Figure 4.
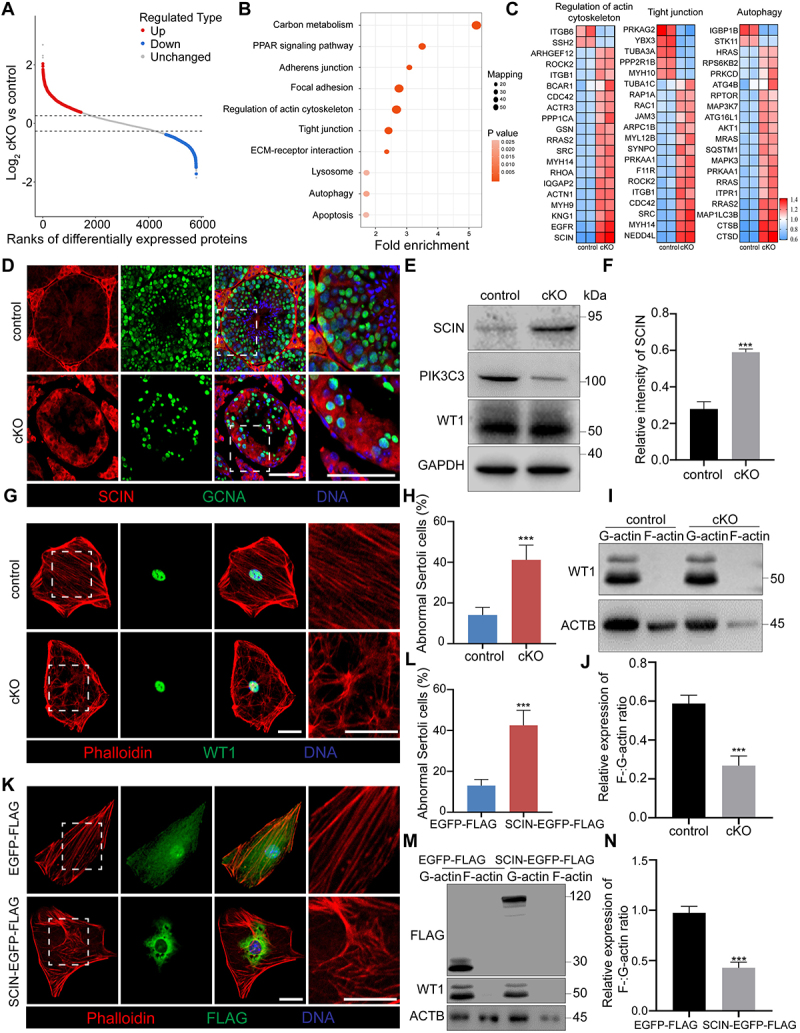
F-actin negative regulator protein SCIN was screened by proteomics. Testes at 8 W of age were collected from control and cKO mice for TMT-labeled quantitative proteomics. (A) Scatter plot displaying differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) comparing control with cKO testes. Horizontal dashed lines indicate cutoff of log21.3FC (0.37851) and -log21.3FC (−0.37851). Red dots: upregulated proteins (FC ≥ 1.3; CV < 0.1). Blue dots: downregulated proteins (FC ≤ 0.769; CV < 0.1). Gray dots: unchanged proteins (0.769 < FC < 1.3; CV ≥ 0.1). FC: Fold Change; CV: Coefficient of Variation. (B) KEGG pathway analysis was performed on DEPs between control and cKO testes. (C) Heatmap showing top 20 DEPs associated with regulation of actin cytoskeleton, tight junctions, and autophagy KEGG pathways. (D) Immunofluorescence of SCIN and GCNA. Bar: 60 μm. (E-F) Increased expression of SCIN in primary Sertoli cells of cKO mice (E). The relative intensity of SCIN was shown as compared to the expression of GAPDH (F). (G-H) Disorganized F-actin cytoskeleton in cKO Sertoli cells. Primary Sertoli cells were isolated from the testes of control and cKO male mice at 8 W of age and cultured on cover slips. Immunofluorescence of phalloidin and WT1 was performed (G). Bar: 30 μm. Graph showing the percentage of Sertoli cells with abnormal F-actin cytoskeleton structure among all Sertoli cells on each cover slip (n = 5) (H). (I-J) F-actin and G-actin from Sertoli cells were segmented and analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody against ACTB (I). Graph showing the relative expression of F-:G-actin ratio in Sertoli cells (n = 3) (J). (K-L) Disturbance of F-actin cytoskeleton after overexpression of SCIN in primary Sertoli cells. Primary Sertoli cells were plated and cultured on cover glass slips from the testes of male mice at 2 W of age. Cells were transfected with EGFP-FLAG and SCIN-EGFP-FLAG. Immunofluorescence of phalloidin and FLAG was performed (K). Bar: 30 μm. Graph showing the percentage of Sertoli cells with abnormal F-actin cytoskeleton structure among all Sertoli cells on each cover glass slip (n = 5) (L). (M-N) F-actin and G-actin from Sertoli cells were segmented and analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody against ACTB (M). Graph showing the relative expression of F-:G-actin ratio in Sertoli cells (n = 3) (N). ***P < 0.01.
