Abstract
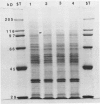
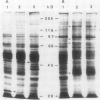
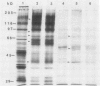
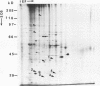
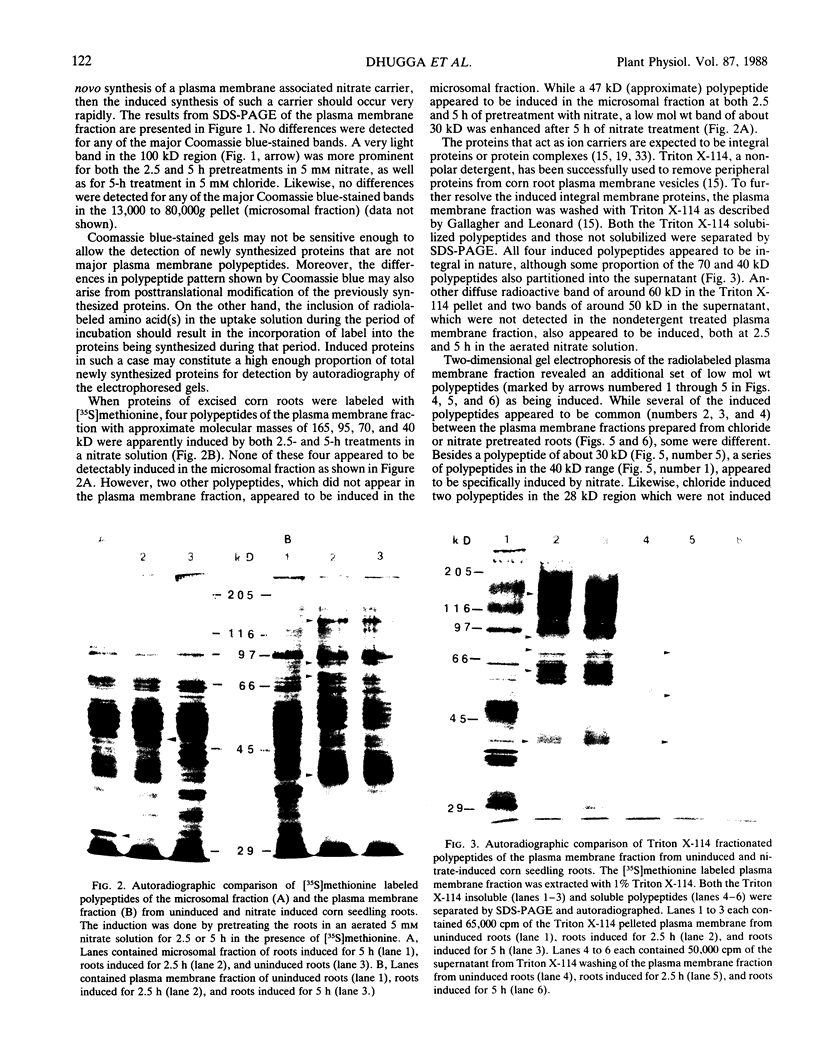
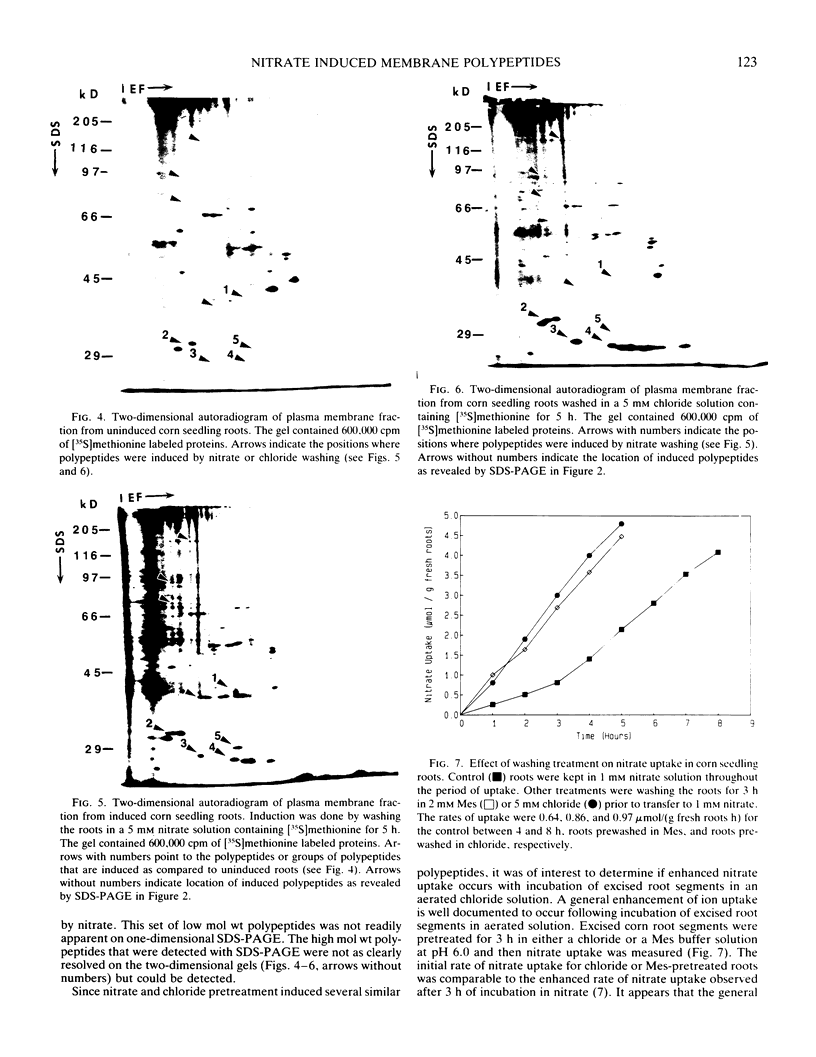
Induction of corn (Zea mays L.) seedling root membrane polypeptides was studied by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in relation to induction of nitrate uptake. When nitrate uptake was studied using freshly harvested roots from 4-day old corn seedlings, a steady state rate of uptake was achieved after a lag of 2 to 3 hours. The plasma membrane fraction from freshly harvested roots (uninduced) and roots pretreated in 5 millimolar nitrate for 2.5 or 5 hours (induced) showed no differences in the major polypeptides with Coomassie blue staining. Autoradiography of the 35S-methionine labeled proteins, however, showed four polypeptides with approximate molecular masses of 165, 95, 70, and 40 kilodaltons as being induced by both 2.5 and 5-hour pretreatment in 5 millimolar nitrate. All four polypeptides appeared to be integral membrane proteins as shown by Triton X-114 (octylphenoxypolyethoxyethanol) washing of the membrane vesicles. Autoradiography of the two-dimensional gels revealed that several additional low molecular weight proteins were induced. A 5-hour pretreatment in 5 millimolar chloride also induced several of the low molecular weight polypeptides, although a polypeptide of about 30 kilodaltons and a group of polypeptides around 40 kilodaltons appeared to be specifically induced by nitrate. The results are discussed in relation to the possibility that some of the polypeptides induced by nitrate treatment may be directly involved in nitrate transport through the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chantarotwong W., Huffaker R. C., Miller B. L., Granstedt R. C. In vivo nitrate reduction in relation to nitrate uptake, nitrate content, and in vitro nitrate reductase activity in intact barley seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):519–522. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deane-Drummond C. E., Glass A. D. Nitrate Uptake into Barley (Hordeum vulgare) Plants : A New Approach Using ClO(3) as an Analog for NO(3). Plant Physiol. 1982 Jul;70(1):50–54. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deane-Drummond C. E., Glass A. D. Short Term Studies of Nitrate Uptake into Barley Plants Using Ion-Specific Electrodes and ClO(3): I. Control of Net Uptake by NO(3) Efflux. Plant Physiol. 1983 Sep;73(1):100–104. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhugga K. S., Waines J. G., Leonard R. T. Nitrate absorption by corn roots : inhibition by phenylglyoxal. Plant Physiol. 1988 Mar;86(3):759–763. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.3.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN E. Mechanism of ion absorption by roots. Nature. 1953 Jan 10;171(4341):83–84. doi: 10.1038/171083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Hagen C. E. A KINETIC STUDY OF THE ABSORPTION OF ALKALI CATIONS BY BARLEY ROOTS. Plant Physiol. 1952 Jul;27(3):457–474. doi: 10.1104/pp.27.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Leonard R. T. Effect of vanadate, molybdate, and azide on membrane-associated ATPase and soluble phosphatase activities of corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1335–1340. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Leonard R. T. Electrophoretic characterization of a detergent-treated plasma membrane fraction from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):265–271. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith J., Livoni J. P., Norberg C. L., Segel I. H. Regulation of Nitrate Uptake in Penicillium chrysogenum by Ammonium Ion. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):362–367. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. A., Flesher D., Hageman R. H. Nitrate Uptake by Dark-grown Corn Seedlings: Some Characteristics of Apparent Induction. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):120–127. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. A., Volk R. J., Jackson W. A. p-Fluorophenylalanine-Induced Restriction of Ion Uptake and Assimilation by Maize Roots. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):718–721. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyra C. A., Hageman R. H. Nitrate uptake and induction of nitrate reductase in excised corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1975 Nov;56(5):692–695. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.5.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. P., Rains D. W. Nitrate Absorption by Barley: II. Influence of Nitrate Reductase Activity. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):59–62. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Andrade F. H., Anderson I. C. Further Evidence that Cytoplasmic Acidosis Is a Determinant of Flooding Intolerance in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):492–494. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Callis J., Jardetzky O., Walbot V., Freeling M. Cytoplasmic acidosis as a determinant of flooding intolerance in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6029–6033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rufty T. W., Thomas J. F., Remmler J. L., Campbell W. H., Volk R. J. Intercellular localization of nitrate reductase in roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):675–680. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]