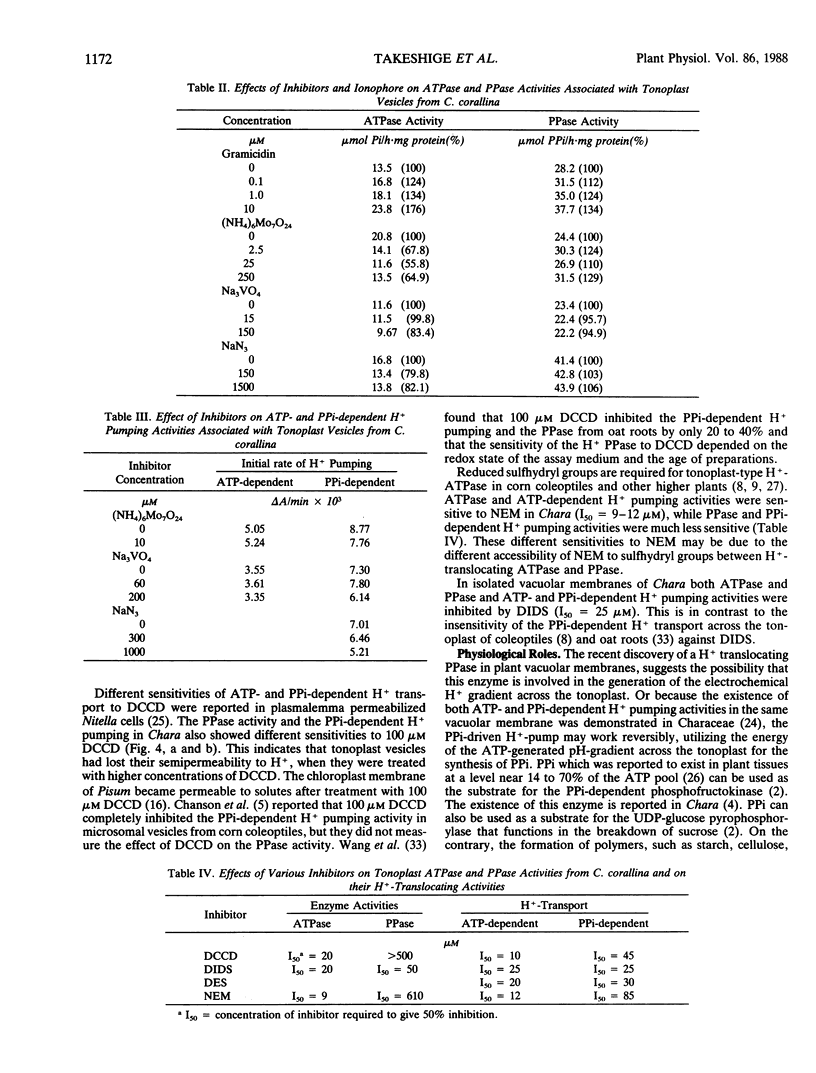
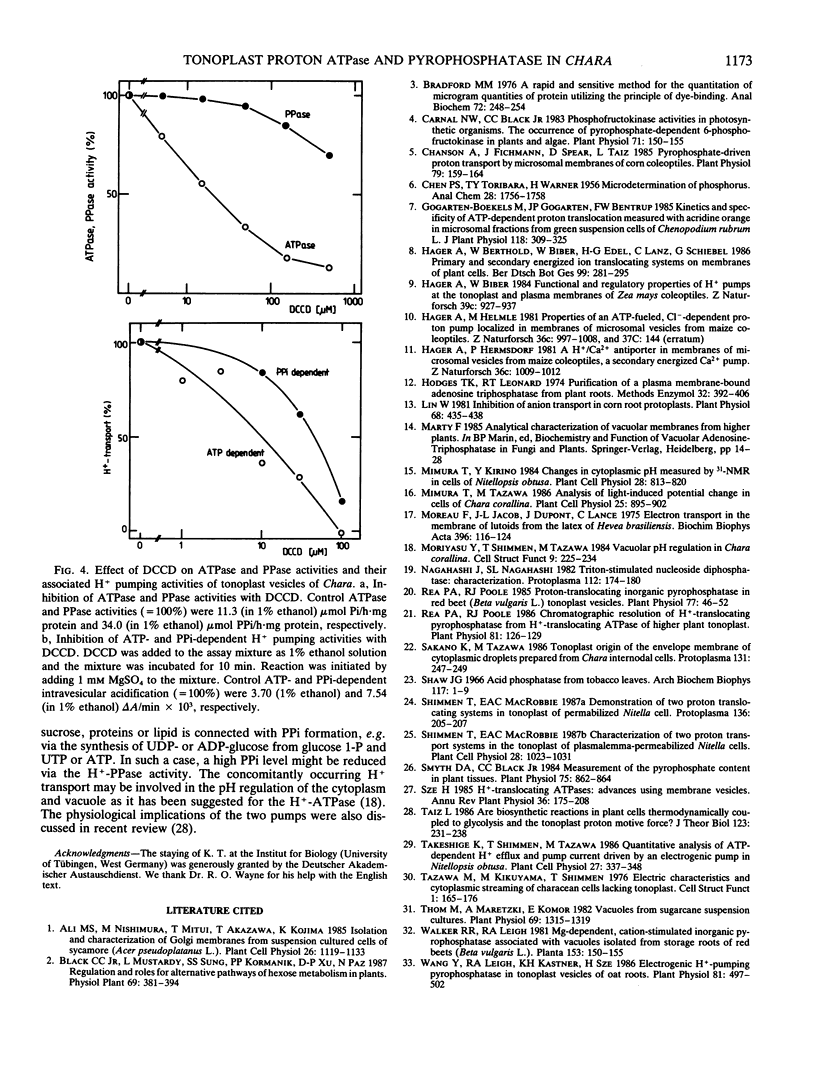
Abstract
Sealed tonoplast vesicles were isolated from single cells of Chara corallina with the aid of an intracellular perfusion technique in combination with a 3/10% Percoll two step gradient centrifugation. The isolated tonoplast fraction was free from plasmalemma and chloroplasts, and showed no activities of cytochrome c oxidase, and latent IDPase, but had about 10% of the NADH-cytochrome c reductase activity. The vesicles had both ATPase and PPase activities, which could be stimulated in the presence of 10 micromolar gramicidin by 170 and 130%, respectively, demonstrating the existence of sealed vesicles. Furthermore, ATP- and PPi-dependent H+ pumping through the membrane into the vesicles was shown. Both ATPase and PPase had pH optima around pH 8.5. At the physiological pH, 7.3, they still had more than 80% of their maximal activities. Ammonium molybdate, azide, and vanadate had no or little effect on the activities of both enzymes or their associated H+ pumping activities. N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide inhibited the ATPase strongly (I50 = 20 micromolar) but the PPase only weakly. The ATPase was also more sensitive to N-ethylmaleimide than the PPase. 4,4′-Stilbenedisulfonic acid affected both enzyme activities and their associated H+ pumping activities. This is in contrast to the H+-PPase of higher plants which is 4,4′-stilbenedisulfonic acid insensitive.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnal N. W., Black C. C. Phosphofructokinase activities in photosynthetic organisms : the occurrence of pyrophosphate-dependent 6-phosphofructokinase in plants and algae. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):150–155. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanson A., Fichmann J., Spear D., Taiz L. Pyrophosphate-driven proton transport by microsomal membranes of corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):159–164. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. Inhibition of anion transport in corn root protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):435–438. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau F., Jacob J. L., Dupont J., Lance C. Electron transport in the membrane of lutoids from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 8;396(1):116–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Chromatographic resolution of h-translocating pyrophosphatase from h-translocating ATPase of higher plant tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):126–129. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Proton-Translocating Inorganic Pyrophosphatase in Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Tonoplast Vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):46–52. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. G. Acid phosphatase from tobacco leaves. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Oct;117(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. A., Black C. C. Measurement of the pyrophosphate content of plant tissues. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):862–864. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom M., Maretzki A., Komor E. Vacuoles from Sugarcane Suspension Cultures : I. ISOLATION AND PARTIAL CHARACTERIZATION. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jun;69(6):1315–1319. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.6.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Leigh R. A., Kaestner K. H., Sze H. Electrogenic h-pumping pyrophosphatase in tonoplast vesicles of oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):497–502. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


